1.意图
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
2.动机
通过拷贝或者“克隆”一个类的实例来创建新的实例。
3.适用性
当一个系统应该独立于它的产品创建、构成和表示时,要使用Prototype模式;以及
- 当要实例化的类是在运行时刻指定时,例如,通过动态装载;或者
- 为了避免创建一个与产品类层次平行的工厂类层次时或者
- 当一个类的实例只能有几个不同状态组合中的一种时。建立相应数目的原型并克隆它们,可能比每次用合适的状态手工实例化该类更方便一些。
4.结构
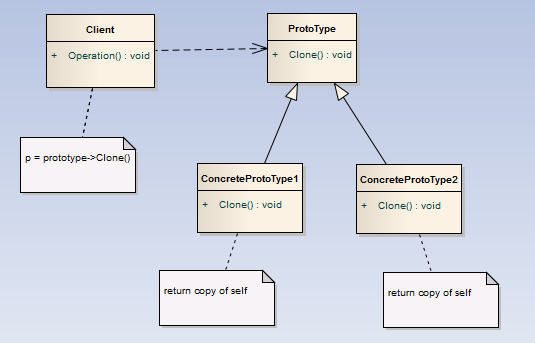
5.代码实例

#include <memory> class Prototype { public: virtual std::shared_ptr<Prototype> Clone() = 0; virtual void PrintState() = 0; virtual void SetState(int state) = 0; }; class ConcretePrototype1 : public Prototype { public: ConcretePrototype1(int state); std::shared_ptr<Prototype> Clone(); void PrintState(); virtual void SetState(int state); private: int m_iState; }; class ConcretePrototype2 : public Prototype { public: ConcretePrototype2(int state); std::shared_ptr<Prototype> Clone(); void PrintState(); virtual void SetState(int state); private: int m_iState; };

#include<map> #include<memory> class Prototype; class ProtoTypeFactory { public: void RegisterPrototype(int key,std::shared_ptr<Prototype> pProtoType); std::shared_ptr<Prototype> GetProtoType(int key); void PrintAllPrototypeState(); private: std::map<int,std::shared_ptr<Prototype>> m_ProtoTypeMap; };

#include "Prototype.h" #include <iostream> ConcretePrototype1::ConcretePrototype1(int state) : m_iState(state) { } std::shared_ptr<Prototype> ConcretePrototype1::Clone() { std::shared_ptr<Prototype> pProtoType(new ConcretePrototype1(*this)); return pProtoType; } void ConcretePrototype1::PrintState() { std::cout << " ConcretePrototype1 State is :" << m_iState <<std::endl; } void ConcretePrototype1::SetState(int state) { m_iState = state; } ConcretePrototype2::ConcretePrototype2(int state) : m_iState(state) { } std::shared_ptr<Prototype> ConcretePrototype2::Clone() { std::shared_ptr<Prototype> pProtoType(new ConcretePrototype2(*this)); return pProtoType; } void ConcretePrototype2::PrintState() { std::cout << " ConcretePrototype2 State is :" << m_iState <<std::endl; } void ConcretePrototype2::SetState(int state) { m_iState = state; }

#include "ProtoTypeFactory.h" #include "Prototype.h" #include <utility> void ProtoTypeFactory::RegisterPrototype(int key,std::shared_ptr<Prototype> pProtoType) { m_ProtoTypeMap[key] = pProtoType; } std::shared_ptr<Prototype> ProtoTypeFactory::GetProtoType(int key) { auto iter = m_ProtoTypeMap.find(key); return iter->second; } void ProtoTypeFactory::PrintAllPrototypeState() { for(auto iter = m_ProtoTypeMap.begin(); iter != m_ProtoTypeMap.end();++iter) { iter->second->PrintState(); } }

#include "ProtoTypeFactory.h" #include "Prototype.h" #include <iostream> void RegisterPrototype(std::shared_ptr<ProtoTypeFactory> pProtoTypeFactory) { std::shared_ptr<Prototype> pConcretePrototype1(new ConcretePrototype1(1)); std::shared_ptr<Prototype> ConcretePrototype2(new ConcretePrototype2(1)); pProtoTypeFactory->RegisterPrototype(1,pConcretePrototype1); pProtoTypeFactory->RegisterPrototype(2,ConcretePrototype2); } int main() { std::shared_ptr<ProtoTypeFactory> pProtoTypeFactory(new ProtoTypeFactory()); std::cout<< "RegisterPrototype in PrototypeFactory"; std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; RegisterPrototype(pProtoTypeFactory); std::cout<< "Print All State in PrototypeFactory:" << std::endl; pProtoTypeFactory->PrintAllPrototypeState(); std::cout<< "Clone Prototype 1:" << std::endl; auto pProtoType = pProtoTypeFactory->GetProtoType(1); std::cout<< "Print State Before Set State" << std::endl; auto pClonedProtoType = pProtoType->Clone(); pClonedProtoType->PrintState(); std::cout<< "Print State After Set State" << std::endl; pClonedProtoType->SetState(3); pClonedProtoType->PrintState(); std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; std::cout<< "Clone Prototype 2:" << std::endl; pProtoType = pProtoTypeFactory->GetProtoType(2); std::cout<< "Print State Before Set State" << std::endl; pClonedProtoType = pProtoType->Clone(); pClonedProtoType->PrintState(); std::cout<< "Print State After Set State" << std::endl; pClonedProtoType->SetState(4); pClonedProtoType->PrintState(); std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; std::cout<< "Print All State in PrototypeFactory:" << std::endl; pProtoTypeFactory->PrintAllPrototypeState(); while(1); }
6.测试结果
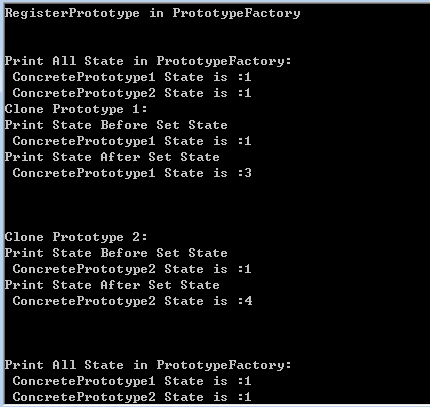
利用原型设计模式时,可以预先注册所需的原型,然后在使用时根据原型创建实例。
7.效果
- 运行时刻增加和删除产品,Prototype允许只通过注册原型实例就可以将一个新的具体产品类并入系统。
- 改变值以指定新对象
- 改变结构以指定新对象
- 减少子类的构造
- 用类动态配置应用。
