1、对象数组的概述和使用
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 public class Student { 4 // 成员变量 5 private String name; 6 private int age; 7 8 // 构造方法 9 public Student() { 10 super(); 11 } 12 13 public Student(String name, int age) { 14 super(); 15 this.name = name; 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 19 // 成员方法 20 // getXxx()/setXxx() 21 public String getName() { 22 return name; 23 } 24 25 public void setName(String name) { 26 this.name = name; 27 } 28 29 public int getAge() { 30 return age; 31 } 32 33 public void setAge(int age) { 34 this.age = age; 35 } 36 37 @Override 38 public String toString() { 39 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 40 } 41 }
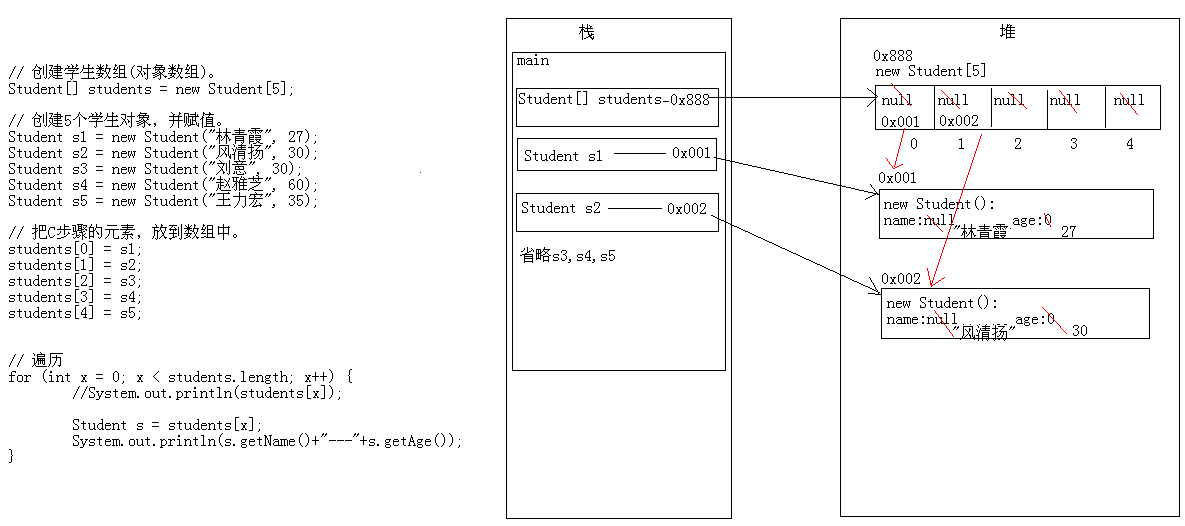
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 /* 4 * 我有5个学生,请把这个5个学生的信息存储到数组中,并遍历数组,获取得到每一个学生信息。 5 * 学生:Student 6 * 成员变量:name,age 7 * 构造方法:无参,带参 8 * 成员方法:getXxx()/setXxx() 9 * 存储学生的数组?自己想想应该是什么样子的? 10 * 分析: 11 * A:创建学生类。 12 * B:创建学生数组(对象数组)。 13 * C:创建5个学生对象,并赋值。 14 * D:把C步骤的元素,放到数组中。 15 * E:遍历学生数组。 16 */ 17 public class ObjectArrayDemo { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 // 创建学生数组(对象数组)。 20 Student[] students = new Student[5]; 21 // for (int x = 0; x < students.length; x++) { 22 // System.out.println(students[x]); 23 // } 24 // System.out.println("---------------------"); 25 26 // 创建5个学生对象,并赋值。 27 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27); 28 Student s2 = new Student("风清扬", 30); 29 Student s3 = new Student("刘意", 30); 30 Student s4 = new Student("赵雅芝", 60); 31 Student s5 = new Student("王力宏", 35); 32 33 // 把C步骤的元素,放到数组中。 34 students[0] = s1; 35 students[1] = s2; 36 students[2] = s3; 37 students[3] = s4; 38 students[4] = s5; 39 40 // 看到很相似,就想循环改 41 // for (int x = 0; x < students.length; x++) { 42 // students[x] = s + "" + (x + 1); 43 // } 44 // 这个是有问题的 45 46 // 遍历 47 for (int x = 0; x < students.length; x++) { 48 //System.out.println(students[x]); 49 50 Student s = students[x]; 51 System.out.println(s.getName()+"---"+s.getAge()); 52 } 53 } 54 }
对象数组的内存图解:
2、集合的概述及基本功能测试
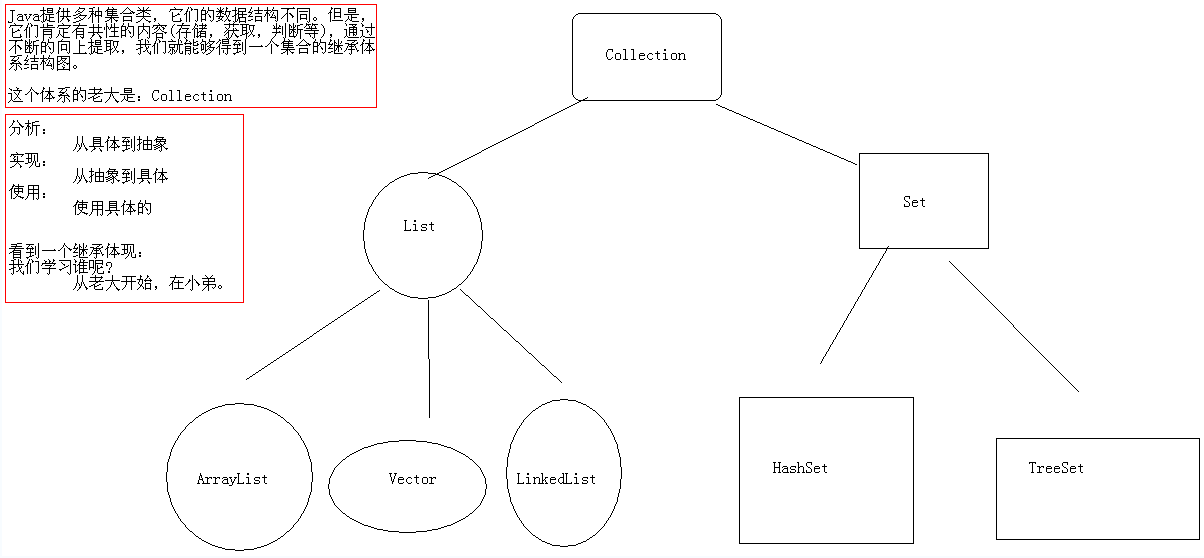
集合的继承体系图解
基本功能测试:
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 /* 7 * 集合的由来: 8 * 我们学习的是面向对象语言,而面向对象语言对事物的描述是通过对象体现的,为了方便对多个对象进行操作,我们就必须把这多个对象进行存储。 9 * 而要想存储多个对象,就不能是一个基本的变量,而应该是一个容器类型的变量,在我们目前所学过的知识里面,有哪些是容器类型的呢? 10 * 数组和StringBuffer。但是呢?StringBuffer的结果是一个字符串,不一定满足我们的要求,所以我们只能选择数组,这就是对象数组。 11 * 而对象数组又不能适应变化的需求,因为数组的长度是固定的,这个时候,为了适应变化的需求,Java就提供了集合类供我们使用。 12 * 13 * 数组和集合的区别? 14 * A:长度区别 15 * 数组的长度固定 16 * 集合长度可变 17 * B:内容不同 18 * 数组存储的是同一种类型的元素 19 * 而集合可以存储不同类型的元素 20 * C:元素的数据类型问题 21 * 数组可以存储基本数据类型,也可以存储引用数据类型 22 * 集合只能存储引用类型 23 * 24 * 刚说过集合是存储多个元的,但是呢,存储多个元素我们也是有不同需求的:比如说,我要这多个元素中不能有相同的元素, 25 * 再比如说,我要这多个元素按照某种规则排序一下。针对不同的需求,Java就提供了不同的集合类,这样呢,Java就提供了很多个集合类。 26 * 这多个集合类的数据结构不同,结构不同不重要的,重要的是你要能够存储东西,并且还要能够使用这些东西,比如说判断,获取等。 27 * 既然这样,那么,这多个集合类是有共性的内容的,我们把这些集合类的共性内容不断的向上提取,最终就能形成集合的继承体系结构。 28 * 29 * 数据结构:数据的存储方式。 30 * 31 * Collection:是集合的顶层接口,它的子体系有重复的,有唯一的,有有序的,有无序的。(后面会慢慢的讲解) 32 * 33 * Collection的功能概述: 34 * 1:添加功能 35 * boolean add(Object obj):添加一个元素 36 * boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合的元素 37 * 2:删除功能 38 * void clear():移除所有元素 39 * boolean remove(Object o):移除一个元素 40 * boolean removeAll(Collection c):移除一个集合的元素(是一个还是所有) 41 * 3:判断功能 42 * boolean contains(Object o):判断集合中是否包含指定的元素 43 * boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断集合中是否包含指定的集合元素(是一个还是所有) 44 * boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空 45 * 4:获取功能 46 * Iterator<E> iterator()(重点) 47 * 5:长度功能 48 * int size():元素的个数 49 * 面试题:数组有没有length()方法呢?字符串有没有length()方法呢?集合有没有length()方法呢? 50 * 6:交集功能 51 * boolean retainAll(Collection c):两个集合都有的元素?思考元素去哪了,返回的boolean又是什么意思呢? 52 * 7:把集合转换为数组 53 * Object[] toArray() 54 */ 55 public class CollectionDemo { 56 public static void main(String[] args) { 57 // 测试不带All的方法 58 59 // 创建集合对象 60 // Collection c = new Collection(); //错误,因为接口不能实例化 61 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 62 63 // boolean add(Object obj):添加一个元素 64 // System.out.println("add:"+c.add("hello")); 65 c.add("hello"); 66 c.add("world"); 67 c.add("java"); 68 69 // void clear():移除所有元素 70 // c.clear(); 71 72 // boolean remove(Object o):移除一个元素 73 // System.out.println("remove:" + c.remove("hello")); 74 // System.out.println("remove:" + c.remove("javaee")); 75 76 // boolean contains(Object o):判断集合中是否包含指定的元素 77 // System.out.println("contains:"+c.contains("hello")); 78 // System.out.println("contains:"+c.contains("android")); 79 80 // boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空 81 // System.out.println("isEmpty:"+c.isEmpty()); 82 83 //int size():元素的个数 84 System.out.println("size:"+c.size()); 85 86 System.out.println("c:" + c); 87 } 88 }
3、Collection集合的高级功能测试
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 /* 7 * boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合的元素 8 * boolean removeAll(Collection c):移除一个集合的元素(是一个还是所有) 9 * boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断集合中是否包含指定的集合元素(是一个还是所有) 10 * boolean retainAll(Collection c):两个集合都有的元素?思考元素去哪了,返回的boolean又是什么意思呢? 11 */ 12 public class CollectionDemo2 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 // 创建集合1 15 Collection c1 = new ArrayList(); 16 c1.add("abc1"); 17 c1.add("abc2"); 18 c1.add("abc3"); 19 c1.add("abc4"); 20 21 // 创建集合2 22 Collection c2 = new ArrayList(); 23 // c2.add("abc1"); 24 // c2.add("abc2"); 25 // c2.add("abc3"); 26 // c2.add("abc4"); 27 c2.add("abc5"); 28 c2.add("abc6"); 29 c2.add("abc7"); 30 31 // boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合的元素 32 // System.out.println("addAll:" + c1.addAll(c2)); 33 34 //boolean removeAll(Collection c):移除一个集合的元素(是一个还是所有) 35 //只要有一个元素被移除了,就返回true。 36 //System.out.println("removeAll:"+c1.removeAll(c2)); 37 38 //boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断集合中是否包含指定的集合元素(是一个还是所有) 39 //只有包含所有的元素,才叫包含 40 // System.out.println("containsAll:"+c1.containsAll(c2)); 41 42 //boolean retainAll(Collection c):两个集合都有的元素?思考元素去哪了,返回的boolean又是什么意思呢? 43 //假设有两个集合A,B。 44 //A对B做交集,最终的结果保存在A中,B不变。 45 //返回值表示的是A是否发生过改变。 46 System.out.println("retainAll:"+c1.retainAll(c2)); 47 48 System.out.println("c1:" + c1); 49 System.out.println("c2:" + c2); 50 } 51 }
4、集合的遍历之集合转数组遍历
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 /* 7 * 集合的遍历。其实就是依次获取集合中的每一个元素。 8 * 9 * Object[] toArray():把集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历 10 */ 11 public class CollectionDemo3 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // 创建集合对象 14 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 15 16 // 添加元素 17 c.add("hello"); // Object obj = "hello"; 向上转型 18 c.add("world"); 19 c.add("java"); 20 21 // 遍历 22 // Object[] toArray():把集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历 23 Object[] objs = c.toArray(); 24 for (int x = 0; x < objs.length; x++) { 25 // System.out.println(objs[x]); 26 // 我知道元素是字符串,我在获取到元素的的同时,还想知道元素的长度。 27 // System.out.println(objs[x] + "---" + objs[x].length()); 28 // 上面的实现不了,原因是Object中没有length()方法 29 // 我们要想使用字符串的方法,就必须把元素还原成字符串 30 // 向下转型 31 String s = (String) objs[x]; 32 System.out.println(s + "---" + s.length()); 33 } 34 } 35 }
练习:Collection存储自定义对象并遍历案例
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 public class Student { 4 // 成员变量 5 private String name; 6 private int age; 7 8 // 构造方法 9 public Student() { 10 super(); 11 } 12 13 public Student(String name, int age) { 14 super(); 15 this.name = name; 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 19 // 成员方法 20 // getXxx()/setXxx() 21 public String getName() { 22 return name; 23 } 24 25 public void setName(String name) { 26 this.name = name; 27 } 28 29 public int getAge() { 30 return age; 31 } 32 33 public void setAge(int age) { 34 this.age = age; 35 } 36 }
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 /* 7 * 练习:用集合存储5个学生对象,并把学生对象进行遍历。 8 * 9 * 分析: 10 * A:创建学生类 11 * B:创建集合对象 12 * C:创建学生对象 13 * D:把学生添加到集合 14 * E:把集合转成数组 15 * F:遍历数组 16 */ 17 public class StudentDemo { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 // 创建集合对象 20 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 21 22 // 创建学生对象 23 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27); 24 Student s2 = new Student("风清扬", 30); 25 Student s3 = new Student("令狐冲", 33); 26 Student s4 = new Student("武鑫", 25); 27 Student s5 = new Student("刘晓曲", 22); 28 29 // 把学生添加到集合 30 c.add(s1); 31 c.add(s2); 32 c.add(s3); 33 c.add(s4); 34 c.add(s5); 35 36 // 把集合转成数组 37 Object[] objs = c.toArray(); 38 // 遍历数组 39 for (int x = 0; x < objs.length; x++) { 40 // System.out.println(objs[x]); 41 42 Student s = (Student) objs[x]; 43 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 44 } 45 } 46 }
5、集合的遍历之迭代器遍历
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 /* 8 * Iterator iterator():迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式 9 * Object next():获取元素,并移动到下一个位置。 10 * NoSuchElementException:没有这样的元素,因为你已经找到最后了。 11 * boolean hasNext():如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true。( 12 */ 13 public class IteratorDemo { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 // 创建集合对象 16 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 17 18 // 创建并添加元素 19 // String s = "hello"; 20 // c.add(s); 21 c.add("hello"); 22 c.add("world"); 23 c.add("java"); 24 25 // Iterator iterator():迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式 26 Iterator it = c.iterator(); // 实际返回的肯定是子类对象,这里是多态 27 28 // Object obj = it.next(); 29 // System.out.println(obj); 30 // System.out.println(it.next()); 31 // System.out.println(it.next()); 32 // System.out.println(it.next()); 33 // System.out.println(it.next()); 34 // 最后一个不应该写,所以,我们应该在每次获取前,如果有一个判断就好了 35 // 判断是否有下一个元素,有就获取,没有就不搭理它 36 37 // if (it.hasNext()) { 38 // System.out.println(it.next()); 39 // } 40 // if (it.hasNext()) { 41 // System.out.println(it.next()); 42 // } 43 // if (it.hasNext()) { 44 // System.out.println(it.next()); 45 // } 46 // if (it.hasNext()) { 47 // System.out.println(it.next()); 48 // } 49 // if (it.hasNext()) { 50 // System.out.println(it.next()); 51 // } 52 53 // 最终版代码 54 while (it.hasNext()) { 55 // System.out.println(it.next()); 56 String s = (String) it.next(); 57 System.out.println(s); 58 } 59 } 60 }
练习:Collection存储自定义对象并遍历案例
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 public class Student { 4 // 成员变量 5 private String name; 6 private int age; 7 8 // 构造方法 9 public Student() { 10 super(); 11 } 12 13 public Student(String name, int age) { 14 super(); 15 this.name = name; 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 19 // 成员方法 20 // getXxx()/setXxx() 21 public String getName() { 22 return name; 23 } 24 25 public void setName(String name) { 26 this.name = name; 27 } 28 29 public int getAge() { 30 return age; 31 } 32 33 public void setAge(int age) { 34 this.age = age; 35 } 36 37 @Override 38 public String toString() { 39 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 40 } 41 42 }
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 /* 8 * 练习:用集合存储5个学生对象,并把学生对象进行遍历。用迭代器遍历。 9 * 10 * 注意: 11 * A:自己的类名不要和我们学习的要使用的API中的类名相同。 12 * B:复制代码的时候,很容易把那个类所在的包也导入过来,容易出现不能理解的问题。 13 */ 14 public class IteratorTest { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // 创建集合对象 17 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 18 19 // 创建学生对象 20 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27); 21 Student s2 = new Student("风清扬", 30); 22 Student s3 = new Student("令狐冲", 33); 23 Student s4 = new Student("武鑫", 25); 24 Student s5 = new Student("刘晓曲", 22); 25 26 // 把学生添加到集合中 27 c.add(s1); 28 c.add(s2); 29 c.add(s3); 30 c.add(s4); 31 c.add(s5); 32 33 // 遍历 34 Iterator it = c.iterator(); 35 while (it.hasNext()) { 36 //System.out.println(it.next()); 37 Student s = (Student) it.next(); 38 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 39 } 40 } 41 }
6、迭代器使用的问题探讨
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 /* 8 * 问题1:能用while循环写这个程序,我能不能用for循环呢? 9 * 问题2:不要多次使用it.next()方法,因为每次使用都是访问一个对象。 10 */ 11 public class IteratorTest2 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // 创建集合对象 14 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 15 16 // 创建学生对象 17 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27); 18 Student s2 = new Student("风清扬", 30); 19 Student s3 = new Student("令狐冲", 33); 20 Student s4 = new Student("武鑫", 25); 21 Student s5 = new Student("刘晓曲", 22); 22 23 // 把学生添加到集合中 24 c.add(s1); 25 c.add(s2); 26 c.add(s3); 27 c.add(s4); 28 c.add(s5); 29 30 // 遍历 31 Iterator it = c.iterator(); 32 while (it.hasNext()) { 33 Student s = (Student) it.next(); 34 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 35 36 // NoSuchElementException 不要多次使用it.next()方法 37 // System.out.println(((Student) it.next()).getName() + "---" 38 // + ((Student) it.next()).getAge()); 39 40 } 41 // System.out.println("----------------------------------"); 42 43 // for循环改写 44 // for(Iterator it = c.iterator();it.hasNext();){ 45 // Student s = (Student) it.next(); 46 // System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 47 // } 48 } 49 }
集合使用步骤图解、迭代器的原理及源码解析:

练习:Collection存储字符串并遍历
1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 /* 8 * 需求:存储字符串并遍历。 9 * 10 * 分析: 11 * A:创建集合对象 12 * B:创建字符串对象 13 * C:把字符串对象添加到集合中 14 * D:遍历集合 15 */ 16 public class CollectionTest { 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 // 创建集合对象 19 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 20 21 // 创建字符串对象 22 // 把字符串对象添加到集合中 23 c.add("林青霞"); 24 c.add("风清扬"); 25 c.add("刘意"); 26 c.add("武鑫"); 27 c.add("刘晓曲"); 28 29 // 遍历集合 30 // 通过集合对象获取迭代器对象 31 Iterator it = c.iterator(); 32 // 通过迭代器对象的hasNext()方法判断有没有元素 33 while (it.hasNext()) { 34 // 通过迭代器对象的next()方法获取元素 35 String s = (String) it.next(); 36 System.out.println(s); 37 } 38 } 39 }
练习:Collection存储学生对象并遍历
1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 7 public Student() { 8 super(); 9 } 10 11 public Student(String name, int age) { 12 super(); 13 this.name = name; 14 this.age = age; 15 } 16 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 21 public void setName(String name) { 22 this.name = name; 23 } 24 25 public int getAge() { 26 return age; 27 } 28 29 public void setAge(int age) { 30 this.age = age; 31 } 32 33 }
1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 /* 8 * 需求:存储自定义对象并遍历Student(name,age) 9 * 10 * 分析: 11 * A:创建学生类 12 * B:创建集合对象 13 * C:创建学生对象 14 * D:把学生对象添加到集合对象中 15 * E:遍历集合 16 */ 17 public class CollectionTest2 { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 // 创建集合对象 20 Collection c = new ArrayList(); 21 22 // 创建学生对象 23 Student s1 = new Student("貂蝉", 25); 24 Student s2 = new Student("小乔", 16); 25 Student s3 = new Student("黄月英", 20); 26 Student s4 = new Student(); 27 s4.setName("大乔"); 28 s4.setAge(26); 29 30 // 把学生对象添加到集合对象中 31 c.add(s1); 32 c.add(s2); 33 c.add(s3); 34 c.add(s4); 35 c.add(new Student("孙尚香", 18)); // 匿名对象 36 37 // 遍历集合 38 Iterator it = c.iterator(); 39 while (it.hasNext()) { 40 Student s = (Student) it.next(); 41 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 42 } 43 } 44 }
7、List存储字符串并遍历
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.List; 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 7 /* 8 * 需求:List集合存储字符串并遍历。 9 */ 10 public class ListDemo { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 创建集合对象 13 List list = new ArrayList(); 14 15 // 创建字符串并添加字符串 16 list.add("hello"); 17 list.add("world"); 18 list.add("java"); 19 20 // 遍历集合 21 Iterator it = list.iterator(); 22 while (it.hasNext()) { 23 String s = (String) it.next(); 24 System.out.println(s); 25 } 26 } 27 }
8、List集合的特点
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 /* 8 * List集合的特点: 9 * 有序(存储和取出的元素一致),可重复的。 10 */ 11 public class ListDemo2 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // 创建集合对象 14 List list = new ArrayList(); 15 16 // 存储元素 17 list.add("hello"); 18 list.add("world"); 19 list.add("java"); 20 list.add("javaee"); 21 list.add("android"); 22 list.add("javaee"); 23 list.add("android"); 24 25 // 遍历集合 26 Iterator it = list.iterator(); 27 while (it.hasNext()) { 28 String s = (String) it.next(); 29 System.out.println(s); 30 } 31 } 32 }
9、List存储学生对象并遍历
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 /* 8 * 存储自定义对象并遍历 9 */ 10 public class ListDemo { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 创建集合对象 13 List list = new ArrayList(); 14 15 // 创建学生对象 16 Student s1 = new Student("白骨精", 30); 17 Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 40); 18 Student s3 = new Student("观音姐姐", 22); 19 20 // 把学生对象添加到集合对象中 21 list.add(s1); 22 list.add(s2); 23 list.add(s3); 24 25 // 遍历 26 Iterator it = list.iterator(); 27 while (it.hasNext()) { 28 Student s = (Student) it.next(); 29 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 30 } 31 } 32 }
10、List集合的特有功能概述和测试
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 /* 7 * List集合的特有功能: 8 * A:添加功能 9 * void add(int index,Object element):在指定位置添加元素 10 * B:获取功能 11 * Object get(int index):获取指定位置的元素 12 * C:列表迭代器 13 * ListIterator listIterator():List集合特有的迭代器 14 * D:删除功能 15 * Object remove(int index):根据索引删除元素,返回被删除的元素 16 * E:修改功能 17 * Object set(int index,Object element):根据索引修改元素,返回被修饰的元素 18 */ 19 public class ListDemo { 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 // 创建集合对象 22 List list = new ArrayList(); 23 24 // 添加元素 25 list.add("hello"); 26 list.add("world"); 27 list.add("java"); 28 29 // void add(int index,Object element):在指定位置添加元素 30 // list.add(1, "android");//没有问题 31 // IndexOutOfBoundsException 32 // list.add(11, "javaee");//有问题 33 // list.add(3, "javaee"); //没有问题 34 // list.add(4, "javaee"); //有问题 35 36 // Object get(int index):获取指定位置的元素 37 // System.out.println("get:" + list.get(1)); 38 // IndexOutOfBoundsException 39 // System.out.println("get:" + list.get(11)); 40 41 // Object remove(int index):根据索引删除元素,返回被删除的元素 42 // System.out.println("remove:" + list.remove(1)); 43 // IndexOutOfBoundsException 44 // System.out.println("remove:" + list.remove(11)); 45 46 // Object set(int index,Object element):根据索引修改元素,返回被修饰的元素 47 System.out.println("set:" + list.set(1, "javaee")); 48 49 System.out.println("list:" + list); 50 } 51 }
11、List集合的特有遍历功能
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 /* 7 * List集合的特有遍历功能: 8 * size()和get()方法结合使用 9 */ 10 public class ListDemo2 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 创建集合对象 13 List list = new ArrayList(); 14 15 // 添加元素 16 list.add("hello"); 17 list.add("world"); 18 list.add("java"); 19 20 // Object get(int index):获取指定位置的元素 21 // System.out.println(list.get(0)); 22 // System.out.println(list.get(1)); 23 // System.out.println(list.get(2)); 24 // IndexOutOfBoundsException 25 // System.out.println(list.get(3)); 26 27 // 用循环改进 28 // for (int x = 0; x < 3; x++) { 29 // System.out.println(list.get(x)); 30 // } 31 // 如果元素过多,数起来就比较麻烦,所以我们使用集合的一个长度功能:size() 32 // 最终的遍历方式就是:size()和get() 33 for (int x = 0; x < list.size(); x++) { 34 // System.out.println(list.get(x)); 35 36 String s = (String) list.get(x); 37 System.out.println(s); 38 } 39 } 40 }
12、List存储自定义对象并遍历
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 /* 8 * 存储自定义对象并遍历,用普通for循环。(size()和get()结合) 9 */ 10 public class ListDemo3 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 创建集合对象 13 List list = new ArrayList(); 14 15 // 创建学生对象 16 Student s1 = new Student("林黛玉", 18); 17 Student s2 = new Student("刘姥姥", 88); 18 Student s3 = new Student("王熙凤", 38); 19 20 // 把学生添加到集合中 21 list.add(s1); 22 list.add(s2); 23 list.add(s3); 24 25 // 遍历 26 // 迭代器遍历 27 Iterator it = list.iterator(); 28 while (it.hasNext()) { 29 Student s = (Student) it.next(); 30 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 31 } 32 System.out.println("--------"); 33 34 // 普通for循环 35 for (int x = 0; x < list.size(); x++) { 36 Student s = (Student) list.get(x); 37 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 38 } 39 } 40 }
13、ListIterator的特有功能
1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 import java.util.ListIterator; 7 8 /* 9 * 列表迭代器: 10 * ListIterator listIterator():List集合特有的迭代器 11 * 该迭代器继承了Iterator迭代器,所以,就可以直接使用hasNext()和next()方法。 12 * 13 * 特有功能: 14 * Object previous():获取上一个元素 15 * boolean hasPrevious():判断是否有元素 16 * 17 * 注意:ListIterator可以实现逆向遍历,但是必须先正向遍历,才能逆向遍历,所以一般无意义,不使用。 18 */ 19 public class ListIteratorDemo { 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 // 创建List集合对象 22 List list = new ArrayList(); 23 list.add("hello"); 24 list.add("world"); 25 list.add("java"); 26 27 // ListIterator listIterator() 28 ListIterator lit = list.listIterator(); // 子类对象 29 // while (lit.hasNext()) { 30 // String s = (String) lit.next(); 31 // System.out.println(s); 32 // } 33 // System.out.println("-----------------"); 34 35 // System.out.println(lit.previous()); 36 // System.out.println(lit.previous()); 37 // System.out.println(lit.previous()); 38 // NoSuchElementException 39 // System.out.println(lit.previous()); 40 41 while (lit.hasPrevious()) { 42 String s = (String) lit.previous(); 43 System.out.println(s); 44 } 45 System.out.println("-----------------"); 46 47 // 迭代器 48 Iterator it = list.iterator(); 49 while (it.hasNext()) { 50 String s = (String) it.next(); 51 System.out.println(s); 52 } 53 System.out.println("-----------------"); 54 55 } 56 }
14、并发修改异常的产生原因及解决方案
1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 import java.util.ListIterator; 7 8 /* 9 * 问题? 10 * 我有一个集合,如下,请问,我想判断里面有没有"world"这个元素,如果有,我就添加一个"javaee"元素,请写代码实现。 11 * 12 * ConcurrentModificationException:当方法检测到对象的并发修改,但不允许这种修改时,抛出此异常。 13 * 产生的原因: 14 * 迭代器是依赖于集合而存在的,在判断成功后,集合的中新添加了元素,而迭代器却不知道,所以就报错了,这个错叫并发修改异常。 15 * 其实这个问题描述的是:迭代器遍历元素的时候,通过集合是不能修改元素的。 16 * 如何解决呢? 17 * A:迭代器迭代元素,迭代器修改元素 18 * 元素是跟在刚才迭代的元素后面的。 19 * B:集合遍历元素,集合修改元素(普通for) 20 * 元素在最后添加的。 21 */ 22 public class ListIteratorDemo2 { 23 public static void main(String[] args) { 24 // 创建List集合对象 25 List list = new ArrayList(); 26 // 添加元素 27 list.add("hello"); 28 list.add("world"); 29 list.add("java"); 30 31 // 迭代器遍历 32 // Iterator it = list.iterator(); 33 // while (it.hasNext()) { 34 // String s = (String) it.next(); 35 // if ("world".equals(s)) { 36 // list.add("javaee"); 37 // } 38 // } 39 40 // 方式1:迭代器迭代元素,迭代器修改元素 41 // 而Iterator迭代器却没有添加功能,所以我们使用其子接口ListIterator 42 // ListIterator lit = list.listIterator(); 43 // while (lit.hasNext()) { 44 // String s = (String) lit.next(); 45 // if ("world".equals(s)) { 46 // lit.add("javaee"); 47 // } 48 // } 49 50 // 方式2:集合遍历元素,集合修改元素(普通for) 51 for (int x = 0; x < list.size(); x++) { 52 String s = (String) list.get(x); 53 if ("world".equals(s)) { 54 list.add("javaee"); 55 } 56 } 57 58 System.out.println("list:" + list); 59 } 60 }
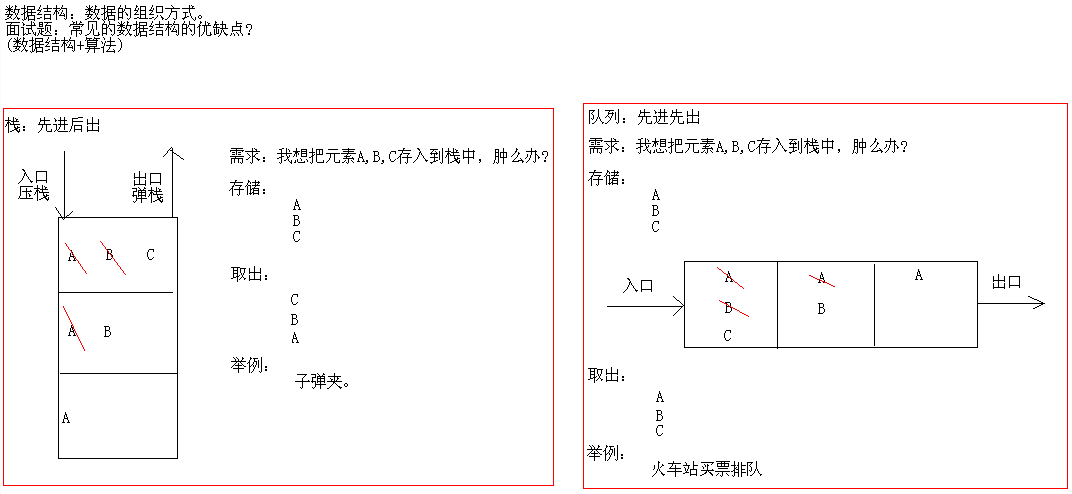
数据结构:栈、队列
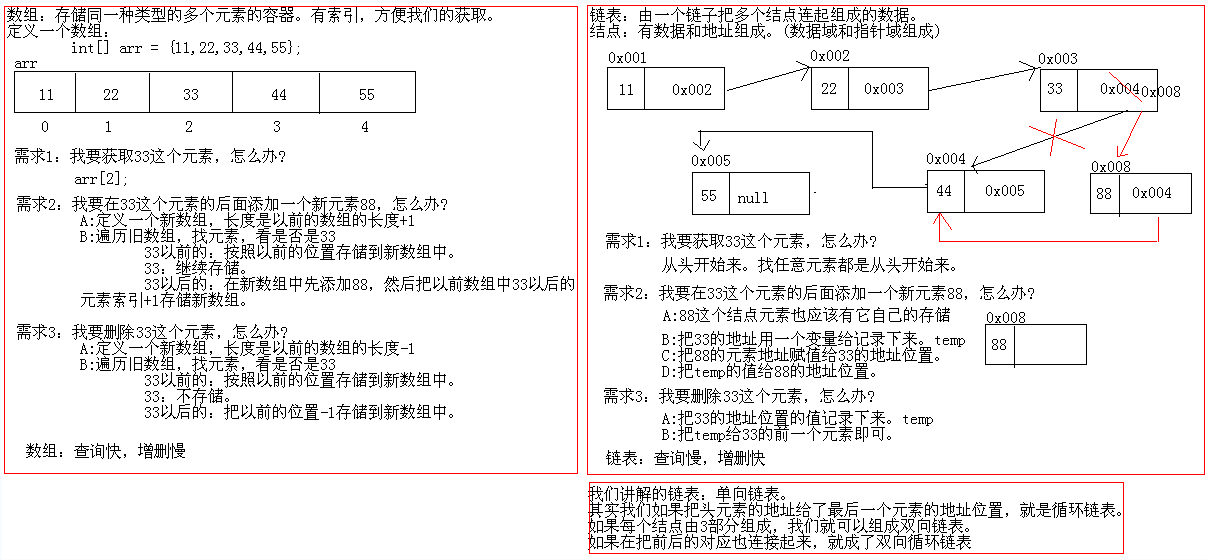
数据结构:数组、链表
 总结:List的三个子类的特点
总结:List的三个子类的特点
ArrayList:
底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢。
线程不安全,效率高。
Vector:
底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢。
线程安全,效率低。
LinkedList:
底层数据结构是链表,查询慢,增删快。
线程不安全,效率高。
List有三个儿子,我们到底使用谁呢?
看需求(情况)。
要安全吗?
要:Vector(即使要安全,也不用这个了,后面有替代的)
不要:ArrayList或者LinkedList
查询多:ArrayList
增删多:LinkedList