转载请注明:
仰望高端玩家的小清新 http://www.cnblogs.com/luruiyuan/
题目大意:
题目传送门:UVa 221 Urban Elevations
给出城市中建筑物的x, y 坐标的最小值:x,y , 再给出其以左下角为坐标原点的关于x轴、y轴上的长度 w, 和 d,最后给出建筑物的高度 h,将建筑物的正视图中,能够看到的建筑物的id打印出来:要求先打印x小的,当x相同时,打印y小的。为了简化,假定建筑物都是长方体。同时,每个输出之间要用一个空行隔开 One blank line must separate output from consecutive input records.(一开始没注意审题,wa在这了┭┮﹏┭┮)
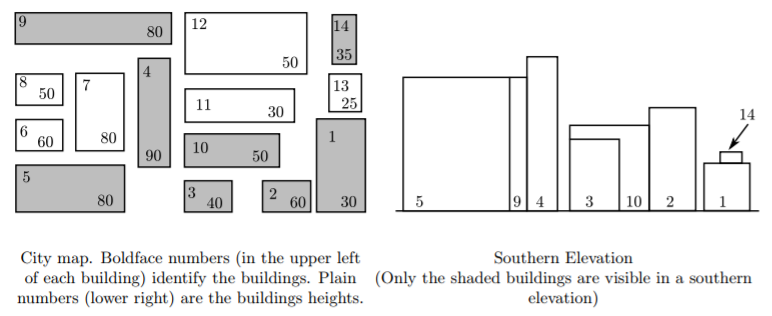
思路:
首先,这个题我本来没什么思路,还是不得不参考一波刘汝佳老师的思路
本题最大的收获是初步认识了 “离散化” :将无限转化为有限的方法。
- 首先,我们注意到,每个建筑物的深度在这里没有影响,因此深度是个干扰项
- 一个关键点是,题目给定的数据是实数,即浮点数,因此我们不能穷举所有的x坐标来遍历,对于无穷问题,我们需要考虑离散化,化无穷为有限
- 对于本题,离散化的关键在于,如何表示建筑物之间的互相重叠的关系
- 必须注意到,每个建筑物有2个x坐标,一个是input中直接给出的x,而另一个是我们可以通过w+x得到的“右边的x坐标”
- 通过2个坐标,我们可以首先对x去重,然后构建出相应的x轴的多个区间,这样,每一组重叠关系必然会落在我们的x区间之中。这也正是代码中x数组开2倍空间的原因,以及用途。
- 我们只需在区间内任选一点,即可作为区间的整体代表元素,来判断某个建筑是否经过了此区间,因此,可以选择比较方便的区间中点。没有经过区间代表元素的,显然不会经过该区间。经过了第5步和这一步,我们就将一个无限问题,转化为有限问题了。
- 对于每个建筑,我们考虑2点:是否经过了区间中点;是否存在y坐标小于它,且高度大于等于它的建筑。上述两点满足任何一点,则该建筑都不可见
- 其他小细节:代码 53 行的 b[j].y < b[i].y 能够保证 i != j; 53行的判定语句的顺序也可以些微提高代码效率,比如将函数调用延迟到最后一个,以降低调用概率,降低平均运行时间;unique() 函数调用前必须首先排序,因为unique函数只能对相邻元素去重,这和unique的原理有关,话说,这里的unique函数真的没有python 里的 set() 好用啊。。。
代码如下:
1 // UVa 221 Urban Elevations 2 // Ruiyuan Lu 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int maxn = 100 + 5; 8 double x[maxn*2]; // each building has 2 coordinates of x axis 9 int n; // number of the buildings 10 11 struct Building{ 12 int id; 13 double x, y, w, d, h; // w: means x_len, d:depth means y_len, h:height 14 bool operator < (const Building& b) const { // sort for output 15 return x < b.x || (x == b.x && y < b.y); 16 } 17 }b[maxn]; 18 19 bool cover(int i, double mx); // determine if the mx is in the range of building's x coordinate 20 bool visible(int i, double mx); // i: the index of buildings; mx: middle x coordinate of an interval 21 22 int main(){ 23 int cnt = 0; 24 while(scanf("%d", &n) == 1 && n > 0){ 25 for(int i=0; i<n;i++){ 26 scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &b[i].x, &b[i].y, &b[i].w, &b[i].d, &b[i].h); 27 b[i].id = i + 1; 28 x[i*2] = b[i].x; x[i*2+1] = b[i].x + b[i].w; // init x for discretization 29 } 30 sort(x, x+n*2); // sort before unique() is invoked 31 sort(b, b+n); // sort for output 32 int m = unique(x, x+maxn*2) - x; // get the number of unique x in the array 33 // print result 34 if(cnt++)printf(" "); // print the ' ' for last output 35 printf("For map #%d, the visible buildings are numbered as follows: %d", cnt, b[0].id); 36 for(int i=1;i<n;i++) 37 for(int j=1;j<m;j++) // check each building if it is visible in any interval of m intervals 38 if(visible(i, (x[j-1] + x[j]) / 2)){ 39 printf(" %d", b[i].id); 40 break; 41 } 42 printf(" "); // as they required: One blank line must separate output from consecutive input records. 43 } 44 } 45 46 bool cover(int i, double mx){ 47 return b[i].x <= mx && b[i].x + b[i].w >= mx; 48 } 49 50 bool visible(int i, double mx){ 51 if(!cover(i, mx)) return false; 52 for(int j=0;j<n;j++) 53 if(b[j].y < b[i].y && b[j].h >= b[i].h && cover(j, mx)) return false; 54 return true; 55 }

啦啦啦,今天就到这里啦~改天见*★,°*:.☆( ̄▽ ̄)/$:*.°★* 。