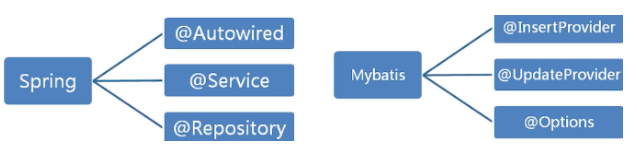
一,概念
注解是jdk1.5之后提供的,自带以下几种注解:
@Deprecated 意思是“废弃的,过时的”
@Override 意思是“重写、覆盖”
@SuppressWarnings 意思是“压缩警告”
很多框架都用到了注解,提高了效率。
二,例子
新建注解类和使用类
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE }) public @interface MyAnnotation { String color(); }
@MyAnnotation(color = "yellow") public class MyAnnotationUse { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean hasAnnotation = MyAnnotationUse.class.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println(hasAnnotation); if (hasAnnotation){ System.out.println(MyAnnotationUse.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class)); System.out.println(MyAnnotationUse.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class).color()); } } }
output:
true
@com.test.annotation.MyAnnotation(color=yellow)
yellow
三,属性解释;
@interface 注解的关键字,就像用clas来说明Java类。实现了java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口
@Retention
Retention 的英文意为保留期的意思。当 @Retention 应用到一个注解上的时候,它解释说明了这个注解的的存活时间。
它的取值如下:
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE 注解只在源码阶段保留,在编译器进行编译时它将被丢弃忽视。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS 注解只被保留到编译进行的时候,它并不会被加载到 JVM 中。
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME 注解可以保留到程序运行的时候,它会被加载进入到 JVM 中,所以在程序运行时可以获取到它们。
@Target
Target 是目标的意思,@Target 指定了注解运用的地方。
你可以这样理解,当一个注解被 @Target 注解时,这个注解就被限定了运用的场景。
类比到标签,原本标签是你想张贴到哪个地方就到哪个地方,但是因为 @Target 的存在,它张贴的地方就非常具体了,比如只能张贴到方法上、类上、方法参数上等等。@Target 有下面的取值
ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE 可以给一个注解进行注解
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR 可以给构造方法进行注解
ElementType.FIELD 可以给属性进行注解
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE 可以给局部变量进行注解
ElementType.METHOD 可以给方法进行注解
ElementType.PACKAGE 可以给一个包进行注解
ElementType.PARAMETER 可以给一个方法内的参数进行注解
ElementType.TYPE 可以给一个类型进行注解,比如类、接口、枚举
四、框架的使用