图
图是一种用顶点和边来表示关系的数据模型,一般用来表示多对多关系。图分为无向图和有向图两种。例如:
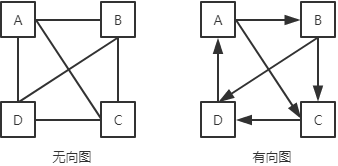
无向图中“A — B”表示A可以直接到达B,B也可以直接到达A;有向图中“A —> B”表示A可以直接到达B,而B不能直接到达A。即无向图的边是双向可达的,有向图的边是单向可达的。
图的表示
图可以用一个二维数组表示,其中0表示不能直接到达,1表示可以直接到达。例如:
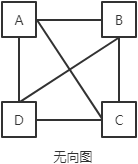
可以表示为:
| A | B | C | D | |
| A | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| B | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| C | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| D | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |

可以表示为:
| A | B | C | D | |
| A | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| B | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| D | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
图还可以用一个链表数组表示,链表中的元素为该顶点可以直接到达的顶点。例如:

可以表示为:
| A | B -> C -> D |
| B | A -> C -> D |
| C | A -> B -> D |
| D | A -> B -> C |

可以表示为:
| A | B -> C |
| B | C -> D |
| C | D |
| D | A |
用链表表示图的代码如下:

1 public class Graph { 2 3 private ArrayList<String> vertices; 4 private ArrayList<LinkedList<String>> edges; 5 6 public Graph() { 7 vertices = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 edges = new ArrayList<LinkedList<String>>(); 9 } 10 11 public void addVertices(String ... vertices) { 12 for (String vertice : vertices) { 13 this.vertices.add(vertice); 14 edges.add(new LinkedList<String>()); 15 } 16 } 17 18 public boolean addEdge(String from, String to, boolean isDirected) { 19 if (! vertices.contains(from)) { 20 System.err.println("起点不存在!"); 21 return false; 22 } 23 if (! vertices.contains(to)) { 24 System.err.println("终点不存在!"); 25 return false; 26 } 27 edges.get(vertices.indexOf(from)).add(to); 28 if (! isDirected) edges.get(vertices.indexOf(to)).add(from); 29 return true; 30 } 31 32 @Override 33 public String toString() { 34 String str = ""; 35 for (int i = 0; i < vertices.size(); i++) { 36 str += vertices.get(i) + ": "; 37 for (String edge : edges.get(i)) { 38 str += edge + " "; 39 } 40 str += " "; 41 } 42 return str; 43 } 44 45 }
其中,vertices表示顶点,edges表示边。
图的遍历
图有两种遍历方式:深度优先遍历(Depth First Search,DFS)和广度优先遍历(Broad First Search,BFS)。
深度优先遍历的步骤如下:
a. 判断当前顶点是否遍历,如果没有则遍历当前顶点。
b. 若当前顶点有可以到达的顶点,则按顺序递归遍历所有可以到达的顶点。
c. 若还有没有遍历的顶点,则返回步骤a,直到遍历完所有结点。
深度优先遍历的代码如下:

1 public void dfs() { 2 System.out.print("深度优先遍历:"); 3 boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[vertices.size()]; 4 for (int i = 0; i < vertices.size(); i++) dfs(i, isVisited); 5 System.out.println(); 6 } 7 8 private void dfs(int start, boolean[] isVisited) { 9 if (isVisited[start]) return; 10 System.out.print(vertices.get(start) + " "); 11 isVisited[start] = true; 12 for (String edge : edges.get(start)) dfs(vertices.indexOf(edge), isVisited); 13 }
例如,从顶点A开始进行深度优先遍历:

a. 遍历顶点A,顶点A有可到达的顶点B和C。
b. 遍历顶点B,顶点B有可到达的顶点C和D。
c. 遍历顶点C,顶点C有可到达的顶点D。
d. 遍历顶点D。
输出结果为:
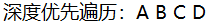
广度优先遍历的步骤如下:
a. 判断当前顶点是否遍历,如果没有则遍历当前顶点。
b. 若当前顶点有可到达的顶点,则按顺序遍历所有可到达的顶点。
c. 按顺序判断当前顶点可到达的顶点是否有可到达的顶点,如果有则返回步骤b。
d. 若还有没有遍历的顶点,则返回步骤a,直到遍历完所有结点。
广度优先遍历的代码如下:

1 public void bfs() { 2 System.out.print("广度优先遍历:"); 3 boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[vertices.size()]; 4 Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>(); 5 for (int i = 0, index; i < vertices.size(); i++) { 6 if (! isVisited[i]) { 7 q.add(i); 8 while (! q.isEmpty()) { 9 index = q.poll(); 10 System.out.print(vertices.get(index) + " "); 11 isVisited[index] = true; 12 for (String edge : edges.get(index)) { 13 index = vertices.indexOf(edge); 14 if (! isVisited[index] && ! q.contains(index)) q.add(index); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 System.out.println(); 20 }
例如,从顶点A开始遍历:

a. 遍历顶点A。
b. 顶点A有可到达的顶点B和C,遍历顶点B和C。
c. 顶点B有可到达的顶点C和D,顶点C已经遍历过,直接遍历顶点D。
输出结果为:

