一、numpy库与matplotlib库的基本介绍
1.安装
(1)通过pip安装:
>> pip install matplotlib

安装完成
安装matplotlib的方式和numpy很像,下面不再介绍。
2.作用
(1)numpy:科学计算包,支持N维数组运算、处理大型矩阵、成熟的广播函数库、矢量运算、线性代数、傅里叶变换、随机数生成,并可与C++/Fortran语言无缝结合。树莓派Python v3默认安装已经包含了numpy。
numPy 是一个运行速度非常快的数学库,主要用于数组计算,包含:
- 一个强大的N维数组对象 ndarray
- 广播功能函数
- 整合 C/C++/Fortran 代码的工具
- 线性代数、傅里叶变换、随机数生成等功能
(2)
matplotlib: 可能是 Python 2D-绘图领域使用最广泛的套件。它能让使用者很轻松地将数据图形化,可以绘制多种形式的图形,包括线图、直方图、饼状图、散点图、误差线图等等并且提供多样化的输出格式。是数据可视化的重要工具。
二、扩展库numpy的简介
导入模块 >>> import numpy as np
生成数组 >>> np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) # 把列表转换为数组 array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) >>> np.array((1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) # 把元组转换成数组 array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) >>> np.array(range(5)) # 把range对象转换成数组 array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) >>> np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) # 二维数组 array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) >>> np.arange(8) # 类似于内置函数range() array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) >>> np.arange(1, 10, 2) array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
生成各种各样的矩阵或数组,下面不再介绍
数组与数值的运算 >>> x = np.array((1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) # 创建数组对象 >>> x array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) >>> x * 2 # 数组与数值相乘,返回新数组 array([ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10]) >>> x / 2 # 数组与数值相除 array([ 0.5, 1. , 1.5, 2. , 2.5]) >>> x // 2 # 数组与数值整除 array([0, 1, 1, 2, 2], dtype=int32) >>> x ** 3 # 幂运算 array([1, 8, 27, 64, 125], dtype=int32) >>> x + 2 # 数组与数值相加 array([3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) >>> x % 3 # 余数 array([1, 2, 0, 1, 2], dtype=int32)
>>> 2 ** x
array([2, 4, 8, 16, 32], dtype=int32)
>>> 2 / x
array([2. ,1. ,0.66666667, 0.5, 0.4])
>>> 63 // x
array([63, 31, 21, 15, 12], dtype=int32)
数组与数组的运算 >>> a = np.array((1, 2, 3)) >>> b = np.array(([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9])) >>> c = a * b # 数组与数组相乘 >>> c # a中的每个元素乘以b中的对应列元素 array([[ 1, 4, 9], [ 4, 10, 18], [ 7, 16, 27]]) >>> c / b # 数组之间的除法运算 array([[ 1., 2., 3.], [ 1., 2., 3.], [ 1., 2., 3.]]) >>> c / a array([[ 1., 2., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6.], [ 7., 8., 9.]]) >>> a + a # 数组之间的加法运算 array([2, 4, 6]) >>> a * a # 数组之间的乘法运算 array([1, 4, 9]) >>> a - a # 数组之间的减法运算 array([0, 0, 0]) >>> a / a # 数组之间的除法运算 array([ 1., 1., 1.])
转置 >>> b = np.array(([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9])) >>> b array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) >>> b.T # 转置 array([[1, 4, 7], [2, 5, 8], [3, 6, 9]])
参考资料:http://www.runoob.com/numpy/numpy-matplotlib.html
三、matplotlib库的简介
matplotlib中最基础的模块是pyplot
因为matplotlib库源于matlab,其操作基本如matlab的操作,以下用绘制一个函数的例子介绍matplotlib库。
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt X = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 256, endpoint=True) C,S = np.cos(X), np.sin(X) plt.plot(X,C) plt.plot(X,S) plt.show()
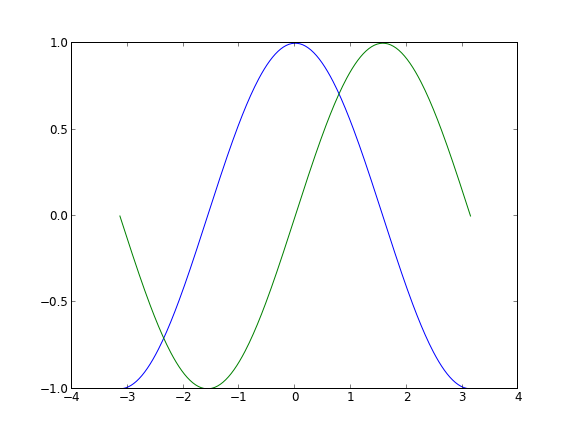
效果如下。
参考资料:http://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/matplotlib-tutorial.html
四、绘制雷达图
代码实现:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei' # 设置字体 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 设置字体 labels = np.array(['发育','死亡','击杀','助攻','团战','出装']) # 设置标签 datas = np.array([5, 2, 9, 13, 11, 7]) # 设置数据 angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 6, endpoint = False) # 设置角度 datas = np.concatenate((datas, [datas[0]])) angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]])) fig = plt.figure(facecolor = 'white') # 创建绘图区域 plt.subplot(111, polar = True) # 极坐标 plt.plot(angles, datas, 'bo-', color = 'g', linewidth = 1) # 画图 plt.fill(angles, datas, facecolor = 'g', alpha = 0.25) # 填充 plt.thetagrids(angles*180/np.pi, labels) # 设置极坐标的位置 plt.figtext(0.52, 0.95, '28-lie', ha = 'center') # 设置标题 plt.grid(True) # 打开网格线 plt.show() # 展示图片
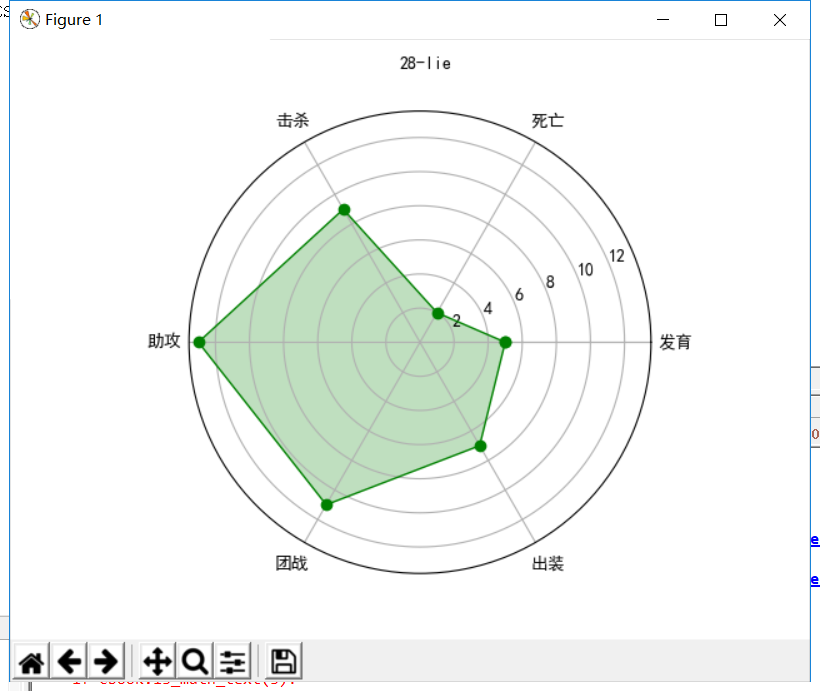
五、此处展示PIL制作手绘风格
1.手绘图像的基本思想是利用像素之间的梯度值重构每个像素值,为了体现光照效果,设计一个光源,建立光源对个点梯度值的影响函数,进而运算出新的像素值,从而体现边界点灰度变化,形成手绘效果。
2.代码实现
from PIL import Image import numpy as np vec_el = np.pi/2.2 # 光源的俯视角度,弧度值 vec_az = np.pi/4. # 光源的方位角度,弧度值 depth = 10. # (0-100) im = Image.open(r'C:Users80939Desktop iantan.jpg').convert('L') a = np.asarray(im).astype('float') grad = np.gradient(a) #取图像灰度的梯度值 grad_x, grad_y = grad #分别取横纵图像梯度值 grad_x = grad_x*depth/100. grad_y = grad_y*depth/100. dx = np.cos(vec_el)*np.cos(vec_az) #光源对x 轴的影响 dy = np.cos(vec_el)*np.sin(vec_az) #光源对y 轴的影响 dz = np.sin(vec_el) #光源对z 轴的影响 A = np.sqrt(grad_x**2 + grad_y**2 + 1.) uni_x = grad_x/A uni_y = grad_y/A uni_z = 1./A a2 = 255*(dx*uni_x + dy*uni_y + dz*uni_z) #光源归一化 a2 = a2.clip(0,255) im2 = Image.fromarray(a2.astype('uint8')) #重构图像 im2.save(r'C:Users80939Desktop iantan1.jpg')
3.效果对比
