java.util.concurrent
ConcurrentHashMap是一个支持并发检索和并发更新的线程安全的HashMap(但不允许空key或value)。
JDK8以CAS+synchronized来保证并发安全。
ConcurrentHashMap、HashMap和HashTable
效率:
- 当期望许多线程访问一个给定collection时,
ConcurrentHashMap通常优于同步的HashMap,ConcurrentSkipListMap通常优于同步的TreeMap - 当期望的读数和遍历远远大于列表的更新数时,
CopyOnWriteArrayList优于同步的ArrayList
ConcurrentHashMap、HashMap和HashTable的区别:
- HashMap 是非线程安全的哈希表,常用于单线程程序中。
- Hashtable 是线程安全的哈希表,由于是通过内置锁 synchronized 来保证线程安全,在资源争用比较高的环境下,Hashtable 的效率比较低。
- ConcurrentHashMap 是一个支持并发操作的线程安全的HashMap,但是他不允许存储空key或value。使用
CAS+synchronized来保证并发安全(在JDK 7之前是通过Lock和Segment(分段锁)实现并发安全),在并发访问时不需要阻塞线程,所以效率是比Hashtable 要高的。
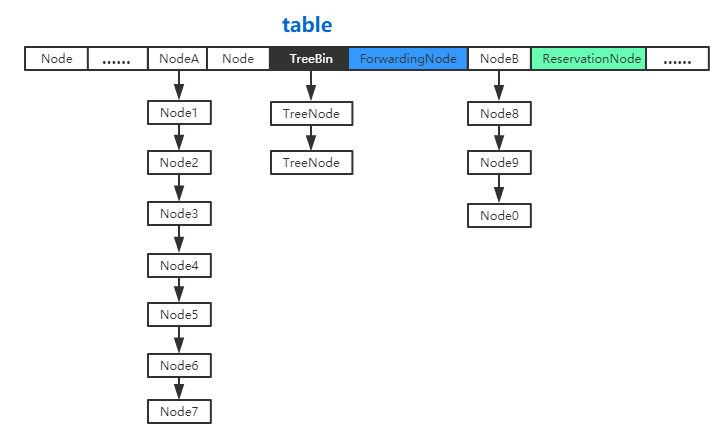
结构
put(K, V)
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//计算hash值
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {//自旋
//f:索引节点; n:tab.length; i:新节点索引 (n - 1) & hash; fh:f.hash
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//初始化
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {//索引i节点为空,直接插入
//cas插入节点,成功则跳出循环
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
//当前节点处于移动状态-其他线程正在进行节点转移操作
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
//帮助转移
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {//check stable
//f.hash>=0,说明f是链表的头结点
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;//记录链表节点数,用于后面是否转换为红黑树做判断
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
//key相同 修改
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
//到这里说明已经是链表尾,把当前值作为新的节点插入到队尾
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
//红黑树节点操作
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
//如果链表中节点数binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),则把链表转化为红黑树结构
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
//更新新元素个数
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
get(Object key)
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
remove(Object key)
public V remove(Object key) {
return replaceNode(key, null, null);
}
final V replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv) {
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||
(f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null)
break;
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
boolean validated = false;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
validated = true;
for (Node<K,V> e = f, pred = null;;) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
V ev = e.val;
if (cv == null || cv == ev ||
(ev != null && cv.equals(ev))) {
oldVal = ev;
if (value != null)
e.val = value;
else if (pred != null)
pred.next = e.next;
else
setTabAt(tab, i, e.next);
}
break;
}
pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null)
break;
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
validated = true;
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> r, p;
if ((r = t.root) != null &&
(p = r.findTreeNode(hash, key, null)) != null) {
V pv = p.val;
if (cv == null || cv == pv ||
(pv != null && cv.equals(pv))) {
oldVal = pv;
if (value != null)
p.val = value;
else if (t.removeTreeNode(p))
setTabAt(tab, i, untreeify(t.first));
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof ReservationNode)
throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update");
}
}
if (validated) {
if (oldVal != null) {
if (value == null)
addCount(-1L, -1);
return oldVal;
}
break;
}
}
}
return null;
}