pstree,ps,pgrep
pkill,pidof
top,htop
glance,pmap,
vmstat,dstat
kill,pkill
job,bg,fg,nohup
sar(内存),tsar,iosstat(磁盘IO),iftop(网络接口数据)
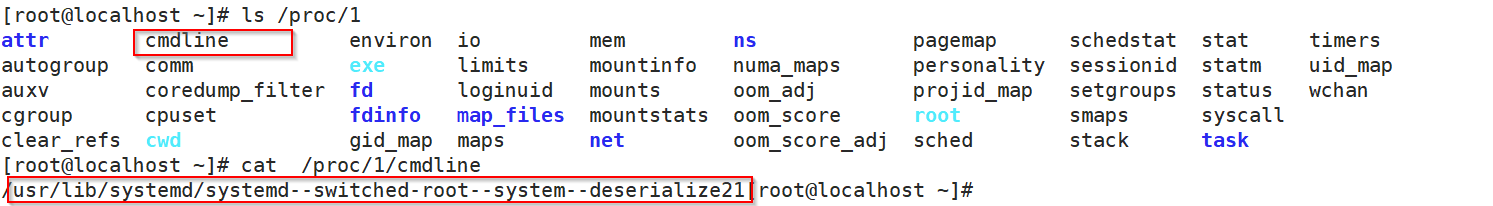
Linux 系统各进程的相关信息均保存在/proc/PID目录下的个文件中,而进程查看的命令都是遍历去读取该目录下的内容
靠什么命令来启动相应进程的 就在cmdline文件中
一、pstree显示进程树
二、ps
2.1、BSD风格:
ps option
a 与终端相关的进程 x 与终端无关的进程 u 与用户相关的进程 Z 安全标签(安全上下文) o 自定义显示格式
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ps aux
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMANDUSER: 进程用户 PID: 进程PID %CPU: 运行占据CPU时间百分比 VSZ:虚拟内存集:可交换出的数据 一般大于RSS RSS: 常驻内存集:不可交换出的数据 TTY: 通过哪个终端启动 (?代表与终端无关) STAT:进程状态 R(Running),S(Interrupt Sleeping),D(uninterrupt Sleeping),T(Stopped),z(zombie) +:前台
l: 多线程进程 N:低优先级
< :高优先级进程 s 领导进程, START: 进程启动时间 TIME: 进程运行过程占据CPU累积时长 COMMAND: 由什么命令启动的相关进程
2.2、System V 风格
ps option
-e:相当于 ax -f:显示详细信息
-F:显示完整格式的进程信息 -H hierarchy 层级结构显示
-eFH :以进程层级格式显示进程相关信息
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ps -ef UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ps -eF
UID PID PPID C SZ RSS PSR STIME TTY TIME CMD自定义显示:
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# ps axo pid,ppid,ni,psr,pri,rtprio,time,cmd
PID PPID NI PSR PRI RTPRIO TIME CMD
ppid: 父进程id,0代表 天造地设
PRI: priority
PSR: 运行在哪个cpu上
rtprio: realtime priority 实时优先级C cpu编号 (多个CPU时会显示不同编号)三、pgrep,pkill
pgrep [option] pattern
pkill [option] pattern
-u euid :effective user 有效用户(suid的属主)
-U uid : real user真实用户
-t terminal 与指定终端相关的进程
-a 完整格式的进程名
-l 显示进程名
-P PPID 显示PPID的子进程列表
pidof :根据进程名获取其PID
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# pgrep sshd 4472 10829 [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# pgrep sshd -l 4472 sshd 10829 sshd [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# pgrep sshd -a 4472 /usr/sbin/sshd -D 10829 sshd: root@pts/0 [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# pgrep -P 4472 10829 [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# pgrep -t pts/0 10831 [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# pgrep -t pts/0 -l 10831 bash [root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# pgrep -t pts/0 -a 10831 -bash
四、top命令
top option
-d # :刷新时间间隔 默认为3秒
-b 批次显示
-n # 显示多少批次 与-b连胜
排序方式:(在键盘上输入如下命令进行排序)
P %CPU 占据CPU百分比(过去几秒占据CPU百分比:几秒由刷新定义)
M %MEM 占据内存百分比
T TIME :累计占据CPU时长
首部信息
第一行: uptime: 可按“l” 显示或取消该行信息
top - 11:20:24 up 30 days, 13:20, 2 user, load average: 0.04, 0.03, 0.05
“11:20:24”为系统当前时刻; “13:20”为系统启动后到现在的运作时间; “2 users”为当前登录到系统的用户,
更确切的说是登录到用户的终端数 -- 同一个用户同一时间对系统多个终端的连接将被视为多个用户连接到系统,这里的用户数也将表现为终端的数目;
load average: 0.03, 0.01, 0.05 过去一分钟、五分钟、十五分钟的平均负载
CPU队列中等待运行的任务的个数,而不是CPU占据百分比
第二行 :tasks: 可按 “t” ---CentOS 6上只有显示或取消,;CentOS 7上以进度条方式显示如图

第三行:显示每个cpu: 可按“1”
%Cpu(s): 0.0 us, 0.1 sy, 0.0 ni,99.9 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
%Cpu:cpu占用百分比 0.0 us:用户空间占用的百分比 0.1 sy:内核空间占用时间的百分比 0.0 ni:对nice调整占用的内存百分比 99.9 id:空闲百分比 0.0 wa:等待IO完成所消耗的百分比 0.0 hi:处理硬件中断所占用的百分比 0.0 si:处理软件中断所占用的百分比(模式切换) 0.0 st:被偷走的百分比(虚拟化程序)
第四行:Mem/Swap: 可按 “m”
进程信息 :
PR 优先级
NI Nice值
VIRT 相当于VRT 虚拟内存集
RES 相当于RSS 常驻内存集
SHR shared 共享内存大小
S STATE 状态
退出top命令 :敲"q"键
修改刷新时间间隔 : 敲“s”键
终止指定进程: 敲“k”键
五、htop
注:需要Fedora-EPEL源
yum 包
[Fedora-EPEL]
name=Fedora EPEL for EL6
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/6/$basearch
gpgcheck=0
选项:
-d # :指定延迟时间
-u UserName : 仅显示指定用户的进程
-s COLOMN:以指定字段进行排序
获取帮助: F1
选定进程后,按如下键
s: syscall 跟踪选定进程的系统调用
t :tree ,层级结构显示
l :显示选定进程打开的文件列表
a :设置进程和cpu亲源性,进程只能运行在某个cpu上,增加缓存命中率
F6 > 以指定字段排序
六、vmstat命令 虚拟内存工具virtual memory state
vmstat [delay[count]]
delay 延迟几秒刷新一次
count 刷新几次
-p partiton
内存信息查看
vmstat -s :显示内存的统计数据
/proc/memoinfo
[root@izpo45bh60h6bsz ~]# vmstat procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ------cpu----- r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st 3 0 0 208496 37940 465952 0 0 21 8 107 256 0 0 99 0 0
procs 进程
r running 等待队列的进程的个数
b block阻塞 --处于不可终端睡眠态的进程个数(被阻塞的队列的长度)
memory 内存
swpd 交换内存使用的总量
free 空闲物理内存总量
buff 内存中buff大小
cache 内存中cache大小
swap (站在交换内存角度)
si 从物理内存加载至swap的速率(kb/s)
so 从swap加载至物理内存的速率
io (站在系统角度)
bi input 从磁盘加载至内存的速率(kb/s)
bo output 从内存加载至磁盘的速率
system 系统
in/int interrupt 中断,每秒多少个中断
cs context switch 进程上下文切换次数(保存现场和恢复现场的切换次数)
cpu
us user space
sy system space/kernel space
id idle
wa wait 等待IO完成的时间比率
st stole 被虚拟化技术偷走的比率
七、pmap报告内存映射表
pmap [-x|-p|-d|-q] pid
-x extend显示扩展格式
-p 显示映射的完整路径
-d 显示设备信息
-q 不显示首尾信息
查看内存映射表
/proc/PID/maps
pmap pid
功能: 线性内存地址和物理地址映射关系
进程只知道线性地址
1、进程将打开的文件存储在进程内存地址空间中,分段存储
2、进程划分的空间为4K的整数倍(内存页的大小为4K)
3、heap堆、stack栈、anon: anonymous 匿名页---进程自己存储数据的位置,不能交换出去
Address Kbytes RSS Dirty Mode Mapping 00007ff5a8000000 164 12 12 rw--- [ anon ] 00007ff5a8029000 65372 0 0 ----- [ anon ] 00007ff5ac94d000 4 0 0 ----- [ anon ] 00007ff5ac94e000 8192 8 8 rw--- [ anon ] 00007ff5ad14e000 4 0 0 ----- [ anon ] 00007ff5ad14f000 8192 8 8 rw--- [ anon ] 00007ff5ad94f000 16 8 0 r-x-- libuuid.so.1.3.0 00007ff5ad953000 2044 0 0 ----- libuuid.so.1.3.0 00007ff5adb52000 4 4 4 r---- libuuid.so.1.3.0 00007ff5adb53000 4 4 4 rw--- libuuid.so.1.3.0 00007ff5adb54000 228 40 0 r-x-- libblkid.so.1.1.0 00007ff5adb8d000 2048 0 0 ----- libblkid.so.1.1.0 00007ff5add8d000 12 12 12 r---- libblkid.so.1.1.0 00007ff5add90000 4 4 4 rw--- libblkid.so.1.1.0
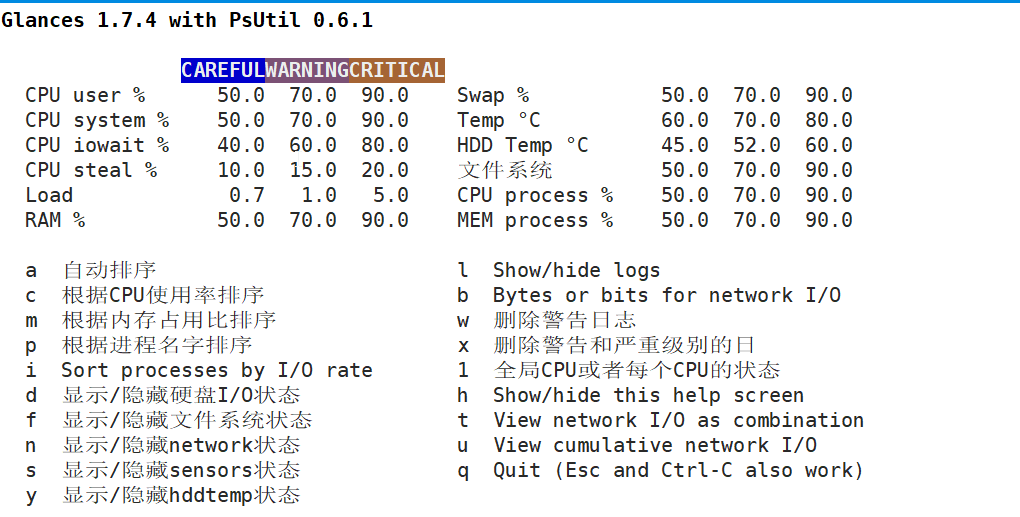
八、glances命令
galances [options...]
-s -B IPADDR 服务端模式
IPADDR:指明监听于本机哪个地址
-c IPADDR 客户端模式
IPADDR:要连入的服务器端地址
常用选项:
b :以字节Byte为单位显示网络速率
m/n/d :控制mount,network,disk模块的显示或隐藏
t # :延迟间隔
1 : 每个cpu信息单独显示
-f /path/to/somefile galance:显示的结果保存至文件中
-o {HTML|CSV} 文件的格式
galance内建命令
服务端
客户端
[root@localhost ~]# glances -c 192.168.1.103 -p 8888 Error: Connection to server failed. Bad password. [root@localhost ~]# glances -c 192.168.1.103 -p 8888 -P "1234" [root@localhost ~]# Connected to 192.168.1.103 | Press 'h' for help
九、dstat
重新换回CLI的颜色使用:reset
vmstat替换工具
dstat options
-c:显示cpu相关信息
-C #,#,..,total (指明CPU代表号)
-d :显示disk相关信息
-D total,/dev/sda,/dev/sdb,...
-g page显示内存数据交换的速率
-i :显示中断速率
-l, --load 显示平均负载
-m,--mem 显示内存相关统计数据;
-n,--net 显示网络相关统计数据;
-p,--proc 进程状态
-r,--io 显示io相关的统计数据
-s,--swap 显示swap 相关的统计数据
-t,--time 时间输出
--aio 异步io
--fs,--filesystem 显示文件系统
--ipc (message queue(signal),semephores,shared memory)
--lock 文件锁
--socket (total,udp,tcp,raw,ip-fragment分片)
--tcp (listen,established,syn,time_wait,close)
--udp (listen,active)
--unix (datagram, stream, listen, active)
----total-cpu-usage---- -dsk/total- -net/total- ---paging-- ---system-- usr sys idl wai hiq siq| read writ| recv send| in out | int csw total-cpu-usage cpu使用状态 dsk/total 磁盘读写速率 net/total 网络的收发速率 paging 页面的换进换出(内存页面,交换内存。 si,so) system 中断和上下文切换 (int: interrupt, csw: context swtich。 in,cs )
使用示例
1、cpu相关的信息
2、硬盘相关
3、页面
4、显示中断
5、平均负载
6、内存
7、网络
8、进程
9、io
10、swap
11、时间
12、异步IO
13、文件系统
14、进程通信
15、文件锁
16、套接字
17、tcp连接
18、udp连接
19、unix连接
20、-a
22、文件系统空闲
23、插件注释
24、显示最占用CPU的进程
25、中断次数最多
26、最占用io的进程
27、最占用内存的进程
28、延迟最大的进程