1. 求单链表中有效结点的个数
/**
* 获取单链表的有效结点个数(头结点不算)
* @param head 链表头结点
* @return 有效节点个数
*/
public static int getLength(HeroNode head) {
if (head.next == null) return 0;
int length = 0;
// 定义临时变量, 用于遍历链表
HeroNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return length;
}
2. 查找单链表中倒数第 k 个结点
/**
* 查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点
* @param head 链表头结点
* @param lastIndex 倒数索引
* @return 找到则对应位置的结点; 否则返回null
*/
public static HeroNode getNodeByLastIndex(HeroNode head, int lastIndex) {
if (head.next == null) return null;
// 1. 遍历得到链表总长度
int length = getLength(head);
// 2. 校验lastIndex
if (lastIndex <= 0 || lastIndex > length) return null;
// 3. 目标结点之前的结点个数
int count = length - lastIndex;
// 4. 从 首结点(第1个结点) 开始遍历, 移动 count 次, 到达 [倒数第k个结点]
HeroNode cur = head.next;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
cur = cur.next;
return cur;
}
3. 反转链表
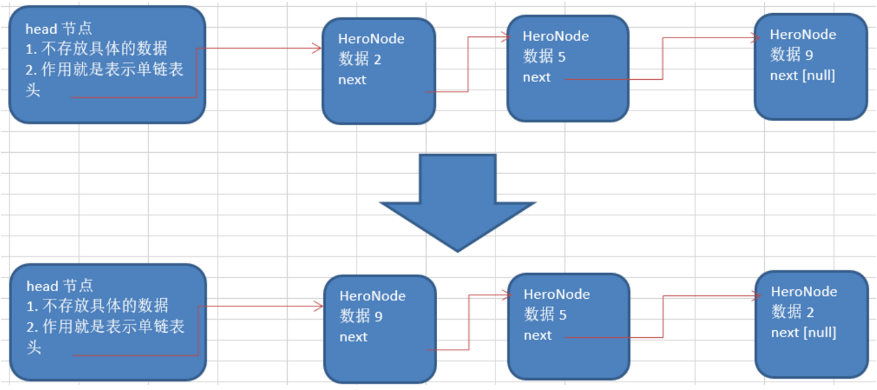
/**
* 链表反转
* @param head 单链表的头结点
*/
public static void reverseList(HeroNode head) {
// 0. 如果当前链表为空 / 只有一个结点, 则无须反转
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null) return;
// 1. 定义一个反转链表头结点 reverseHead
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
// 2. 创建临时节点
// 2.1 指向当前遍历到的结点
HeroNode cur = head.next;
// 2.2 存放当前遍历到的结点cur的next结点
HeroNode next;
// 3. 从头到尾遍历原来的链表, 每遍历到一个结点, 就将其取出, 放在新链表的最前面
while(cur != null) {
// 保存下一个要访问的结点地址
next = cur.next;
// 把当前结点链接到反转链表头部
cur.next = reverseHead.next;
reverseHead.next = cur;
// 结点后移
cur = next;
}
// 4. 让原链表的 head.next = reverseHead.next
head.next = reverseHead.next;
}
4. 逆序打印单链表(要求不改变链表本身的结构)
/**
* 逆序打印单链表(栈:先进后出)
* @param head 头结点
*/
public static void reversePrintList(HeroNode head) {
if(head.next == null) return;
// 1. 创建一个栈, 用来存储链表元素
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<>();
HeroNode cur = head.next;
// 2. 将结点压入栈中
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 3. 顺序出栈即逆序遍历
while (stack.size() > 0)
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
5. 链表中环的检测
public class DetectLoopTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 12, 13, 14 };
int[] loopArr = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 };
DetectLoopTest linkedList = new DetectLoopTest();
Node head = linkedList.buildLoopLinkedList(arr, loopArr);
boolean detectFalg = linkedList.detectLoop(head);
System.out.println("detect loop: " + detectFalg);
}
private static class Node {
final Integer item;
Node next;
Node(Integer item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 通过数组构造一个带有环的链表
* @param arr
* @return
*/
public Node buildLoopLinkedList(int[] arr, int[] loopArr) {
Node head = new Node(arr[0], null);
Node p = head;
if (arr.length >= 2) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
Node temp = new Node(arr[i], null);
p.next = temp;
p = temp;
}
}
// 构造一个环形链表
Node loopHead = new Node(loopArr[0], null);
if (loopArr.length >= 2) {
Node q = loopHead;
for (int i = 1; i < loopArr.length; i++) {
Node temp = new Node(loopArr[i], null);
q.next = temp;
q = temp;
}
q.next = loopHead;
}
p.next = loopHead;
return head;
}
/**
* 检查是否存在环形链表
* @param head
* @return
*/
public boolean detectLoop(Node head) {
Node pSlow = head, pFast = head;
boolean detectFlag = false;
// 只包含一个结点
if (head.next == null) return detectFlag;
List<Integer> slowPassNodes = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> fastPassNodes = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
pSlow = pSlow.next;
pFast = pFast.next.next;
slowPassNodes.add(pSlow.item);
if (pFast != null) {
fastPassNodes.add(pFast.item);
}
if (pFast == null) {
break;
}
if (pSlow == pFast) {
detectFlag = true;
break;
}
}
System.out.println("slow pointer traverse node list: " + slowPassNodes);
System.out.println("fast pointer traverse node list: " + fastPassNodes);
return detectFlag;
}
}
