目录
自定义频率、自动生成文档、JWT
自定义频率
#自定义频率需要写两个方法
#判断是否限次,没有限次True,否则False
def allow_request(self,request,view):
#限次后,返回等待的时间
def wait(self):
#my_ipthrottle.py
import time
class IPThrottle():
VISIT_DIC = {}
def __init__(self):
self.history_list = []
def allow_request(self,request,view):
ip = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
ctime = time.time()
if ip not in self.VISIT_DIC:
self.VISIT_DIC[ip] = [ctime,]
return True
self.history_list=self.VISIT_DIC[ip] #当前访问者时间列表拿出来
while True:
if ctime-self.history_list[-1] > 60:
self.history_list.pop()# 把最后一个移除
else:
break
if len(self.history_list) < 3:
self.history_list.insert(0,ctime)
return True
else:
return False
def wait(self):
ctime = time.time()
return 60-(ctime-self.history_list[-1])
#views.py
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
class TestAPIView(APIView):
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return Response({'status':100,'msg':'请求成功'})
#全局配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': (
'app01.utils.my_ipthrottle.IPThrottle',
),
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'luffy': '3/m' # key要跟类中的scop对应
},
}
#局部配置
#views.py
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from app01.utils.my_ipthrottle import IPThrottle
class TestAPIView(APIView):
throttle_classes = [IPThrottle,]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return Response({'status':100,'msg':'请求成功'})
#settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'luffy': '3/m' # key要跟类中的scop对应
},
}
自动生成接口文档
1 安装 pip3 install coreapi
2 路由中配置,根据已有的路由生成接口文档
from rest_framework.documentation import include_docs_urls
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('test2/',views.Test2APIView.as_view()),
#自动生成文档路由
path('docs/',include_docs_urls(title='luffy'))#title自定义的站点标题
]
3 继承自APIView及其子类可以自动生成文档,效果图看图1
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
class Test2APIView(APIView):
"""
get:
获取图书信息.
post:
增加图书
put:
修改图书信息
delete:
删除图书信息
"""
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return Response({'status':100,'msg':'请求成功'})
def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
...
def put(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
...
def delete(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
...
#继承视图集的,效果图看图2
from rest_framework.viewsets import GenericViewSet
from rest_framework import mixins
from app01.models import Book
from app01.ser import BookModelSerializer
class BookInfoViewSet(mixins.ListModelMixin, mixins.RetrieveModelMixin, GenericViewSet,mixins.DestroyModelMixin):
"""
list:
返回图书列表数据
retrieve:
返回图书详情数据
latest:
返回最新的图书数据
read:
修改图书的阅读量
"""
queryset = Book
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
#如果遇到报错,AttributeError: 'AutoSchema' object has no attribute 'get_link',配置下面这句加入即可
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.schemas.coreapi.AutoSchema',
# 新版drf schema_class默认用的是rest_framework.schemas.openapi.AutoSchema}
图1

图2

Json Web Token(jwt)简单使用
#原理
1 jwt分三段式:头(head)、体(payload)、签名(sgin)
2 头和体是可逆加密,让服务器可以反解除user对象,签名不可逆加密,保证整个token的安全性
3 这3部分都是采用json格式的字符串,进行加密,可逆加密采用base64,不可逆采用hash(md5)
4 头包含的是基本信息:如公司信息,项目组信息
5 体包含的是关键信息:用户主键,用户名,签发时客户端信息(设备号、地址),过期时间
6 签名包含的是安全信息:加密过的头和加密过的体加服务器不对外公开的安全码,之后经过hash(md5)加密
#效验
1 将token按.拆分为三段字符串,第一段是头加密结果,不用做人去处理
2 第二段是体加密结果,反解出用户主键,通过主键从user表获得当前登录用户,过期时间和设备信息都是安全信息,确保token没过期,切是同一设备
3 再用 第一段和第二段加服务器安全码 不可逆hash(md5)加密,与第三段签名,进行碰撞效验,通过后才能代表第二段效验得到的user对象就是合法的登录用户
#drf项目的jwt认证完整使用(重点)
1 用账号密码访问登录接口,登录接口逻辑中调用token算法,得到token,返回给客户端,客户端自动存到cookies
2 效验token的算法应该写认证类中(在认证类中调用),全局配置认证组件,所有视图都会经过认证类,请求带了token就可以反解出user对象,在视图中就能request.user获取到登录用户
#登录接口需要认证类和权限类禁用
#简单实用
1 安装 pip3 install django-rest-framework-jwt
2 新建一个User表,继承AbstractUser
#models.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser
class UserInfo(AbstractUser):
mobilephone = models.CharField(max_length=11)
3 创建超级用户
PyCharm终端python3 manage.py createsuperuser
4 urls.py中加入路由
from rest_framework_jwt.views import obtain_jwt_token
path('login/', obtain_jwt_token),
#全局配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# 认证模块
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework_jwt.authentication.JSONWebTokenAuthentication',),}
#局部配置,视图类里加上authentication_classes
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import JSONWebTokenAuthentication
class TestAPIView(APIView):
# authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication,]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return Response('ok')
#app中一定要注册
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'rest_framework_jwt',
'rest_framework',]
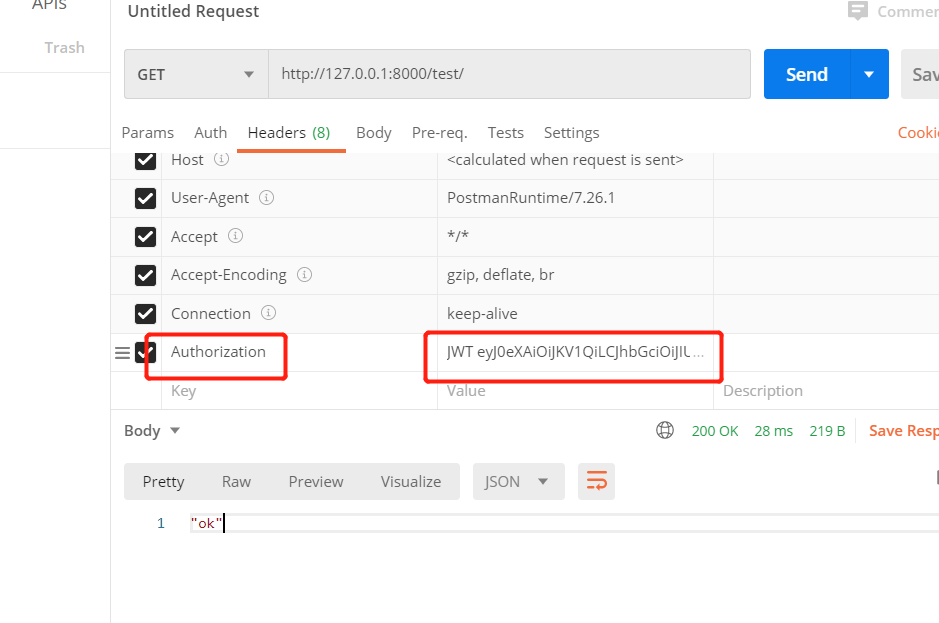
#携带token注意事项,JWT空格再加token看图1 ,
#简单使用jwt是内置的不带Authorization也可以通过,之后需要自定义JWT认证
图1
自定义JWT认证
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import jwt_decode_handler
from rest_framework import exceptions
class MyAuthentication(BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
jwt_value = str(request.META.get('HTTP_AUTHORIZATION'))
#认证
try:
payload = jwt_decode_handler(jwt_value)
except Exception:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed("认证失败")
user = self.authenticate_credentials(payload)
return user,None
#全局配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ('app01.utils.authenticate.MyAuthentication',),}
#局部配置
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
#自定义jwt认证
from app01.utils.authenticate import MyAuthentication
class TestAPIView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return Response('ok')
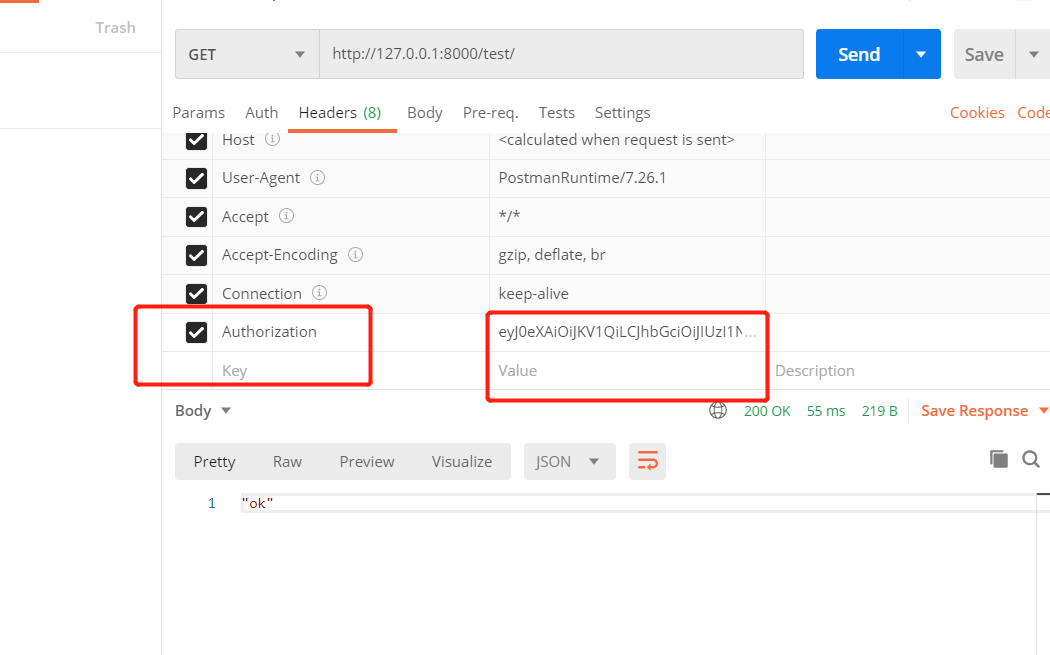
#使用方式不需要JWT加空格了看下图,其他配置跟上面简单使用一致
控制用户登录才能访问
#用户通过内置的jwt认证获得token,permission_classes就能获取到登录用户,否则不登录就无法访问
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import JSONWebTokenAuthentication
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
class TestAPIView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated, ]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return Response('ok')
控制登录接口返回的数据格式
#第一种方案
自己写登录接口
#第二种方案,控制内置的登录接口返回的数据格式
#还是采用内置的jwt认证,所以携带token还是得JWT空格token的方式,不然不会给你认证
#app01utilsjwt_response.py
def jwt_response_payload_handler(token, user=None, request=None):
return {
'status':100,
'msg':'登录成功',
'username':user.username,
'token': token,
}
#settins.py
JWT_AUTH = {
'JWT_RESPONSE_PAYLOAD_HANDLER':'app01.utils.jwt_response.jwt_response_payload_handler',
'JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA': datetime.timedelta(days=7), # token过期时间,手动配置
}
自定义基于JWT权限类
#app01utilsmyjwt.py
import jwt
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
from rest_framework_jwt.utils import jwt_decode_handler
from app01 import models
#第一种
class MyJwtAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
jwt_value=request.META.get('HTTP_AUTHORIZATION')
if jwt_value:
try:
payload = jwt_decode_handler(jwt_value)
except jwt.ExpiredSignature:
raise AuthenticationFailed('签名过期')
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
raise AuthenticationFailed('用户非法')
except Exception as e:
raise AuthenticationFailed(str(e))
#第一张获取用户名方式,数据库查
# user = models.User.objects.get(pk=payload.get('user_id'))
#第二种,不查库
user = models.User(id=payload.get('user_id'),username=payload.get('username'))
return user,jwt_value
raise AuthenticationFailed('你没有携带认证信息')
#第二种
class MyJwtAuthentication2(BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
jwt_value = request.META.get('HTTP_AUTHORIZATION')
if jwt_value:
try:
payload = jwt_decode_handler(jwt_value)
except jwt.ExpiredSignature:
raise AuthenticationFailed('签名过期')
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
raise AuthenticationFailed('用户非法')
except Exception as e:
raise AuthenticationFailed(str(e))
user = self.authenticate_credentials(payload)
return user, jwt_value
raise AuthenticationFailed('你没携带认证信息')
#全局配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": ['app01.utils.myjwt.MyJwtAuthentication2']
}
#局部配置
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from app01.utils.myjwt import MyJwtAuthentication
class TestAPIView(APIView):
#局部认证
authentication_classes = [MyJwtAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated, ]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
return Response('ok')
手动签发token(多方式登录)
#使用用户名,手机号,邮箱都可以登录
#前端需要传的格式
{
"username":"用户名或手机号或邮箱",
"password":"密码"
}
#views.py
from rest_framework.viewsets import ViewSet
from app01.utils.ser import LoginModelSerializer
class Login2View(ViewSet): # 跟上面完全一样
authentication_classes = []
def login(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 1 需要 有个序列化的类
login_ser = LoginModelSerializer(data=request.data,context={'request':request})
# 2 生成序列化类对象
# 3 调用序列号对象的is_validad
login_ser.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
token=login_ser.context.get('token')
# 4 return
return Response({'status':100,'msg':'登录成功','token':token,'username':login_ser.context.get('username')})
#app01utilsser.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from app01 import models
import re
from rest_framework.exceptions import ValidationError
from rest_framework_jwt.utils import jwt_encode_handler,jwt_payload_handler
class LoginModelSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
username=serializers.CharField() # 重新覆盖username字段,数据中它是unique,post,认为你保存数据,自己有校验没过
class Meta:
model=models.User
fields=['username','password']
def validate(self, attrs):
print(self.context)
# 在这写逻辑
username=attrs.get('username') # 用户名有三种方式
password=attrs.get('password')
# 通过判断,username数据不同,查询字段不一样
# 正则匹配,如果是手机号
if re.match('^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$',username):
user=models.User.objects.filter(mobile=username).first()
elif re.match('^.+@.+$',username):# 邮箱
user=models.User.objects.filter(email=username).first()
else:
user=models.User.objects.filter(username=username).first()
if user: # 存在用户
# 校验密码,因为是密文,要用check_password
if user.check_password(password):
# 签发token
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user) # 把user传入,得到payload
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload) # 把payload传入,得到token
self.context['token']=token
self.context['username']=user.username
return attrs
else:
raise ValidationError('密码错误')
else:
raise ValidationError('用户不存在')
JWT配置参数
#settings.py
import datetime
JWT_AUTH = {
'JWT_RESPONSE_PAYLOAD_HANDLER':'app01.utils.jwt_response.jwt_response_payload_handler',
'JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA': datetime.timedelta(days=7), # 过期时间,手动配置
}
基于角色的权限控制(Django内置的的auth体系)
#Role-Based Access Control(RBAC)是基于角色的访问控制,用于公司内部系统
#Django的auth就是一套基于RBAC的权限系统
#django中,
user表
permission表
group表
user_groups表是user和group的中间表
group_permissions表是group和permission中间表
user_permissions表是user和permission中间表
#后端,需要三大认证(认证,权限,频率)
Django缓存
# 前端混合开发缓存的使用
-缓存的位置,通过配置文件来操作(以文件为例)
-缓存的粒度:
-全站缓存
中间件
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.cache.UpdateCacheMiddleware',
。。。。
'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware',
]
CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_SECONDS=10 # 全站缓存时间
-单页面缓存
在视图函数上加装饰器
from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page
@cache_page(5) # 缓存5s钟
def test_cache(request):
import time
ctime=time.time()
return render(request,'index.html',context={'ctime':ctime})
-页面局部缓存
{% load cache %}
{% cache 5 'name' %} # 5表示5s钟,name是唯一key值
{{ ctime }}
{% endcache %}
# 前后端分离缓存的使用
- 如何使用
from django.core.cache import cache
cache.set('key',value可以是任意数据类型)
cache.get('key')
-应用场景:
-第一次查询所有图书,你通过多表联查序列化之后的数据,直接缓存起来
-后续,先去缓存查,如果有直接返回,没有,去连表查,返回之前再缓存
base64使用
#base64编码和解码,base63可变长,可反解,hash(md5)固定长度,不可逆加密
#base64编码
import base64
import json
dic = {'name':'joab','age':18,'sex':'男'}
dic_str = json.dumps(dic)
ret = base64.b64encode(dic_str.encode('utf-8'))
#base64解码
ret2 = base64.b64decode(ret)