Spring源码从入门到放弃-Controller注册
{toc}
@contact:zhangxin@benmu-health.com
@update:2017-03-23 02:18:31
@spirng.version:4.3.7.RELEASE
引
本文主要介绍SpringMVC中如何注册Controller
SpringMVC中Controller由@Controller和@RequestMapping注解定义,@Controller定义对象为一个Controller,@RequestMapping定义了请求url路径,SpringMVC内部将Controller的方法抽象为多个org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod,将Method的@RequestMapping注解抽象成org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo,一个到来的http请求,经过DispatcherServlet转发,通过RequestMappingInfo匹配路径,找到对应的HandlerMethod处理请求。这里的HandlerMethod可以理解为Controller的一个方法。
1.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping类的初始化过程完成了对@Controller和@RequestMapping两个注解的解析该类由spring容器初始化过程解析。解析<mvc:annotation-driven />标签时会自动向spring容器注册该类。并在DispatcherServlet初始化的时候,在initHandlerMappings()方法中会从Spring容器中将该HandlerMapping作为DispatcherServlet的成员,用以处理http请求。
继承关系:
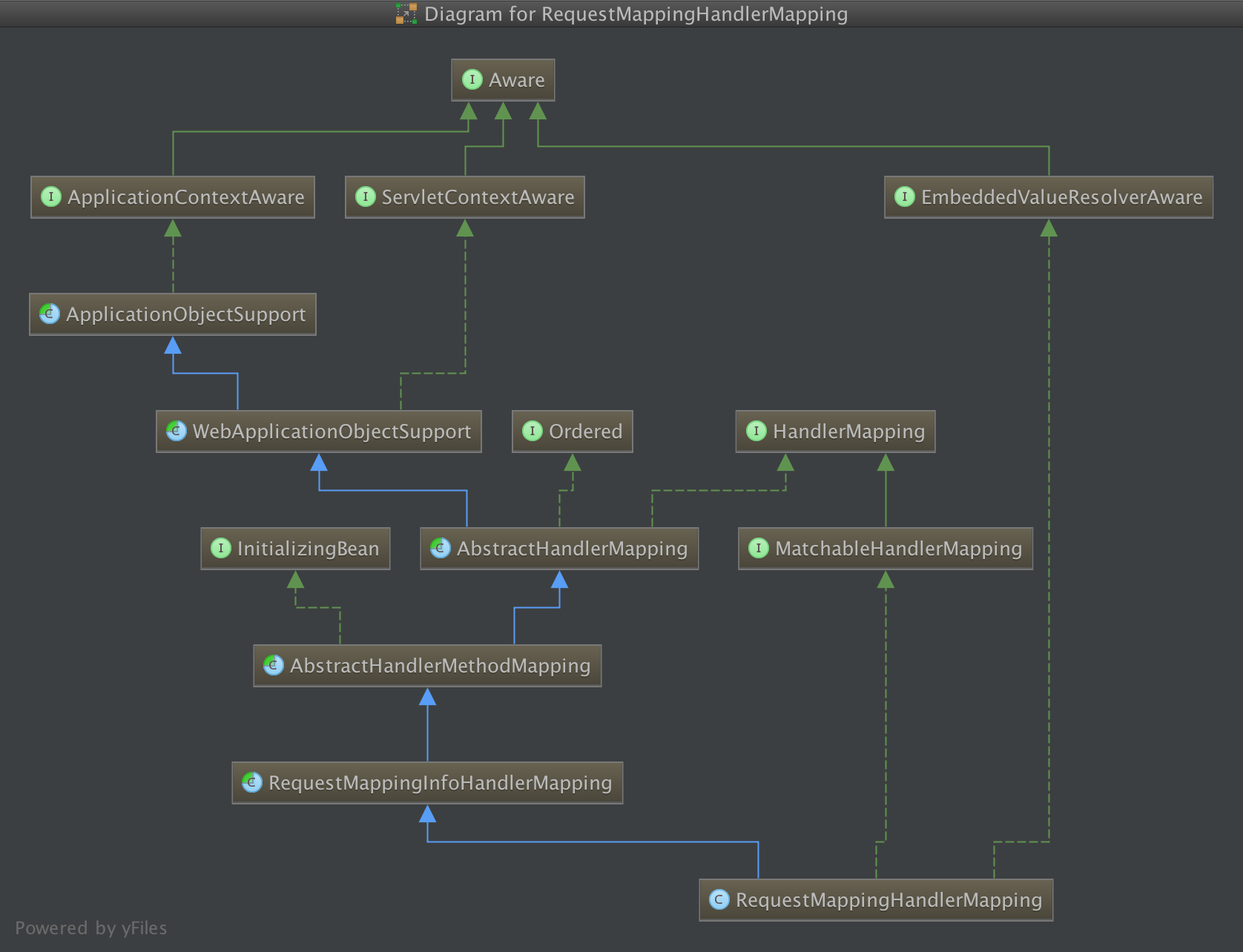
该类实现了HandlerMapping和InitializingBean两个接口,初始化方法afterPropertiesSet()完成了对@Controller和@RequestMapping的解析和注册。
2.afterPropertiesSet
Controller注册是在初始化方法afterPropertiesSet中,首先拿到Spring容器中所有的Bean,对每一个Bean判断是否为Controller
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
/**
* Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods.
* @see #isHandler(Class)
* @see #getMappingForMethod(Method, Class)
* @see #handlerMethodsInitialized(Map)
*/
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
//拿到所有bean的名字
String[] beanNames = getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
//拿到Class
beanType = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
//如果改bean带有@Controller和@RequestMapping注解
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
//注册hanler mapping即Controller
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
3.解析RequestMappingInfo
detectHandlerMethods完成对一个Controller的解析,将@RequestMapping方法解析成映射和可执行的HandlerMethod,映射抽象为RequestMappingInfo(即url pattern),将可执行的HandlerMethod和RequestMappingInfo一起注册到MappingRegistry中,DispatcherServlet收到一个请求的时候会从MappingRegistry中取出与url匹配的handler method来执行。
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
//拿到用户实际注册的类,防止CGLIB代理
final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
//选出该类打@RequestMapping的方法,并转成Map<Method,RequestMappingInfo>
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>() {
@Override
public T inspect(Method method) {
//对每一个method,转成RequestMappingInfo,如果不带@RequestMapping注解则返回null
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
});
for (Map.Entry<Method, T> entry : methods.entrySet()) {
//包装成一个可执行方法
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
//实际为RequestMappingInfo
T mapping = entry.getValue();
//将RequestMappingInfo和handler注册到MappingRegistry
//DispatcherServlet收到一个请求的时候会从MappingRegistry中取出与url匹配的handler来执行
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
}
}
getMappingForMethod()方法中完成了将带有@RequestMapping注解的方法转为RequestMappingInfo。
分别将Class和Method上的@RequestMapping拿到,用属性生成RequestMappingInfo。然后将两个RequestMappingInfo合并成一个。e.g. Class上的注解为path=/test,Method上的注解为path=/hello,method=POST,合并之后就是path=/test/hello,method=POST,并且为每一个RequestMappingInfo生成一个PatternsRequestCondition,用来完成DispatchServlet分发请求时url匹配。
@Override
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
//解析method的@RequestMapping
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
//解析Class的@RequestMapping
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
//将两个@RequestMapping合并
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
//拿到注解
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, null) : null);
}
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
//用@RequestMapping的属性生成RequestMappingInfo
return RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))//e.g. /test
.methods(requestMapping.method())//e.g. POST
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name())
.customCondition(customCondition)
.options(this.config)
.build();
}
@Override
public RequestMappingInfo build() {
ContentNegotiationManager manager = this.options.getContentNegotiationManager();
//生成路径匹配类,DispatcherServlet中分发url请求时调用
PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition = new PatternsRequestCondition(
this.paths, this.options.getUrlPathHelper(), this.options.getPathMatcher(),
this.options.useSuffixPatternMatch(), this.options.useTrailingSlashMatch(),
this.options.getFileExtensions());
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.mappingName, patternsCondition,
new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(methods),
new ParamsRequestCondition(this.params),
new HeadersRequestCondition(this.headers),
new ConsumesRequestCondition(this.consumes, this.headers),
new ProducesRequestCondition(this.produces, this.headers, manager),
this.customCondition);
}
4.RequestMappingInfo与handler注册
handler最终会被封装成HandlerMethod,
RequestMappingInfo与HandlerMethod都注册到org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry中,MappingRegistry有两个属性,Map<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod>和Map<url, HandlerMethod>,维护了路径和HandlerMethod的关系。注册@Controller即生成这两个Map。
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
//通过Bean和Method,抽象成可执行的HandlerMethod,即Controller的带有@RequestMapping注解的Method
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
//注册Map<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod>
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
//注册Map<url, HandlerMethod>
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
//http跨域配置
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
//注册Map<RequestMappingInfo, MappingRegistration<RequestMappingInfo>>
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
} finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
5.DispatcherServlet与MappingRegistry
这里顺带提一下DispatcherServlet如何找到处理当前Http Request的HandlerMethod,最终http请求由匹配到的HandlerMethod来处理。
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
//从Map<url, HandlerMethod>中找
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
//从所有的RequestMappingInfo中找
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
//本质为Comparator<RequestMappingInfo>
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
//选出最匹配当前Request的RequestMappingInfo
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
//校验
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" +
request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
//处理url上的template variables, matrix variables
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
//拿到handlerMethod
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
} else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}