写在前面
在工作中遇到一个问题,就是使用 SpringMVC自带定时器 时,发现了定时任务执行两次的问题。虽然问题当是是解决了。但是却给我留下来一个大大的疑问,为什么这样配置?
-
是不是一定要使用 ContextLoaderListener ?
-
是不是一定增加 <context-param /> 中名为 contextConfigLocation 的属性?
为了解决这个疑问,首先,我们需要理解 ContextLoaderListener 加载过程。
概述 ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderListener 实现了 ServletContextListener 接口,ServletContextListener 是 Java EE 标准接口之一,类似 Jetty,Tomcat,JBoss 等 java 容器启动时便会触发该接口的 contextInitialized。
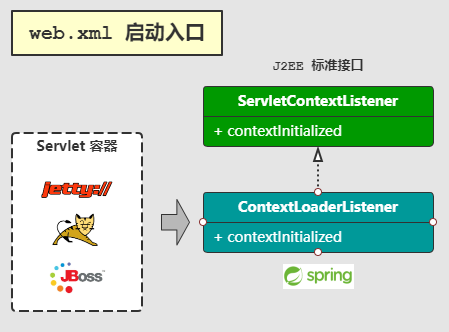
ContextLoaderListener 是由 Spring 公司 提供的一个类,您需要做的就是在 J2EE Servlet 标准的 web.xml 中 <web-app/> 声明一个 <listener/>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
ContextLoaderListener 初始化过程
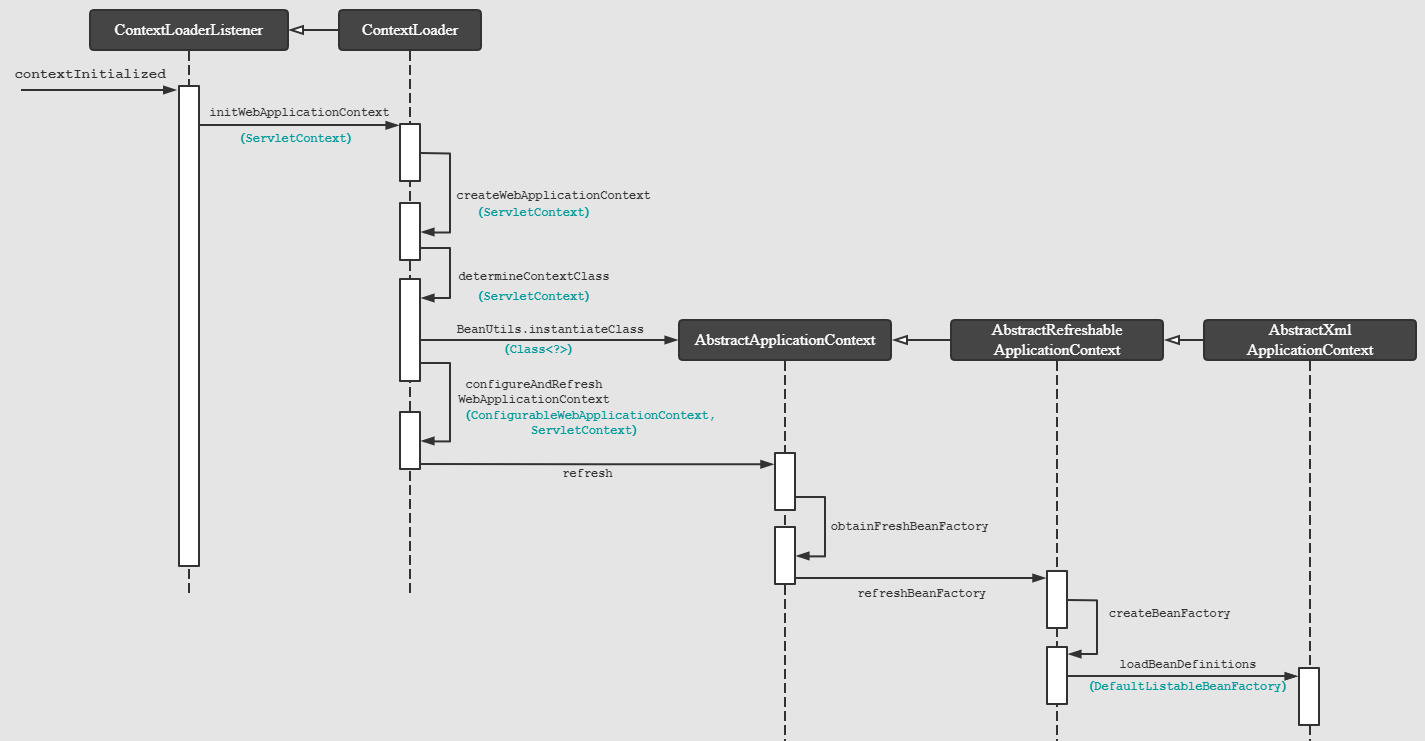
网上关于 ContextLoaderListener 加载过程的文章已经很多很全面了,所以我就结合排名第一的文章,画了一张时序图。如果你是电脑查看的,你可以右击图片,然后“在新标签页中打开图片” 查看大图。
总的来看有几个点很重要:
-
contextInitialized 通知 Spring Web 应用程序 Servlet 上下文发生变更。
-
我们需要为 Spring Web 应用程序创建一个 WebApplicationContext,一般来说,这个实现类是 XmlWebApplicationContext
-
我们需要为 Spring 应用程序上下文创建一个 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory,一般来说,这个实现类是 DefaultListableBeanFactory
-
最后,在 Spring 容器加载 Bean 定义时,会调用 loadBeanDefinitions 从 configLocations 即配置文件路径下,读取和解析配置文件。
1. contextInitialized
首先,ContextLoaderListener 是 ContextLoader 的子类,并且实现了 ServletContextListener 接口。
第三方 Servlet 容器主动调用 contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)。参数 ServletContextEvent 是一个事件类,用于通知 web 应用程序的 Servlet 上下文的更改。
2.1 实例化 Spring Web 应用程序上下文对象
紧接着调用 initWebApplicationContext 并且把 ServletContext 作为参数。接口 WebApplicationContext 是 ApplicationContext 的子类,是 Spring Web 应用程序的上下文。
createWebApplicationContext(ServletContextEvent event) 方法会 new 一个 WebApplicationContext 实例。具体的做法是先通过 determineContextClass 来决定应用上下文的类对象 contextClass,然后通过 BeanUtils.instantiateClass 来实例化对象。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
// 主要是通过反射的方式,调用类默认构造函数创建实例
// 这个方法跟主要流程关系不太大,所以就不具体展开说明了
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
determineContextClass
public class ContextLoader {
public static final String CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM = "contextClass";
protected Class determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
}
优先从 web.xml 中获取上下文参数,这里的<context-param /> 是 Servlet 的上下文参数,不是Spring 应用的上下文参数!但是这段代码实际效果是,在 Servlet 的上下文参数中,指定了接下来要创建的 Spring 应用的 ApplicationContext 的实现类名称。
<context-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value>org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param /> 标签内的参数可以通过 Java 代码 ServletContext # getInitParameter 方法得到,具体的代码是由 Servlet 容器来实现的。
如果没有指定 contextClass 的名称,那么就会去获取默认的 contextClass 类名。默认 contextClass 类名需要从 defaultStrategies 中去获得。这个静态成员变量的初始化代码如下:
defaultStrategies 初始化
public class ContextLoader {
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
知道这个默认配置,也就是知道有这么一回事儿,学个思路。实际上这个配置是在打包的 jar 文件中的,我们开发者也没办法自定义。
有兴趣的可以点击展开看看。
ContextLoader.properties
ContextLoader.properties 在 jar 包中的路径
ContextLoader.properties 的内容
# Default WebApplicationContext implementation class for ContextLoader. # Used as fallback when no explicit context implementation has been specified as context-param. # Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
一般来说我们使用 Spring MVC 框架时,用到的都是 XmlWebApplicationContext,即解析 xml 文件生成 WebApplicationContext
2.2 配置和刷新 Spring Web 应用程序上下文
经过上一步,我们已经创建出一个 XmlWebApplicationContext,但是光有对象还是不够的,我们还需要configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext来配置和刷新上下文。
第一段代码:设定 XmlWebApplicationContext 的 id
contextId 对于完整的流程而言只算一个小细节,有兴趣的可以点击展开
contextId
为 Spring Web 应用程序上下文设置一个更有意义的 ID
// 这是 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 的第一块代码
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default v
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
// 默认 contextId 前缀 + contextPath
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
默认的 contextId 前缀是org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext:
/**
* Prefix for ApplicationContext ids that refer to context path and/or servlet name.
*/
String APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ":";
第二段代码:设定 XmlWebApplicationContext 的 configLocation
contextConfigLocation
// 这是 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 的第二块代码
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
从这段代码可以知道,我们可以用 <context-param /> 设置 contextConfigLocation 参数,为 WebApplicationContext 自定义配置文件的路径。
/**
* Name of servlet context parameter (i.e., {@value}) that can specify the
* config location for the root context, falling back to the implementation's
* default otherwise.
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext#DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION
*/
public static final String CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM = "contextConfigLocation";
如果不自定义的话,默认会去加载 /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
/** Default config location for the root context. */
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml";
但是,这个 /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml 还是需要你自己创建的,不然会抛出异常。
java.io.FileNotFoundException: Could not open ServletContext resource [/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml]
最后一行:wac.refresh()
中间有配置环境变量的,有点复杂,等下次有机会遇到与之相关的问题再做分析。所以本次跳过了。
3. 创建 Bean 工厂
“破后而立” 之 refreshBeanFactory
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
// 刷新 Bean 工厂
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// “破”:如果刷新时,Spring上下文实例中已经有一个Bean工厂了,那么就先销毁它
if (this.hasBeanFactory()) {
this.destroyBeans();
this.closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// “立”:重新创建一个新的 Bean 工厂实例
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId());
this.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 为 Bean 工厂加载 Bean 定义
this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
// 为 Bean 工厂赋值新创建的工厂对象
synchronized(this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
} catch (IOException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + this.getDisplayName(), var5);
}
}
}
4. 从 xml 配置文件中加载 Bean 定义
为 Bean 工厂加载 Bean 定义,本文使用的 xml 配置方式。XmlWebApplicationContext 用的是 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 来读取文件中的 Bean 定义。
public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext {
// 接着上面的
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
}
还记得上文中 ContextLoader # configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 中的那段代码吗?
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
现在,<context-param/> 中配置的 contextConfigLocatin 就是在这里被使用的。
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException {
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
for (String configLocation : configLocations) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
}
}
}
加载 Bean 定义的具体过程可以去查询 XmlWebApplicationContext # loadBeanDefinitions 方法。
参考文献
Spring Web MVC - Other Web Frameworks - Common Configuration