树状数组实现区间更新区间查询:
要实现区间更新区间查询操作必须像这篇文章里面一样,引入一个数组a[],区间加就只要在这个数组区间左加增量,区间右后一个位置减增量。下面公式org[]表示变化之前的数据。
sum(x) = org[1] +... ...+ org[x] + (a[1]) + (a[1]+a[2]) + ... ...+ (a[1]+... ...a[x])
= org[1] +... ...+ org[x] + x*(a[1]) + (x-1)*a[2] + ... ... + a[x]
= org[1] +... ...+ org[x] + (x+1)*( a[1] +... ...+a[x] ) - ( a[1] + 2*a[2] +... ...+ x*a[x] )
这其实就是三个数组org[i], a[i]和a[i]*i的前缀和,org[i]的前缀和保持不变,事先就可以求出来,a[i]和
a[i]*i的前缀和是不断变化的,可以用两个树状数组来维护。
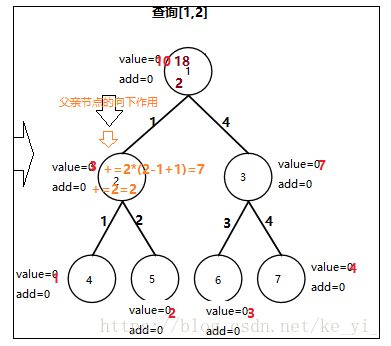
线段树实现区间更新区间查询:
需要引入一个add延迟变量,也就是每一次更新的时候我们只要将延迟变量作用到对应的区间而不要将增量作用到区间每一个元素,只有在查询的时候我们再将延迟变量向下作用产生;
题目描述:
A Simple Problem with Integers
| Time Limit: 5000MS | Memory Limit: 131072K | |
| Total Submissions: 134669 | Accepted: 41771 | |
| Case Time Limit: 2000MS | ||
Description
You have N integers, A1, A2, ... , AN. You need to deal with two kinds of operations. One type of operation is to add some given number to each number in a given interval. The other is to ask for the sum of numbers in a given interval.
Input
The first line contains two numbers N and Q. 1 ≤ N,Q ≤ 100000.
The second line contains N numbers, the initial values of A1, A2, ... , AN. -1000000000 ≤ Ai ≤ 1000000000.
Each of the next Q lines represents an operation.
"C a b c" means adding c to each of Aa, Aa+1, ... , Ab. -10000 ≤ c ≤ 10000.
"Q a b" means querying the sum of Aa, Aa+1, ... , Ab.
Output
You need to answer all Q commands in order. One answer in a line.
Sample Input
10 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Q 4 4
Q 1 10
Q 2 4
C 3 6 3
Q 2 4
Sample Output
4
55
9
15题目大意:输入一点序列,输入几组测试数据,测试数据有更新和查询,更新Q i,j,表示查询[i,j]区间和,C i j a,表示更新区间[i,j]每个元素加a;
树状数组实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN=1e5+10;
ll org[MAXN],a[MAXN],ai[MAXN];//org表示原数据,a表示增量,ai表示a[i]*i
int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll add(ll *d,int n,ll v){
while(n<MAXN){
d[n]+=v;
n+=lowbit(n);
}
}
ll sum(ll *d,int n){
ll s=0;
while(n){
s+=d[n];
n-=lowbit(n);
}
return s;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int i,N,Q,l,r,v;
cin>>N>>Q;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(ai,0,sizeof(ai));
org[0]=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;i++){
cin>>org[i];
org[i]+=org[i-1];
}
char op[2];
while(Q--){
cin>>op;
if(op[0]=='Q'){
cin>>l>>r;
ll sumr=org[r]+(r+1)*sum(a,r)-sum(ai,r);
ll suml=org[l-1]+(l)*sum(a,l-1)-sum(ai,l-1);
printf("%lld
",sumr-suml);
}
else{
cin>>l>>r>>v;
add(a,l,(ll)v);
add(a,r+1,(ll)-v);
add(ai,l,(ll)l*v);
add(ai,r+1,(ll)(r+1)*(-v));
}
}
return 0;
}线段树实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define N1 200001
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct node{
ll left,right,value,lazy;
}tree[4*N1];//线段树
int n,q;
ll a[N1];
void Sum(int i){//求子节点和
tree[i].value=tree[i<<1].value+tree[i<<1|1].value;
return;
}
void BuildTree(int i,int L,int R){//建立一颗[L,R]的树
tree[i].left=L;
tree[i].right=R;
tree[i].lazy=0;
if(L==R){
tree[i].value=a[L];
return ;
}
BuildTree(i<<1,L,(L+R)>>1);
BuildTree(i<<1|1,((L+R)>>1)+1,R);
Sum(i);
return ;
}
void PushDown(int i){//判断延迟父节点的延迟变量,作用到子节点
if(tree[i].lazy){
tree[i<<1].value+=tree[i].lazy*(tree[i<<1].right-tree[i<<1].left+1);
tree[i<<1|1].value+=tree[i].lazy*(tree[i<<1|1].right-tree[i<<1|1].left+1);//更新左右子节点的value
tree[i<<1].lazy+=tree[i].lazy;
tree[i<<1|1].lazy+=tree[i].lazy;//更新左右子节点的lazy
tree[i].lazy=0;//将lazy传给子节点后字节归零
}
return ;
}
void Update(int L,int R,ll s,int i){//更新[L,R]区间加s
if(L<=tree[i].left&&R>=tree[i].right){
tree[i].value+=s*(tree[i].right-tree[i].left+1);//如果区间更新包括i节点的区间,则更新value
tree[i].lazy+=s;//将lazy加上更新量
return ;
}
PushDown(i);//否则,将i的延迟变化量作用到左右子节点上
if(L<=tree[i<<1].right) Update(L,R,s,i<<1);
if(R>=tree[i<<1|1].left) Update(L,R,s,i<<1|1);
Sum(i);
return;
}
ll Query(int L,int R,int i){//查询[L,R]区间,从i开始查询
if(L<=tree[i].left&&R>=tree[i].right) return tree[i].value;
PushDown(i);
ll t=0;
if(L<=tree[i<<1].right) t+=Query(L,R,i<<1);
if(R>=tree[i<<1|1].left) t+=Query(L,R,i<<1|1);
return t;
}
int main(){
int Q,N;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>Q>>N;
for(int i=1;i<=Q;i++)cin>>a[i];
BuildTree(1,1,Q);
while(N--){
char op;
int l,r;
ll v;
cin>>op;
if(op=='Q'){
cin>>l>>r;
cout<<Query(l,r,1)<<endl;
}
else{
cin>>l>>r>>v;
Update(l,r,v,1);
}
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}