一:程序的主题
1.题目
在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
2.自己写的程序
1 package com.jianke.it; 2 3 public class FindNumFromTwoArray { 4 /* 5 [1,2,8,9], 6 [2,4,9,12], 7 [4,7,10,13], 8 [6,8,11,15] 9 */ 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 long start=System.nanoTime(); 12 int array[][]={{1,2,8,9},{2,4,9,12},{4,7,10,13},{6,8,11,15}}; 13 int target=7; 14 boolean flag=Find(target,array); 15 long end=System.nanoTime(); 16 System.out.println("boolean="+flag); 17 System.out.println("spend time:"+(end-start)+"ns"); 18 } 19 public static boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) { 20 boolean flag=false; 21 int count=array.length; 22 for(int i=0;i<count;i++) { 23 for(int j=0;j<array[i].length;j++) { 24 if(target==array[i][j]) { 25 return true; 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 return flag; 30 } 31 32 }
3.结果

4.程序二
/* 思路
* 矩阵是有序的,从左下角来看,向上数字递减,向右数字递增,
* 因此从左下角开始查找,当要查找数字比左下角数字大时。右移
* 要查找数字比左下角数字小时,上移
*/
1 package com.jianke.it; 2 3 public class FindNumFromTwoArray { 4 /* 5 [1,2,8,9], 6 [2,4,9,12], 7 [4,7,10,13], 8 [6,8,11,15] 9 */ 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 long start=System.nanoTime(); 12 int array[][]={{1,2,8,9},{2,4,9,12},{4,7,10,13},{6,8,11,15}}; 13 int target=7; 14 boolean flag=Find(target,array); 15 long end=System.nanoTime(); 16 System.out.println("boolean="+flag); 17 System.out.println("spend time:"+(end-start)+"ns"); 18 } 19 public static boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) { 20 int len=array.length-1; 21 int i=0; 22 while(len>=0&&(array[0].length>i)) { 23 if(array[len][0]>target) { 24 len--; 25 }else if(array[len][i]<target){ 26 i++; 27 }else { 28 return true; 29 } 30 } 31 return false; 32 } 33 34 }
5.程序三
/*思路
*把每一行看成有序递增的数组,*利用二分查找,*通过遍历每一行得到答案,*时间复杂度是mlogn,每行的时间复杂度是O(logn)。*/
1 package com.jianke.it; 2 3 public class FindNumFromTwoArray { 4 /* 5 [1,2,8,9], 6 [2,4,9,12], 7 [4,7,10,13], 8 [6,8,11,15] 9 */ 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 long start=System.nanoTime(); 12 int array[][]={{1,2,8,9},{2,4,9,12},{4,7,10,13},{6,8,11,15}}; 13 int target=7; 14 boolean flag=Find(target,array); 15 long end=System.nanoTime(); 16 System.out.println("boolean="+flag); 17 System.out.println("spend time:"+(end-start)+"ns"); 18 } 19 public static boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) { 20 for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++) { 21 int low=0; 22 int high=array[i].length-1; 23 while(low<=high) { 24 int mid=(low+high)/2; 25 if(target<array[i][mid]) { 26 high=mid-1; 27 }else if(target>array[i][mid]) { 28 low=mid+1; 29 }else { 30 return true; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 return false; 35 } 36 37 }
二:思考
1.为什么从左下角开始查找
为什么不从左上角开始搜寻,左上角向右和向下都是递增,那么对于一个点,对于向右和向下会产生一个岔路;
如果我们选择从左下脚开始搜寻的话,如果大于就向右,如果小于就向下
2.时间复杂度
法1:从左下搜索,遇大上移,遇小右移,时间复杂度O(m+n)
法2:每行都进行二分查找,时间复杂度O(mlogn)
3.二分查找的时间复杂度(快速理解)
二分查找的基本思想是将n个元素分成大致相等的两部分,去a[n/2]与x做比较,如果x=a[n/2],则找到x,算法中止;如果x<a[n/2],则只要在数组a的左半部分继续搜索x,如果x>a[n/2],则只要在数组a的右半部搜索x.
时间复杂度无非就是while循环的次数!
总共有n个元素,
渐渐跟下去就是n,n/2,n/4,....n/2^k,其中k就是循环的次数
由于你n/2^k取整后>=1
即令n/2^k=1
可得k=log2n,(是以2为底,n的对数)
所以时间复杂度可以表示O()=O(logn)
4.二分查找的时间复杂度(有点粗糙,但是是对的)
假设数据的规模为N(即每次调用时的high-low),程序执行的比较次数表示为C(N),假设程序查找的是一个不存在的数据,则此时执行的次数是最多的:
执行第一次时,有:
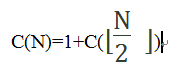
1代表执行了一次x和data[mid]的比较过程,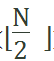 代表下一次递归调用find方法时high-low的值,也就是新的数据规模每次较少一半以上。
代表下一次递归调用find方法时high-low的值,也就是新的数据规模每次较少一半以上。
递归上面的公式,有:
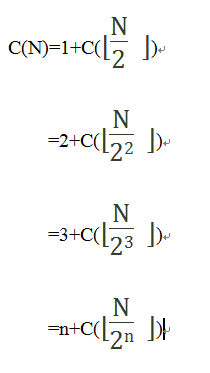
我们知道每一个整数都可以表示为2i+k的形式,如1=20+0,5=22+1,10=23+2,因此
设N=2i+k
令上面公式的n=i(为什么是n=i,因为n理解为次数,与i的意思相同),则有:
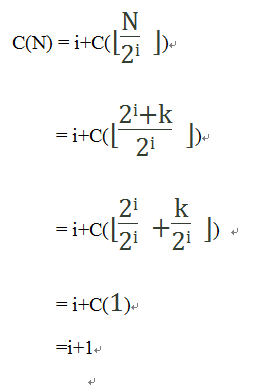
因为N=2i+k,则有i=⌊lgN⌋,因此:
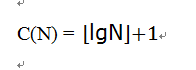
因为我们一直以来的假设是要查找到的元素是找不到的,所以现在的情况是C(N)最大的情况,对于一般情况,则有:
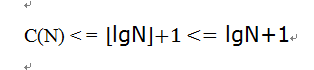
因此二分查找的时间复杂度是logN。