前言
学习Java阻塞队列的时候,了解到了ConcurrentLinkedQueue队列使用了堆结构,就整理一下堆结构的逻辑
原理
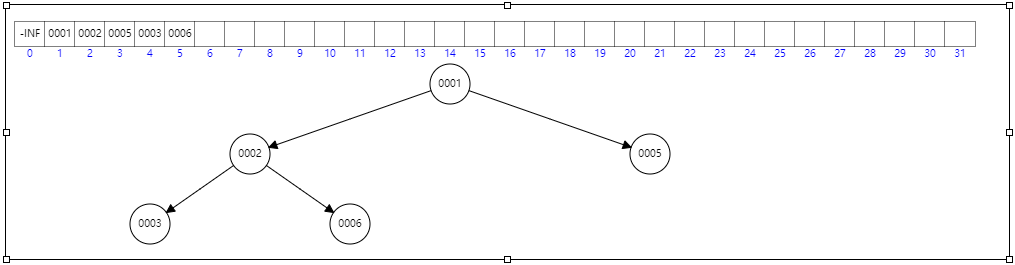
堆是一颗满二叉树(除了最后一层的节点可以不满,其他层都必须是满的),元素存储在数组中,头结点必定是最大或者最小值(大小顶堆)。
结构图
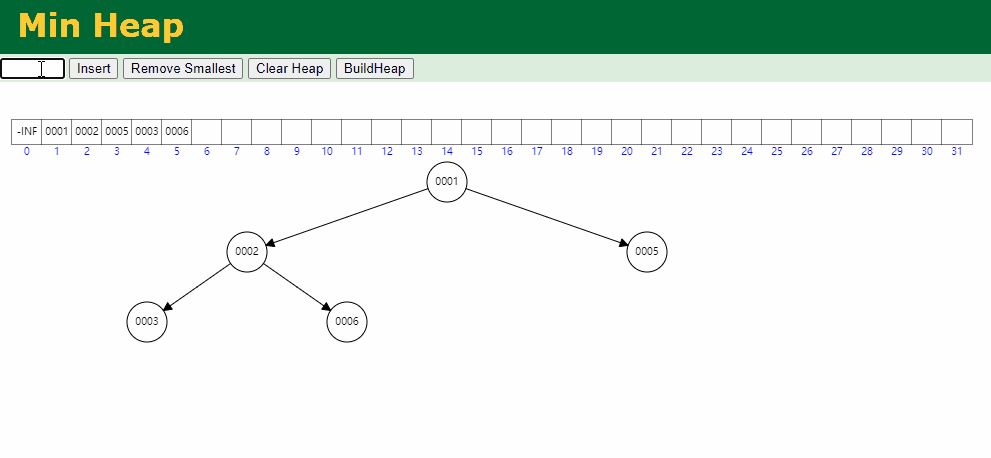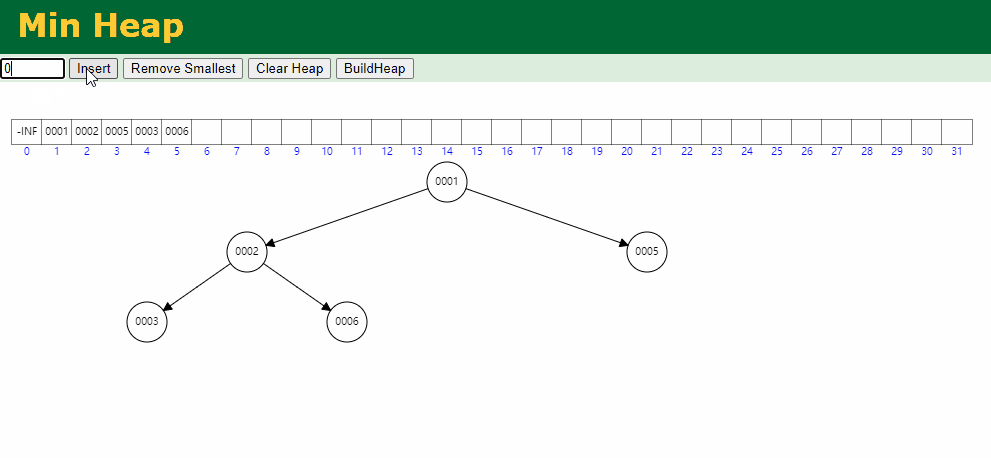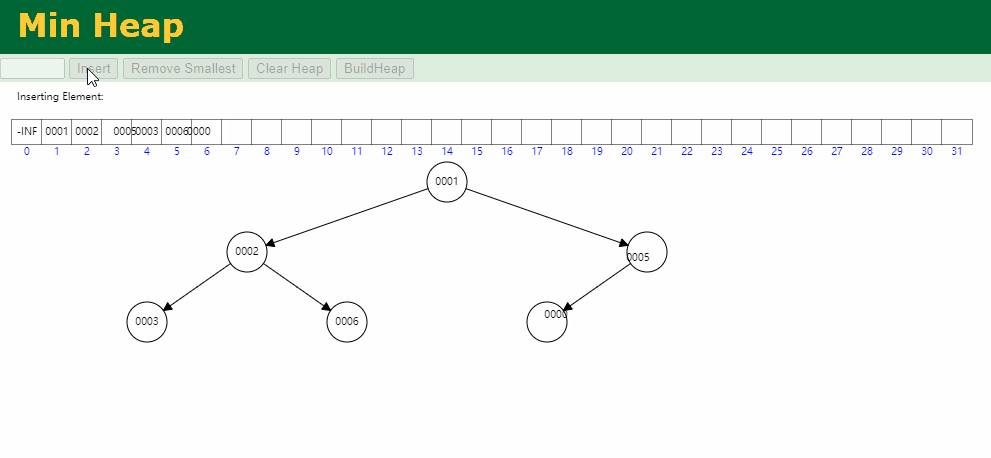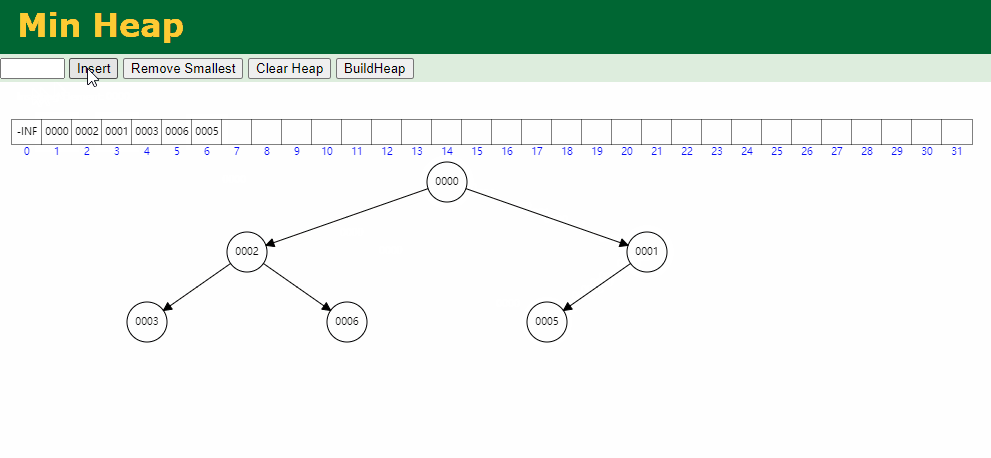
入队逻辑:保证小顶堆不变
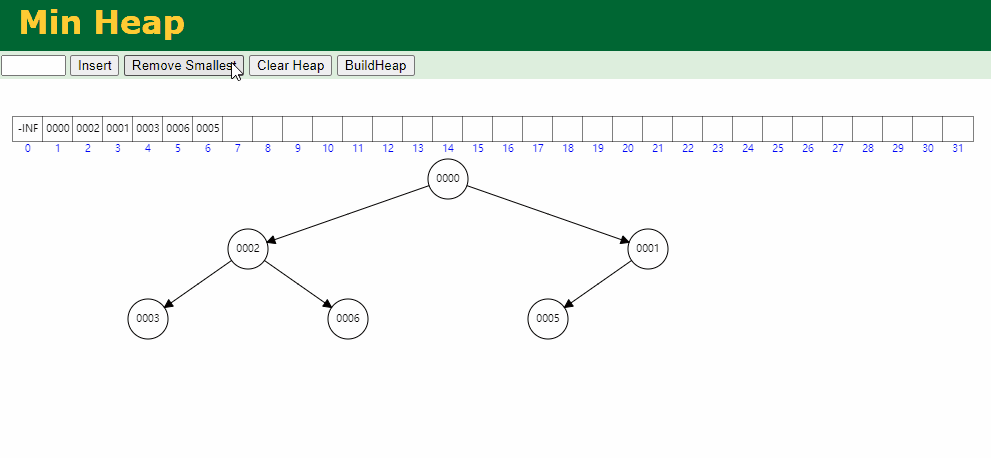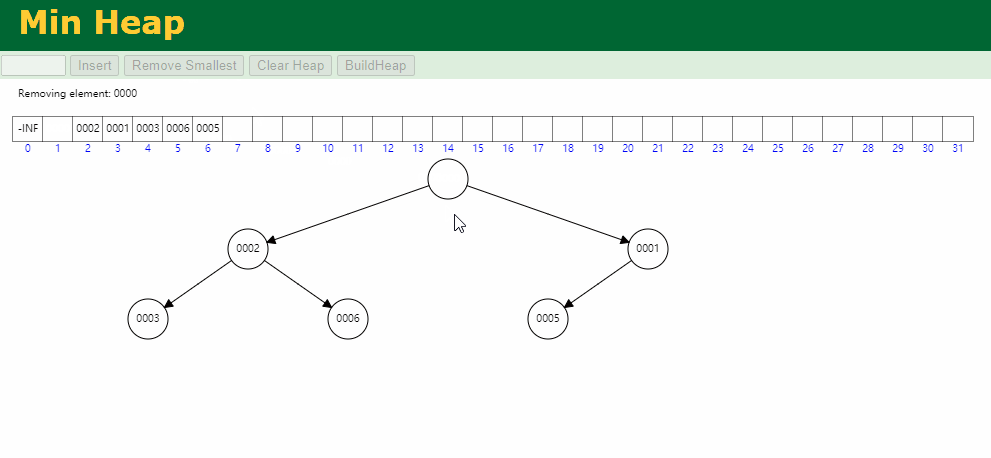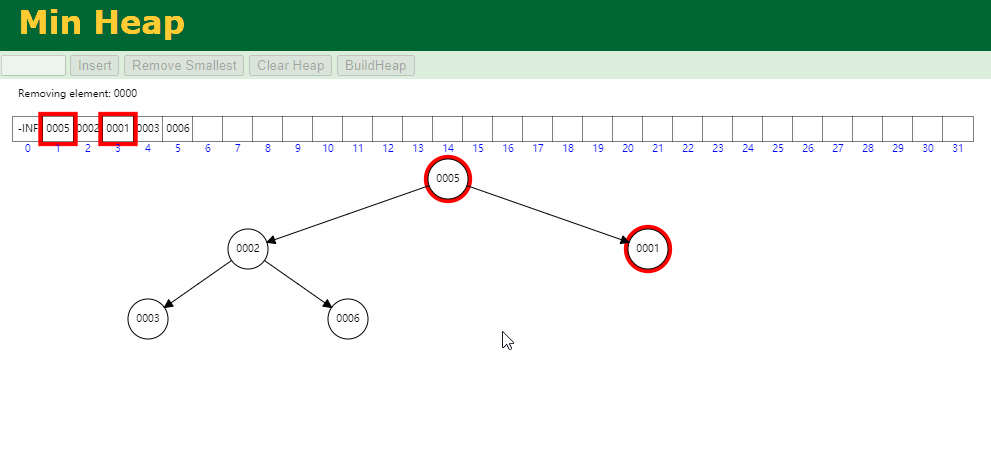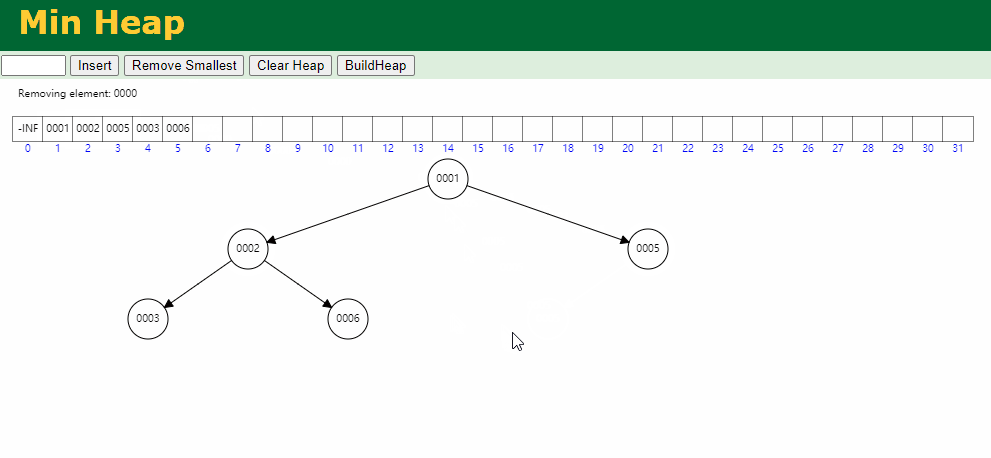
出队逻辑:
代码模拟实现
public class BinaryHeap { /** * 默认数组长度 */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 100; /** * 数组长度 */ private int currentSize; // Number of elements in heap private Comparable[] array; // The heap array public BinaryHeap() { this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY); } public BinaryHeap(Comparable[] items) { currentSize = items.length; array = new Comparable[(currentSize + 2) * 11 / 10]; int i = 1; for (Comparable item : items) { array[i++] = item; } buildHeap(); } public BinaryHeap(int capacity) { currentSize = 0; array = new Comparable[capacity + 1]; } public void insert(Comparable x) { // Percolate up int hole = ++currentSize; for (; hole > 1 && x.compareTo(array[hole / 2]) < 0; hole /= 2) array[hole] = array[hole / 2]; array[hole] = x; } public Comparable findMin() { if (isEmpty()) return null; return array[1]; } public Comparable deleteMin() { if (isEmpty()) return null; Comparable minItem = findMin(); array[1] = array[currentSize--]; percolateDown(1); return minItem; } private void buildHeap() { for (int i = currentSize / 2; i > 0; i--) percolateDown(i); } public boolean isEmpty() { return currentSize == 0; } public boolean isFull() { return currentSize == array.length - 1; } public void makeEmpty() { currentSize = 0; } private void percolateDown(int hole) { int child; Comparable tmp = array[hole];//保存变量 for (; hole * 2 <= currentSize; hole = child) { child = hole * 2;//获取左子树结点 //如果左子树结点不是堆的长度并且左子树大于右子树的值 if (child != currentSize && array[child + 1].compareTo(array[child]) < 0) child++;//child指向右子树 if (array[child].compareTo(tmp) < 0)//如果孩子比tmp小 array[hole] = array[child];//交换值 else break; } array[hole] = tmp; } public static void main(String[] args) { int numItems = 10; BinaryHeap h = new BinaryHeap(numItems); int i = 37; try { for (i = 37; i != 0; i = (i + 37) % numItems){ h.insert(i); } System.out.println("插入数据之后展示====================="); for (int j=1;j<=h.currentSize;j++){ System.out.print(h.array[j]+" "); } System.out.println(); h.deleteMin(); System.out.println("删除数据之后展示====================="); for (int j=1;j<=h.currentSize;j++){ System.out.print(h.array[j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Overflow (expected)! " + i); } } }
运行结果:

总结
堆是专门为优先级排序准备的一种数据结构,最小/最大的值永远在顶部,从底部获取就可以保证优先级。