1.具体算法
/**
* Created by huazhou on 2015/12/6.
*/
public class TestSearch {
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph G = new Graph(new In(args[0]));
int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
// DepthFirstSearch search = new DepthFirstSearch(G, s);
// Paths search = new Paths(G, s);
DepthFirstSearch search = new DepthFirstSearch(G,s);
// BreadthFirstPaths search = new BreadthFirstPaths(G,s);
// testConnected(search, G);
findAllPaths(search, G, s);
}
private static void findAllPaths(DepthFirstSearch search, Graph G, int s){
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++){
StdOut.print(s + " to " + v + ": ");
if(search.hasPathTo(v)){
for (int x : search.pathTo(v)){
if(x == s){
StdOut.print(x);
}
else{
StdOut.print("-" + x);
}
}
}
StdOut.println();
}
}
}
/**
* 无向图数据结构
* Created by huazhou on 2015/12/6.
*/
public class Graph {
private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator");
private int V; //顶点数目
private int E; //边的数目
private Bag<Integer>[] adj; //邻接表
//创建一个含有V个顶点但不含有边的图
public Graph(int V){
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
adj = (Bag<Integer>[])new Bag[V]; //创建邻接表
//将所有链表初始化为空
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++){
adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>();
}
}
//从标准输入流in读入一幅图
public Graph(In in){
this(in.readInt()); //读取V并将图初始化
int E = in.readInt(); //读取E
//添加一条边
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++){
int v = in.readInt(); //读取一个顶点
int w = in.readInt(); //读取另一个顶点
addEdge(v, w); //添加一条连接它们的边
}
}
//顶点数
public int V(){
return V;
}
//边数
public int E(){
return E;
}
//向图中添加一条边v-w
public void addEdge(int v, int w){
adj[v].add(w); //将w添加到v的链表中
adj[w].add(v); //将v添加到w的链表中
E++;
}
//和v相邻的所有顶点
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){
return adj[v];
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append(V + " vertices, " + E + " edges " + NEWLINE);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
s.append(v + ": ");
for (int w : adj[v]) {
s.append(w + " ");
}
s.append(NEWLINE);
}
return s.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
Graph G = new Graph(in);
StdOut.println(G);
}
}
/**
* 算法4.1 深度优先搜索
* Created by huazhou on 2015/12/8.
*/
public class DepthFirstSearch {
private boolean[] marked; //这个顶点上调用过dfs()了吗?
private int count;
private int[] edgeTo; //从起点到一个顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点
private int s; //起点
public DepthFirstSearch(Graph G, int s){
marked = new boolean[G.V()];
edgeTo = new int[G.V()];
this.s = s;
dfs(G, s);
}
private void dfs(Graph G, int v){
marked[v] = true;
count++;
for (int w : G.adj(v)){
if(!marked[w]){
dfs(G, w);
edgeTo[w] = v;
}
}
}
public boolean marked(int w){
return marked[w];
}
public int count(){
return count;
}
public boolean hasPathTo(int v){
return marked[v];
}
public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v){
if(!hasPathTo(v)){
return null;
}
Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int x = v; x != s; x = edgeTo[x]){
path.push(x);
}
path.push(s);
return path;
}
}
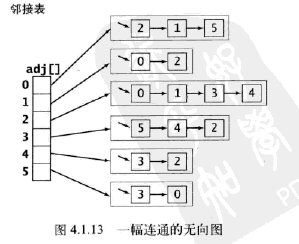
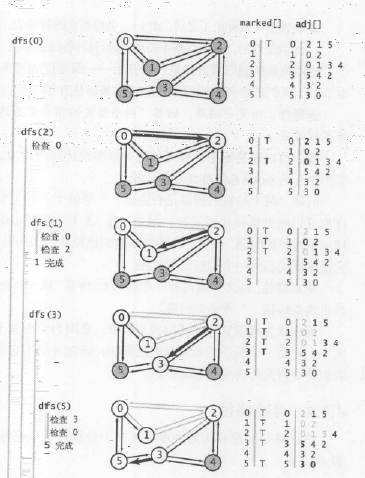
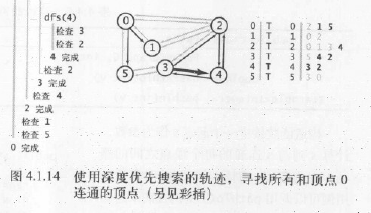
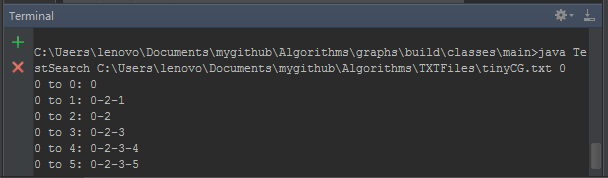
2.执行过程
3.算法分析
命题:深度优先搜索标记与起点连通的所有顶点所需的时间和顶点的度数之和成正比
命题:使用深度优先搜索得到从给定起点到任意标记顶点的路径所需的时间与路径的长度成正比
【源码下载】