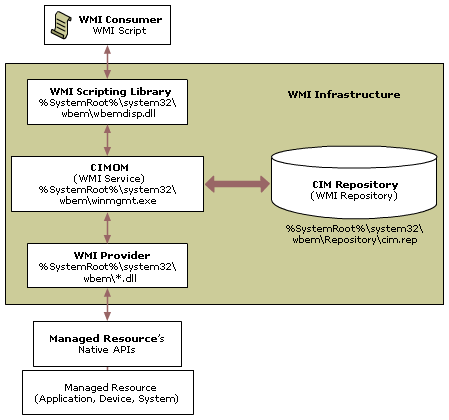






135端口:Microsoft在这个端口运行DCE RPC end-point mapper为它的DCOM服务。这与UNIX 111端口的功能很相似。使用DCOM和RPC的服务利用计算机上的end-point mapper注册它们的位置。远端客户连接到计算机时,它们查找end-point mapper找到服务的位置。
135端口主要用于使用RPC(Remote Procedure Call,远程过程调用)协议并提供DCOM(分布式组件对象模型)服务,通过RPC可以保证在一台计算机上运行的程序可以顺利地执行远程计算机上的代码;使用DCOM可以通过网络直接进行通信,能够跨包括HTTP协议在内的多种网络传输。
Windows Firewall: Allow Remote Administration Exception
The Windows Firewall: Allow remote administration exception setting allows you to specify whether computers running Windows XP with SP2 can be remotely administered by applications that use TCP ports 135 and 445 (such as MMC and WMI), and is shown in the following figure.

Services that use these ports to communicate are using remote procedure calls (RPC) and Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) to access remote hosts. In effect, Windows Firewall adds Svchost.exe and Lsass.exe to the program exceptions list and allows those services to open additional, dynamically assigned ports, typically in the range of 1024 to 1034. Windows Firewall also allows incoming ICMP Echo messages (also known as the ICMP Echo Request messages).
You can select the following:
-
Not Configured (default)
Remote administration is not allowed.
-
Enabled
Windows Firewall allows the computer to receive the unsolicited incoming messages associated with remote administration. InAllow unsolicited incoming messages from, type * to specify traffic originating from any source IPv4 address or a comma-separated list of sources. The sources can be LocalSubnet to specify traffic originating from a directly reachable IPv4 address or one or more IPv4 addresses or IPv4 address ranges separated by commas. IPv4 address ranges typically correspond to subnets. For IPv4 addresses, type the IPv4 address in dotted decimal notation. For IPv4 address ranges, you can specify the range using a dotted decimal subnet mask or a prefix length. When you use a dotted decimal subnet mask, you can specify the range as an IPv4 network ID (such as 10.47.81.0/255.255.255.0) or by using an IPv4 address within the range (such as 10.47.81.231/255.255.255.0). When you use a network prefix length, you can specify the range as an IPv4 network ID (such as 10.47.81.0/24) or by using an IPv4 address within the range (such as 10.47.81.231/24). The following is an example list of sources:
Note This command is shown on multiple lines for better readability; enter them as a single line.
LocalSubnet,10.91.12.56,10.7.14.9/255.255.255.0,10. 116.45.0/255.255.255.0,172.16.31.11/24,172.16.111.0/24IPv6 traffic supports the * and LocalSubnet scopes.
Note If you have any spaces between the entries in the list of sources or any other invalid characters, the scope is ignored and the setting behaves as if it were disabled. Please double-check your scope syntax before saving changes.
Host names, DNS names, or DNS suffixes are not supported.
-
Disabled
Remote administration is not allowed. Windows Firewall blocks port 135 and does not open 445. Also, in effect, it adds SVCHOST.EXE and LSASS.EXE to the program exceptions list with the Status of Disabled. Because disabling this policy setting does not block TCP port 445, it does not conflict with the Windows Firewall: Allow file and printer sharing exceptionsetting. This does not prevent these programs from running or their corresponding ports from being opened.
Malicious users and programs often attempt to attack networks and computers using RPC and DCOM traffic. We recommend that you contact the manufacturers of your critical programs to determine if they require RPC and DCOM communication. If they do not, then do not enable this setting.
Note If you only want to open a subset of the ports that this setting opens, leave this setting set to Not Configured and use theWindows Firewall: Define port exceptions setting to selectively open ports.
Windows Server Firewall Exceptions for Remote Administration Tools
by ADMIN on APRIL 17, 2008
Microsoft has a web page that lists the various tools you can use to remotely administer a Windows Server system. The page lists each remote administration tool and the steps that are required to successfully use the tool with the Windows Firewall service enabled on the local or remote machine.
Firewall configuration details for the following remote administration tools are provided:
- Active Directory Domains and Trusts (Windows Firewall: domain)
- Active Directory Management (Windows Firewall: admgmt)
- Active Directory Schema Management (Windows Firewall: schmmgmt)
- Active Directory Sites and Services (Windows Firewall: dssite)
- Active Directory Users and Computers (Windows Firewall: dsa)
- Authorization Manager (Windows Firewall: azman)
- Certificate Templates (Windows Firewall: certtmpl)
- Certificates (Windows Firewall: certmgr)
- Certification Authority (Windows Firewall: certsrv)
- Certutil command (Windows Firewall: certutil)
- Cluster Administrator (Windows Firewall: cluadmin)
- Cluster command (Windows Firewall: cluster)
- Component Services (Windows Firewall: comexp)
- Computer Management (Windows Firewall: compmgmt)
- Connection Manager Administration Kit Binaries (Windows Firewall: cmbins)
- Connection Manager Administration Kit Wizard (Windows Firewall: cmak)
- Device Manager (Windows Firewall: devmgr)
- Dfscmd command (Windows Firewall: dfscmd)
- DHCP (Windows Firewall: dhcpmgmt)
- Directory Service Utilities (Windows Firewall: ntdsutil)
- Disk Defragmenter (Windows Firewall: dfrg)
- Disk Management (Windows Firewall: diskmgmt)
- Distributed File System (Windows Firewall: dfsgui)
- DNS Management (Windows Firewall: dnsmgmt)
- Dsadd command (Windows Firewall: dsadd)
- Dsget command (Windows Firewall: dsget)
- Dsmod command (Windows Firewall: dsmod)
- Dsmove command (Windows Firewall: dsmove)
- Dsquery command (Windows Firewall: dsquery)
- Dsrm command (Windows Firewall: dsrm)
- Event Viewer (Windows Firewall: eventvwr)
- Fax client console (Windows Firewall: fxsclnt)
- Fax Service Manager (Windows Firewall: fxsadmin)
- File Server Management (Windows Firewall: filesvr)
- Group Policy Object Editor (Windows Firewall: gpedit)
- IIS Application Management script (Windows Firewall: iisapp)
- IIS Backup script (Windows Firewall: iisback)
- IIS Configuration script (Windows Firewall: iiscnfg)
- IIS FTP script (Windows Firewall: iisftp)
- IIS FTP Virtual Directory script (Windows Firewall: iisftpdr)
- IIS Help script (Windows Firewall: iisschlp)
- IIS Service Extension script (Windows Firewall: iisext)
- IIS Virtual Directory script (Windows Firewall: iisvdir)
- IIS Web Management script (Windows Firewall: iisweb)
- Indexing Service (Windows Firewall: ciadv)
- Internet Authentication Service (Windows Firewall: iasmsc)
- Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager (Windows Firewall: iis)
- IP Security Monitor (Windows Firewall: ipsecmon)
- IP Security Policies (Windows Firewall: ipsecpol)
- Local Security Settings (Windows Firewall: secpol)
- Local Users and Groups (Windows Firewall: lusrmgr)
- Network Load Balancing Manager (Windows Firewall: nlbmgr)
- Network Monitor tools (Windows Firewall: netmon)
- Performance (Windows Firewall: perfmon)
- POP3 Service (Windows Firewall: p3server)
- Public Key Management (Windows Firewall: pkmgmt)
- Remote Desktops (Windows Firewall: tsmmc)
- Remote Storage (Windows Firewall: rsadmin)
- Removable Storage (Windows Firewall: ntmsmgr)
- Removable Storage Operator Requests (Windows Firewall: ntmsoprq)
- Resultant Set of Policy (Windows Firewall: rsop)
- Routing and Remote Access (Windows Firewall: rrasmgmt)
- Security Configuration and Analysis (Windows Firewall: sca)
- Services (Windows Firewall: services)
- Shared Folders (Windows Firewall: fsmgmt)
- Telephony (Windows Firewall: tapimgmt)
- Terminal Services Configuration (Windows Firewall: tscc)
- Terminal Services Manager (Windows Firewall: tsadmin)
- UDDI Services Console (Windows Firewall: uddi)
- Windows Management Infrastructure (Windows Firewall: wmimgmt)
- Windows Media Services (Windows Firewall: wmsadmin)
- Windows Server 2003 Administration Tools Pack (Windows Firewall: adminpak)
- WINS (Windows Firewall: winsmgmt)
- Wireless Monitor (Windows Firewall: wiremon)
Microsoft also has a guide to Windows firewall configuration by server role.