Port Selector技术原理图
简单来说,端口选择器就是为一个硬盘提供两条连线连接到控制器,其中一条是冗余的(即多出来的意思)。这种设计的好处是万一其中一条连线断了,还有另一条可以连接。由此看来,不但可以用RAID防止硬盘损坏,还能用这个Port Selector来防止连接线损坏。
SATA 1.0的一个缺点就是可连接性不好,即连接多个硬盘的扩展性不好。因为在SATA 1.0规范中,一个SATA接口只能连接一个设备。SATA的制定者们显然也意识到了这个问题,于是他们在SATA2.0中引入了Port Multiplier的概念。Port Multiplier是一种可以在一个控制器上扩展多个SATA设备的技术,它采用4位(bit)宽度的Port Multiplier端口字段,其中控制端口占用一个地址,因此最多能输出15个设备连接----与并行SCSI相当。Port Multiplier的上行端口只有1个,在带宽为150MB/s的时候容易成为瓶颈,但如果上行端口支持300MB/s的带宽,就与Ultra320
SCSI十分接近了。Port Multiplier技术对需要多硬盘的用户很有用,不过目前提供这种功能的芯片组极少。
NCQ

RAID

PATA vs SATA

Four communication layers
There are four layers in the SATA architecture: Command, Transport, Link, and PHY as depicted inFigure 3. The layers are used for communication on both ends of a storage system which are the Host and the Device. The Command layer is responsible for overall ATA command execution, and the Host may interact with the Command layer through a register interface that is equivalent to that presented by a traditional PATA Host adapter.
 |
Figure 3: SATA has four communication layers. |
The Transport layer is responsible for creating the packets for transmitting between the Host and Device. These packets (or frames) include the combination of control information and data into a format known as a Frame Information Structure (FIS).
The Link layer is responsible for taking the constructed frames, encoding or decoding the data using the common 8b/10b encoding scheme, and inserting control characters so that the 10-bit interface can be decoded correctly.
And finally, the PHY is responsible for transmitting and receiving the encoded information as a serial data stream on the SATA cable. SATA has two main data transfer modes for communication between the Host and the Device, Programmed Input Output (PIO) and DMA mode. The main drawback to the PIO mode is that it requires a great deal of CPU overhead to configure a data transaction and transfer the data. However, it is still useful in applications that don't demand high performance because of the simple logic necessary to implement this mode. The DMA mode allows direct access for the memory to increase the performance.
IV. Port Multiplier—A Port Multiplier is a mechanism for one active Host connection to communicate with multiple devices. A Port Multiplier can be thought of as a simple "demultiplexer" where one active Host connection is demultiplexed to multiple device connections, as shown in Figure 4. Only one active Host connection to the Port Multiplier is supported. The Port Multiplier is an extensible design that supports up to 15 endpoint device connections and utilizes the full bandwidth of the Host connection.
 |
Figure 4: Port Multiplier overview. |
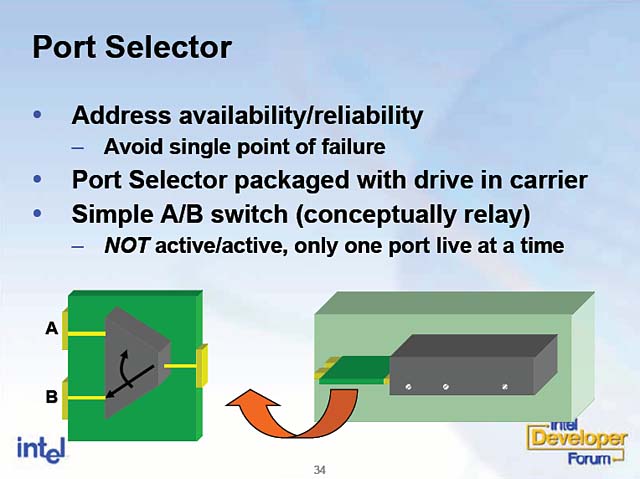
V. Port Selector—A Port Selector allows two different Host ports to connect to the same Device in order to create a redundant path to that Device. In combination with a Redundant Array of Independent Drives (RAID), the Port Selector allows system providers to build fully redundant solutions. The upstream ports of a Port Selector may also be attached to a Port Multiplier to provide redundancy in a more complex topology. A Port Selector can be thought of as a simple multiplexer as shown in Figure 5.
VI. External SATA—External SATA (eSATA) solutions have two major SATA connections using shielded cables and connectors. It enables an external direct attached storage for notebooks, desktops, consumer electronics, and entry servers with high performance, cost effective expansion storage. eSATA enables new usage models outside of the box with up to six times faster than existing external storage solutions: USB 2.0, 1394 based on robust and user friendly external connection.
SATA implementation: Host and device controllers
Mentor Graphics offers two examples of the SATA interface with either a Host or Device controller configuration, along with a PHY layer. Mentor's SATA Host controller can be implemented to map the SATA protocol layers functionality from the host side in an embedded SOC implementation environment.
As designed, the SATA Host controller sits between a Host system and the standard SATA physical layer (SATA PHY). The SATA PHY is responsible for sending packets from the SATA Host controller to the SATA link. The SATA Host controller also has two AHB connections on the Host system bus along with a master connection to allow DMA to start memory read/write operations.
 |
Figure 5: Port Selector overview. |
Conversely, the SATA Device controller core is designed to interface to a device CPU and DMA interface on one end, and the SATA Physical Layer controller on the other end. The Application Layer controller, Transport Layer controller, and Link Layer controller are the three core sub-modules that control the overall operation. These three modules coordinate their actions and utilize resources to transfer data between a Device system and a Host system on the other end.
SATA II Availability
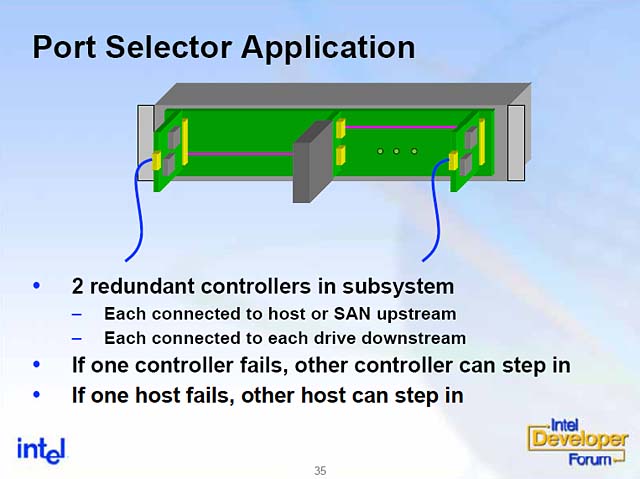
There is no room for compromise when it comes to data availability--no matter what the application, SATA RAID controllers offer the latest data availability features including failover capability with port selectors to handle failures in the data path. A port selector is a component that enables redundant data paths in the event of a failure. Two initiator ports connect to the same SATA device. If the primary or active initiator goes down, the standby initiator can signal the port-selector to make the standby port the new active port thus allowing it to control the device. Port selectors can be attached to Port Multipliers in order to provide redundant paths between separate devices.
