程序执行流程
- 顺序结构
- 判断结构
- 选择结构
顺序结构
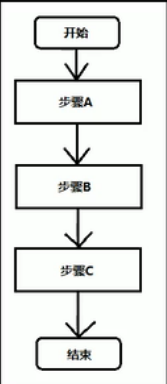
/* 顺序结构 */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("流水线"); System.out.println("买菜"); System.out.println("洗菜"); System.out.println("切菜"); System.out.println("炒菜"); System.out.println("装盘"); } }
if判断结构
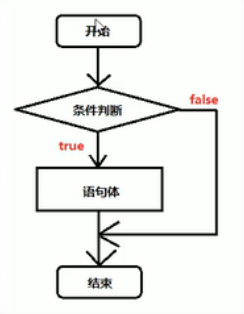
-
/* 判断结构 单if语句 格式: if(判断语句){ 语句体 } */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("想去网吧上网,go!出发"); int age=16; if (age>=18){ System.out.println("欢迎,请进入"); } System.out.println("饿了,回家吃饭"); } }
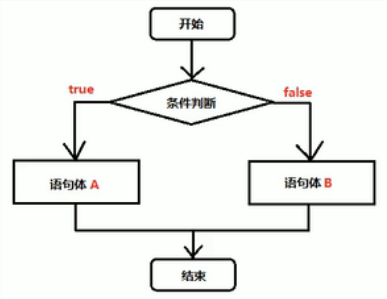
-
/* 判断结构 if....else 语句 格式: if(判断语句){ 语句体1; }else{ 语句体2; } */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("想去网吧上网,go!出发"); int age=16; if (age>=18){ System.out.println("欢迎,请进入"); }else{ System.out.println("抱歉,您的年龄未满18周岁,不能入内"); } System.out.println("饿了,回家吃饭"); } }
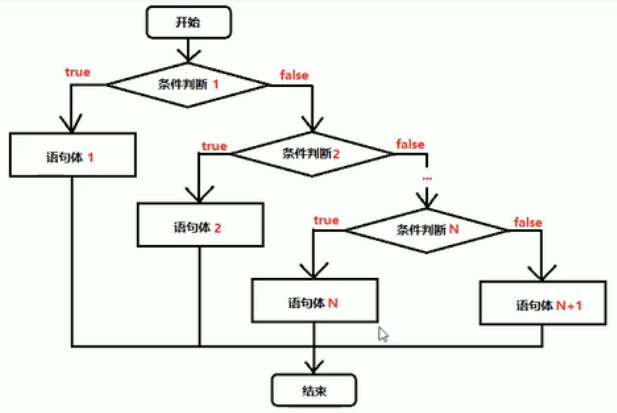
-
/* 判断结构 if....else if....else语句 格式: if(判断语句1){ 执行语句1; }else if(判断语句2){ 执行语句2; }else if(判断语句3){ 执行语句3; } ....... }else if(判断语句n){ 执行语句n; }esle{ 执行语句n+1; } 例:X和Y的关系满足如下: 如果x>=3,那么y=2X+1; 如果-1<X<3,那么y=2x; 如果x<=-1,那么y=2x-1; */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ int x=10; int y; if (x>=3){ y=2*x+1; }else if(x>-1&& x<3){ y=2*x; }else{ y=2*x-1; } System.out.println(y); } }
/* 例子:使用三元运算符和标准的if-else 语句分别实现,取两个数值之间的最大值 */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ int x=10; int y=9; //使用标准的if-else if(x>y){ System.out.println("最大值为"+x); }else{ System.out.println("最大值为"+y); } max();//调用max()方法 } //使用三元运算符 public static void max(){ int x=200; int y=500; int res=x>y?x:y; System.out.println("最大值为"+res); } }
switch选择语句

-
/* 选择语句-switch switch语句格式: switch(表达式){ case 常量1: 语句体1; break; case 常量2: 语句体2; break; ..... default: 语句体n+1; break; } */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ int num=1; switch (num){ case 1: System.out.println("星期一"); break; case 2: System.out.println("星期二"); break; case 3: System.out.println("星期三"); break; case 4: System.out.println("星期四"); break; case 5: System.out.println("星期五"); break; case 6: System.out.println("星期六"); break; case 7: System.out.println("星期七"); break; default: System.out.println("数据不合理"); break;//最后这个break语句可以省略,一般不建议省略 } } }
注意事项:
1、多个case后面的数值不可以重复
2、stwich后面小括号中只能使用下列数据类型
基本数据类型:byte/short/char/int
引用数据类型:String字符串、enum枚举
3、switch语句格式可以灵活使用,前后顺序可以颠倒,break语句还可以省略。没有break语句时,会穿透下面的case语句,直到遇到break或者程序结束
循环语句
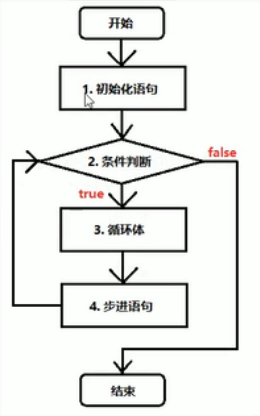
- 循环结构的基本组成部分,一般分为四部分
- 初始化语句:在循环开始最初执行,而且只做唯一一次
- 条件判断:如果成立,则循环继续;如果不成立,则循环退出
- 循环体:重复要做的事情的内容
- 步进语句:每次循环之后都要进行的扫尾工作
- for循环语句
-
/* 循环结构的基本组成部分,一般分为四部分 1、初始化语句:在循环开始最初执行,而且只做唯一一次 2、条件判断:如果成立,则循环继续;如果不成立,则循环退出 3、循环体:重复要做的事情的内容 4、步进语句:每次循环之后都要进行的扫尾工作 for循环语句格式: for(初始化表达式;布尔表达式;步进表达式){ 循环体; } */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ int i=0; int num=0; for(i=0;i<=10;i++){ num=num+i; } System.out.println(num); } }
-
while循环
-
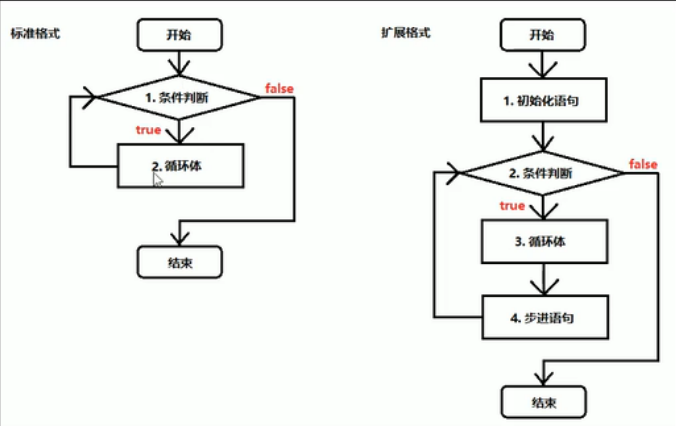
/* while循环标准格式 while(条件判断){ 循环体; } while循环扩展格式: 初始化语句; while(条件判断){ 循环体; 步进语句; } */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){ System.out.println("我错了,对不起"+i); } System.out.println("==============="); int i=1;//初始化语句 while(i<=10){//条件判断语句 System.out.println("我错了,对不起"+i);//循环体 i++;//步进语句 } } }
do - while循环
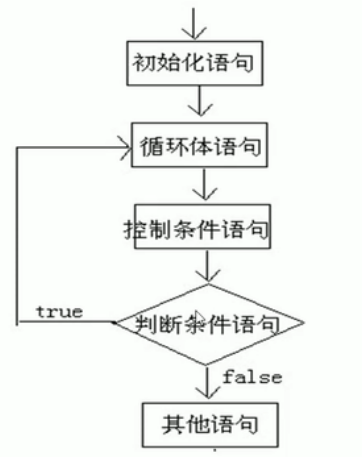
/* do-while循环标准格式 do{ 循环体; }while(条件判断); do-while扩展格式 初始化语句; do{ 循环体; 步进语句; }while(条件判断); 注意事项: 1、do-while 循环会无条件执行一次循环体 */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){ System.out.println("没关系"+i); } System.out.println("==============="); int i=1; do{ System.out.println("没关系"+i); i++; }while(i<=10); } }
-
题目:求1~100之间的偶数和
-
/* 求1~100之间的偶数和 */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ //使用for循环 int i=1; int sum=0; for (i=1;i<=100;i++){ if(i%2==0) sum=sum+i; } System.out.println("结果为:"+sum); //使用while循环 int a=1; int sum1=0; while(a<=100){ if(a%2==0){ sum1=sum1+a; } a++; } System.out.println("结果为:"+sum1); //使用do-while循环 int b=1; int sum2=0; do{ if(b%2==0){ sum2=sum2+b; } b++; }while(b<=100); System.out.println("结果为:"+sum2); } }
循环控制语句-break
/* break关键字的用法有常见的两种: 1、可以用在switch语句中,一旦执行,整个switch语句立刻结束 2、还可以用在循环语句中,一旦执行,整个循环语句立刻结束,打断循环 建议 凡是次数确定的场景多用for循环,否则使用while循环 */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){ //希望从第四次开始结束输出,就要打断循环 if(i==4){ break; } System.out.println("hello"+i); } } }
循环控制语句-continue
/* 循环控制语句continue关键字 一旦执行,立刻跳过当前循环语句剩余内容,马上开始下一次循环(停止当次循环,开始下一次循环) */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){ if(i==4){ continue; } System.out.println(i+"层到了"); } } }
死循环
/* 死循环:永远停不下来的循环 死循环的标准格式 while(true){ 循环体; } */ public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args){ while(true){ System.out.println("I LOVE YOU"); } } }