1.1 算法目的
现在网络架构一般是Client-Server架构,所以网络流量一般是分 C-S 和 S-C 两个方向。tcpdump等抓包工具获取的pcap包,两个流向的数据没有被区分。流量方向的区分有什么好处?这种拆分至少有两个好处,一是在抓包基础上定制数据包,可以支持单独修改一个流向的IP,MAC等字段。二是实际测试被测设备的时候,可以将两个流向的流量通过不同的端口发送出来。Tcpprep支持了这种拆分(早先版本这部分功能混合在tcpreplay中,后来独立拆分成为tcpprep工具)
Tcpprep3.4.4 支持了以下流量拆分的参数
-a, --auto=str Auto-split mode 自动模式
-c, --cidr=str CIDR-split mode 子网匹配模式
-r, --regex=str Regex-split mode 正则匹配模式
-p, --port Port-split mode 端口匹配模式
-e, --mac=str Source MAC split mode MAC匹配模式
-reverse Matches to be client instead of server
其中,auto 模式支持5种子模式
Auto = bridge|router|client|server|first
另外,下面两个参数也是流量拆分相关的,当 auto=router 时,用户可选下面的参数配合,
-m, --minmask=num Minimum network mask length in auto mode
-M, --maxmask=num Maximum network mask length in auto mode
1.2 算法思想
考虑一个问题,如何判断一个packets 是 C->S 还是 S->C ?
一种思路是用户指定,比如用户指定某个IP或MAC是C->S,或者更进一步,IP匹配某个正则表达式就是C->S,这种情况下,实际上是用户‘手动’判断,不需要特别的算法。上面各种模式中,除了 auto 模式,其余模式都属于这类‘手动’方法,前提是用户必须对这些pcap包非常熟悉。
那么,如何实现‘自动’识别C->S还是S->C?
答案是,利用网络包的协议特征。因为一般的网络流量都基于TCP或UDP,以TCP为例,SYN,ACK等标志位就可以支持流量方向的判断了。Tcpprep3.4.4 使用到的协议特征
包括如下:
Tcpprep3.4.4 使用到的协议特征
C->S 客户端特征:
Sending a TCP Syn packet to another host
Making a DNS request
Recieving an ICMP port unreachable
S->C 服务端特征:
Sending a TCP Syn/Ack packet to another host
Sending a DNS Reply
Sending an ICMP port unreachable
所以,自动流量拆分算法的基本思路是:解析pcap的每一个packet,判断其特征位的值,对比客户端特征和服务端特征,得到一个比较结果,通过比较结果来判断流量方向。
考虑上述思路,是逐个packet单独计算,但是,一个pcap的许多packet,其IP,MAC,PORT等都是相同的,换句话说,是属于一个方向。因此,特征匹配运算的基本单位,不应该是一个packet,而应该是以IP为单位。
Tcpprep在实现的时候根据IP大小建立了一颗红黑树,相同IP的packet不再单独生成节点,而是将特征匹配的运算结果累计在相同IP的节点上,最后某个IP属于哪个方向是由红黑树的对应节点的累计结果得到的。该算法需要大量查找和插入操作,用红黑树比较合适。
上面两段落的描述即是 auto=bridge 的算法思路,也是自动拆分流量的基本算法。其他4种自动拆分方向算法都建立在bridge之上,它们之间的关系是,都先使用 bridge 模式运算得到红黑树,对于树上还无法归入 C->S 或 S->C 的节点,再使用对应模式的策略。在auto=server ,就是剩下的节点全部视为 S->C,在 auto=client ,就是剩下的节点全部视为
C->S,在 auto=first ,就是剩下的节点全部视为与第一个packet 方向一致。
auto=router 的策略比较复杂,使用到了 CIDR 这种数据结构,CIDR其实是一个链表,每个链表节点存放一个 cidr 地址,它的思路是,如果这个无法判断的节点的IP刚好落在一个其余IP都是S->C的cidr里,那么它就是 S->C,相反,如果改节点的IP刚好落在某个cidr,而树上其他在该cidr 里的节点都是 C->S,那么该节点也是 C->S。
1.3 算法流程
Tcpprep 主流程
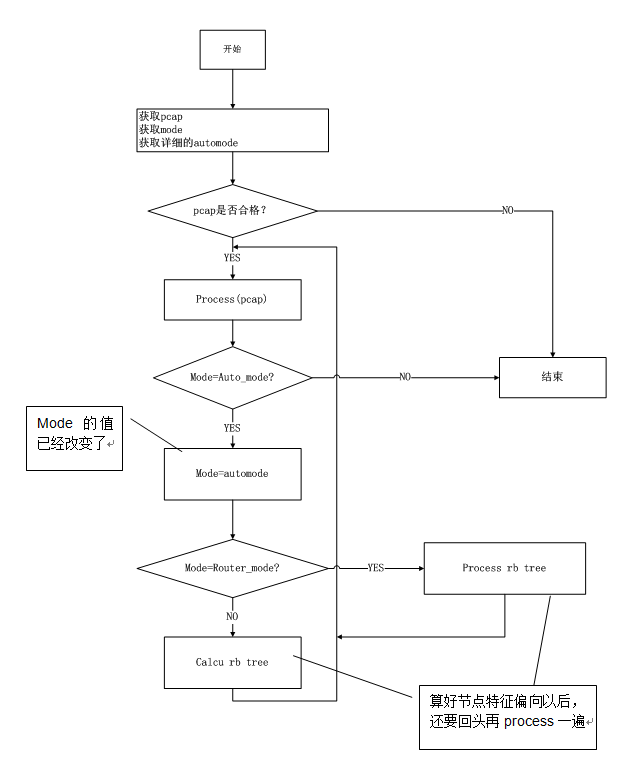
Process(pcap) 流程
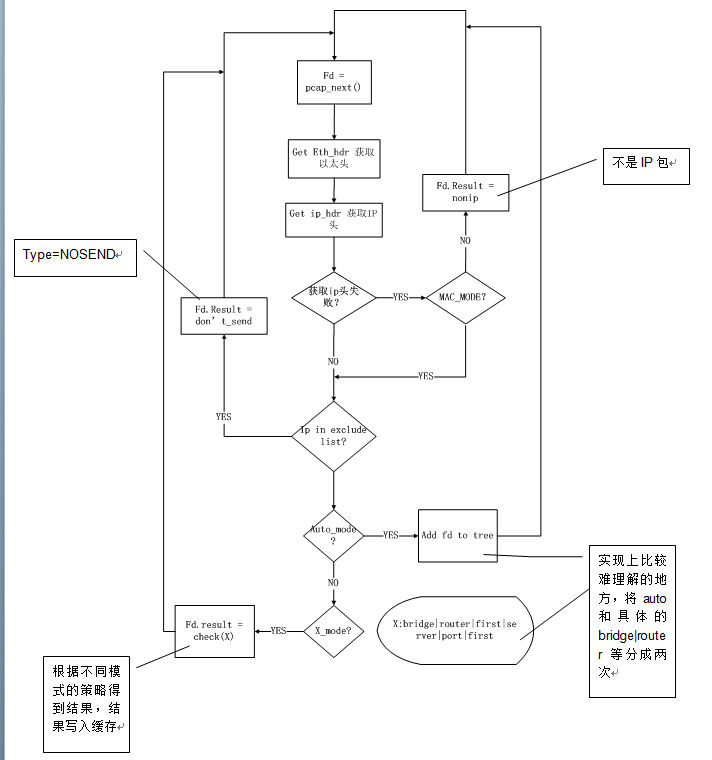
1.1 算法实现
1.1.1 数据结构
/*tcpprep 控制结构*/
struct tcpprep_opt_s {
pcap_t *pcap; /*pcap包控制句柄*/
int verbose;
char *tcpdump_args;
tcpr_cache_t *cachedata; /*缓存数据子控制结构,具体见缓存算法相关描述*/
tcpr_cidr_t *cidrdata;/*cidir 链表控制结构*/
char *maclist; /*mac 地址列表,适用于mode = MAC*/
tcpr_xX_t xX; /*exclude ip 列表*/
tcpr_bpf_t bpf;
tcpr_services_t services;
char *comment; /* cache file comment */
int nocomment; /* don't include the cli in the comment */
int mode; /* mode */
int automode; /* our auto mode */
int min_mask; /*这两个适用于 auto=router */
int max_mask;
double ratio; /*server 和 client 的比率*/
regex_t preg; /*适用于 mode = grex */
int nonip;
};
typedef struct tcpprep_opt_s tcpprep_opt_t;
/*红黑树节点控制结构*/
typedef struct tcpr_tree_s {
RB_ENTRY(tcpr_tree_s) node; /*在 redblack.h 中定义*/
int family;
union {
unsigned long ip; /* ip/network address in network byte order */
struct tcpr_in6_addr ip6;
} u;
u_char mac[ETHER_ADDR_LEN]; /* mac address of system */
int masklen; /* CIDR network mask length */
/*下面这两个变量就是用来累计客户端和服务端特征的变量*/
int server_cnt; /* count # of times this entry was flagged server */
int client_cnt; /* flagged client */
/*运算结果是什么方向存放在下面这个type里*/
int type; /* 1 = server, 0 = client, -1 = undefined */
} tcpr_tree_t;
/* *根节点*/
typedef struct tcpr_data_tree_s {
tcpr_tree_t *rbh_root;
} tcpr_data_tree_t;
1.1.2 主要函数实现
/**
* 使用 libpcap library 解析 packets
* 根据流量拆分算法运算结果生成cache file,去掉了部分无关代码
*/
static COUNTER
process_raw_packets(pcap_t * pcap)
{
ipv4_hdr_t *ip_hdr = NULL; /*ipv4 头结构,定义在 libpcap library*/
ipv6_hdr_t *ip6_hdr = NULL; /*ipv6 头结构*/
eth_hdr_t *eth_hdr = NULL; /*以太帧头结构*/
struct pcap_pkthdr pkthdr; /*pcap头控制结构,定义在 libpcap library*/
const u_char *pktdata = NULL;
COUNTER packetnum = 0;
int l2len, cache_result = 0;
u_char ipbuff[MAXPACKET], *buffptr;
tcpr_dir_t direction; /*流量方向*/
/*下面是主循环*/
while ((pktdata = pcap_next(pcap, &pkthdr)) != NULL) {
packetnum++;
/*下面检查exclude list,如果匹配,缓存写入 DON’T_SEND,continue处理下一个*/
/* look for include or exclude LIST match */
if (options.xX.list != NULL) {
if (options.xX.mode < xXExclude) {
if (!check_list(options.xX.list, packetnum)) {
add_cache(&(options.cachedata), DONT_SEND, 0);
continue;
}
}
else if (check_list(options.xX.list, packetnum)) {
add_cache(&(options.cachedata), DONT_SEND, 0);
continue;
}
}
/*获取ip头,如果获取不到,除非用户设定了MAC模式,在MAC模式下,还可以通过mac值判定方向,否则直接将 type=NONIP写入缓存,continue在下一个packet*/
eth_hdr = (eth_hdr_t *)pktdata;
if (options.mode != MAC_MODE) {
buffptr = ipbuff;
/* 获取IPv4 */
if ((ip_hdr = (ipv4_hdr_t *)get_ipv4(pktdata, pkthdr.caplen,
pcap_datalink(pcap), &buffptr))) {
dbg(2, "Packet is IPv4");
}
/* 获取IPv6 */
else if ((ip6_hdr = (ipv6_hdr_t *)get_ipv6(pktdata, pkthdr.caplen,
pcap_datalink(pcap), &buffptr))) {
dbg(2, "Packet is IPv6");
}
/* we're something else... */
else { /*都获取不到,写对应packet缓存为 nonip*/
if (options.mode != AUTO_MODE) {
dbg(3, "Adding to cache using options for Non-IP packets");
add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND, options.nonip);
}
/* go to next packet */
continue;
}
/*下面判定 exclude ip 列表,如果匹配,则缓存写入 DON’T_SEND,continue处理下一个packet*/
l2len = get_l2len(pktdata, pkthdr.caplen, pcap_datalink(pcap));
/* look for include or exclude CIDR match */
if (options.xX.cidr != NULL) {
if (ip_hdr) {
if (!process_xX_by_cidr_ipv4(options.xX.mode, options.xX.cidr, ip_hdr)) {
add_cache(&options.cachedata, DONT_SEND, 0);
continue;
}
} else if (ip6_hdr) {
if (!process_xX_by_cidr_ipv6(options.xX.mode, options.xX.cidr, ip6_hdr)) {
add_cache(&options.cachedata, DONT_SEND, 0);
continue;
}
}
}
}
/*下面分别处理各种拆分模式*/
switch (options.mode) {
case REGEX_MODE: /*正则表达式模式*/
if (ip_hdr) {/*拿源IP跟用户设定的regex匹配得到结果,写入缓存*/
direction = check_ipv4_regex(ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr);
} else if (ip6_hdr) {
direction = check_ipv6_regex(&ip6_hdr->ip_src);
}
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND, direction);
break;
case CIDR_MODE: /*cidr列表模式*/
if (ip_hdr) {/*拿源IP跟用户设定的cidr列表匹配得到结果,写入缓存*/
direction = check_ip_cidr(options.cidrdata, ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr) ? TCPR_DIR_C2S : TCPR_DIR_S2C;
} else if (ip6_hdr) {
direction = check_ip6_cidr(options.cidrdata, &ip6_hdr->ip_src) ? TCPR_DIR_C2S : TCPR_DIR_S2C;
}
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND, direction);
break;
case MAC_MODE: /*MAC模式*/
direction = macinstring(options.maclist, (u_char *)eth_hdr->ether_shost);
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND, direction);
break;
case AUTO_MODE: /*auto模式
比如 auto=bridge,会分成两次运行,第一次检测 auto_mode,创建红黑树,第二次检测 bridge_mode,对树做运算并将结果写入缓存,router等模式也是一样的处理*/
/* first run through in auto mode: create tree */
if (options.automode != FIRST_MODE) {
if (ip_hdr) {
add_tree_ipv4(ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr, pktdata);
} else if (ip6_hdr) {
add_tree_ipv6(&ip6_hdr->ip_src, pktdata);
}
} else {
if (ip_hdr) {
add_tree_first_ipv4(pktdata);
} else if (ip6_hdr) {
add_tree_first_ipv6(pktdata);
}
}
break;
case ROUTER_MODE:
/* 具体到router,第二次运行,根据树的结果生成cache
*/
if (ip_hdr) {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip_tree(options.nonip, ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr));
} else {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip6_tree(options.nonip, &ip6_hdr->ip_src));
}
break;
case BRIDGE_MODE:
/* 具体到bridge,第二次运行,根据树的结果生成cache
*/
if (ip_hdr) {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip_tree(DIR_UNKNOWN, ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr));
} else {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip6_tree(DIR_UNKNOWN, &ip6_hdr->ip_src));
}
break;
case SERVER_MODE:
/* 具体到server,第二次运行,根据树的结果生成cache
*/
if (ip_hdr) {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip_tree(DIR_SERVER, ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr));
} else {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip6_tree(DIR_SERVER, &ip6_hdr->ip_src));
}
break;
case CLIENT_MODE:
/* 具体到client,第二次运行,根据树的结果生成cache
*/
if (ip_hdr) {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip_tree(DIR_CLIENT, ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr));
} else {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip6_tree(DIR_CLIENT, &ip6_hdr->ip_src));
}
break;
case PORT_MODE:
/*port模式,根据目的端口得到方向
*/
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_dst_port(ip_hdr, ip6_hdr, (pkthdr.caplen - l2len)));
break;
case FIRST_MODE:
/* 具体到first,第二次运行,根据树的结果生成cache
*/
if (ip_hdr) {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip_tree(DIR_UNKNOWN, ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr));
} else {
cache_result = add_cache(&options.cachedata, SEND,
check_ip6_tree(DIR_UNKNOWN, &ip6_hdr->ip_src));
}
break;
default:
errx(-1, "Whops! What mode are we in anyways? %d", options.mode);
}
return packetnum;
}
/*
*从上面代码的实现可以看到,auto模式的(包括bridge,router,client,server,first)都需要两次处理,第一次根据pcap生成一颗树,第二次根据这棵树生成缓存。非auto模式的只需要执行一次,逐个解析pcap的每个packet,得到结果后马上写入缓存
*/
Auto-bridge算法最终归于对红黑树的操作,包括addtree,processtree,calcutree,checkiptree等操作,auto-router涉及tree2cidr,checkipcidr操作
/*
*下面函数实现了将一个packet解析后变成红黑树一个node的方法
*/
tcpr_tree_t *
packet2tree(const u_char * data)
{
tcpr_tree_t *node = NULL;
eth_hdr_t *eth_hdr = NULL;
ipv4_hdr_t ip_hdr;
ipv6_hdr_t ip6_hdr;
tcp_hdr_t tcp_hdr;
udp_hdr_t udp_hdr;
icmpv4_hdr_t icmp_hdr;
dnsv4_hdr_t dnsv4_hdr;
u_int16_t ether_type;
u_char proto = 0;
int hl = 0;
node = new_tree();
eth_hdr = (eth_hdr_t *) (data);/*将data存放在eth_hdr结构体中*/
/* prevent issues with byte alignment, must memcpy */
memcpy(ðer_type, (u_char*)eth_hdr + 12, 2);/*取出 ether_type*/
/*下面判断ether_type的类型,做不同操作*/
/* drop VLAN info if it exists before the IP info */
if (ether_type == htons(ETHERTYPE_VLAN)) {
dbg(4,"Processing as VLAN traffic...");
/* prevent issues with byte alignment, must memcpy */
memcpy(ðer_type, (u_char*)eth_hdr + 16, 2);
hl += 4;
}
if (ether_type == htons(ETHERTYPE_IP)) {
memcpy(&ip_hdr, (data + TCPR_ETH_H + hl), TCPR_IPV4_H);/*取IP头*/
node->family = AF_INET;
node->u.ip = ip_hdr.ip_src.s_addr;/*node存放的IP是源IP*/
proto = ip_hdr.ip_p;/*proto 存放连接层的协议,是下面判断流向的基础*/
hl += ip_hdr.ip_hl * 4;
} else if (ether_type == htons(ETHERTYPE_IP6)) {
memcpy(&ip6_hdr, (data + TCPR_ETH_H + hl), TCPR_IPV6_H);
node->family = AF_INET6;
node->u.ip6 = ip6_hdr.ip_src;
proto = ip6_hdr.ip_nh; /*proto 存放连接层的协议,是下面判断流向的基础*/
hl += TCPR_IPV6_H;
} else {
dbgx(2,"Unrecognized ether_type (%x)", ether_type);
}
/* copy over the source mac */
strncpy((char *)node->mac, (char *)eth_hdr->ether_shost, 6);
/*下面处理 TCP 的情况*/
if (proto == IPPROTO_TCP) {
/* memcpy it over to prevent alignment issues */
memcpy(&tcp_hdr, (data + TCPR_ETH_H + hl), TCPR_TCP_H);
/* ftp-data is going to skew our results so we ignore it */
if (tcp_hdr.th_sport == 20)
return (node);
/* set TREE->type based on TCP flags */
if (tcp_hdr.th_flags == TH_SYN) {
node->type = DIR_CLIENT;
}
else if (tcp_hdr.th_flags == (TH_SYN | TH_ACK)) {
node->type = DIR_SERVER;
}
else {
dbg(3, "is an unknown");
}
}
/*下面处理 UDP 的情况*/
else if (proto == IPPROTO_UDP) {
/* memcpy over to prevent alignment issues */
memcpy(&udp_hdr, (data + TCPR_ETH_H + hl), TCPR_UDP_H);
switch (ntohs(udp_hdr.uh_dport)) {/*由目的端口判断是dns协议的情况*/
case 0x0035: /* dns */
/* prevent memory alignment issues */
memcpy(&dnsv4_hdr,
(data + TCPR_ETH_H + hl + TCPR_UDP_H), TCPR_DNS_H);
if (dnsv4_hdr.flags & DNS_QUERY_FLAG) {
/* bit set, response */
node->type = DIR_SERVER;
}
else {
/* bit not set, query */
node->type = DIR_CLIENT;
}
return (node);
break;
default:
break;
}
switch (ntohs(udp_hdr.uh_sport)) {/*由源端口判断是dns协议的情况*/
case 0x0035: /* dns */
/* prevent memory alignment issues */
memcpy(&dnsv4_hdr,
(data + TCPR_ETH_H + hl + TCPR_UDP_H),
TCPR_DNS_H);
/*通过检查特定标志位的值,判断是哪个流向*/
if ((dnsv4_hdr.flags & 0x7FFFF) ^ DNS_QUERY_FLAG) {
node->type = DIR_SERVER;
}
else {
node->type = DIR_CLIENT;
}
return (node);
break;
default:
dbgx(3, "unknown UDP protocol: %hu->%hu", udp_hdr.uh_sport,
udp_hdr.uh_dport);
break;
}
}
/*下面处理 ICMP的情况*/
else if (proto == IPPROTO_ICMP) {
/* prevent alignment issues */
memcpy(&icmp_hdr, (data + TCPR_ETH_H + hl), TCPR_ICMPV4_H);
/* if port unreachable, then source == server, dst == client */
if ((icmp_hdr.icmp_type == ICMP_UNREACH) &&
(icmp_hdr.icmp_code == ICMP_UNREACH_PORT)) {
node->type = DIR_SERVER;
dbg(3, "is a server with a closed port");
}
}
return (node);
}
/*
*从函数实现可以看出,基本上是根据协议规范解析packet,通过检测特定协议的特定标志位的值来判断该packet的流向
*/
1.1.1 实验结果
1.1.1.1 实验1
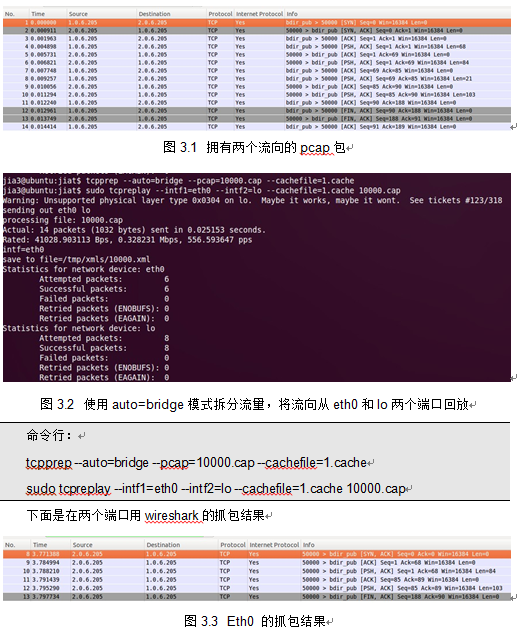
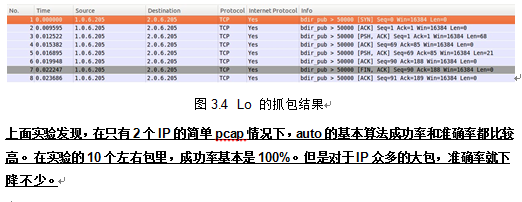
1.1.1.1 实验2
下面是使用 auto=router的实验情况:
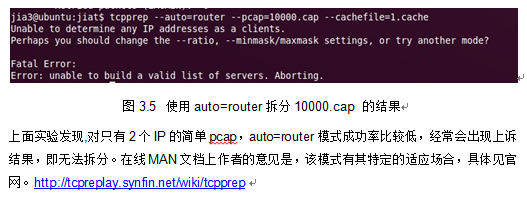
1.1.1.1 实验3
本文使用了wireshark在局域网中随机抓取了一个包,使用auto=router拆分成功,准确率一般。结果如下:
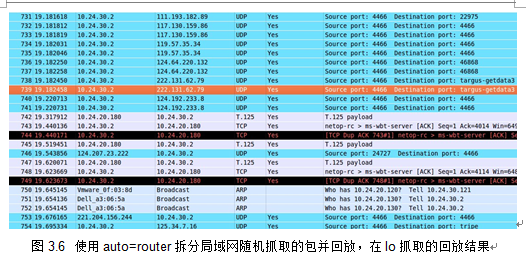
1.1.1 发现该算法的一个问题
算法简单回顾:整个pcap包含的packet的源IP都被整合进入一颗红黑树,然后遍历整棵红黑树,算每个节点的比例,得出结果是C还是S。使用的时候,通过取packet的IP,看它是在红黑树的哪个节点,拿那个节点的值。
问题:
假设有一种情况,一个IP同时作为客户端和服务器(在本机上架设一个webserver,然后用本机的浏览器请求页面),这种情况下,本机IP事实上同时是C和S,但根据tcpprep的红黑树算法,它的最终结果要么是C要么是S。