北京电子科技学院(BESTI)
实 验 报 告
课程:信息安全系统设计基础 班级:1453
姓名:吉东云。马月 学号:20145329、20145337
指导教师:娄嘉鹏老师 实验日期: 2016-11-8 10:10~12:40
必修/选修:必修 实验序号:(二)
实验名称:
实验目的与要求:
- 学习、读懂 02_pthread 03_tty中的代码。
实验仪器:
- 名称 型号 数量
- 计算机 Lenovo 1
- Linux环境 Redhat 9.0 1
- 开发板 UP-NETARM2410-CL 1
一. 实验内容
学习、读懂 02_pthread 03_tty中的代码。
二.实验步骤
1.开发环境的配置同实验一
- (1)设置xp系统、redhat虚拟机、arm机的ip在同一网段。
- (2)安装arm编译器
- (3)进入虚拟机,在命令行中输入./install.sh,安装脚本程序将会自动建立目录,配置编译环境。
2.将实验代码拷贝到共享文件夹中bc中
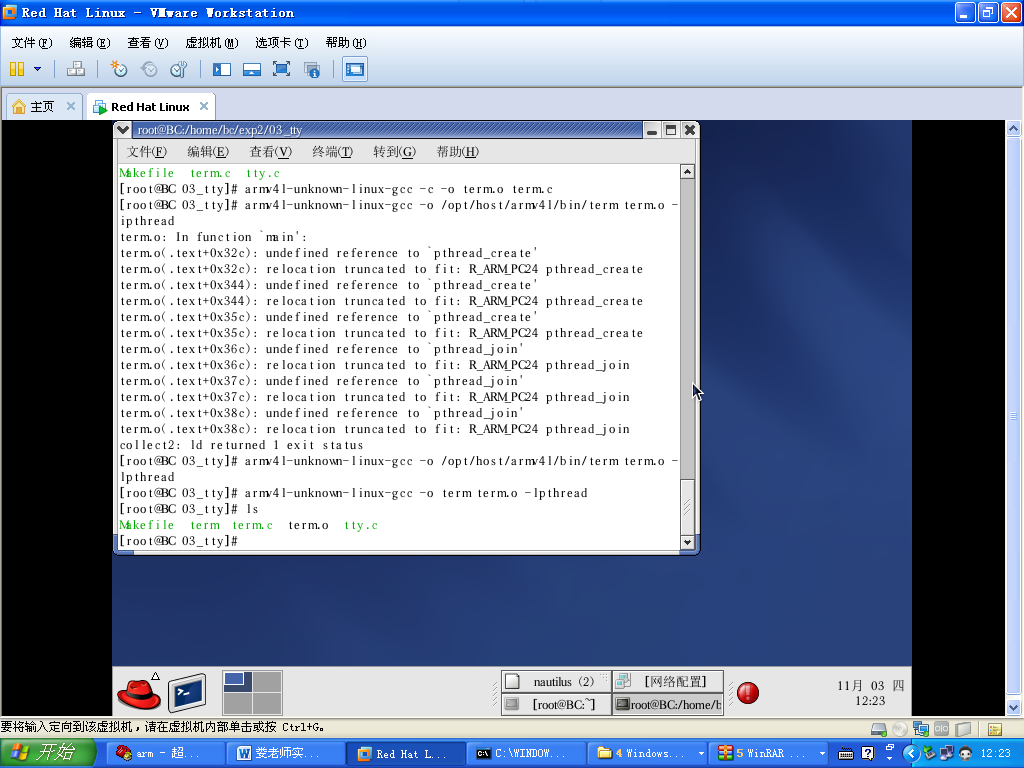
3.在虚拟机中编译代码。
4.下载调试
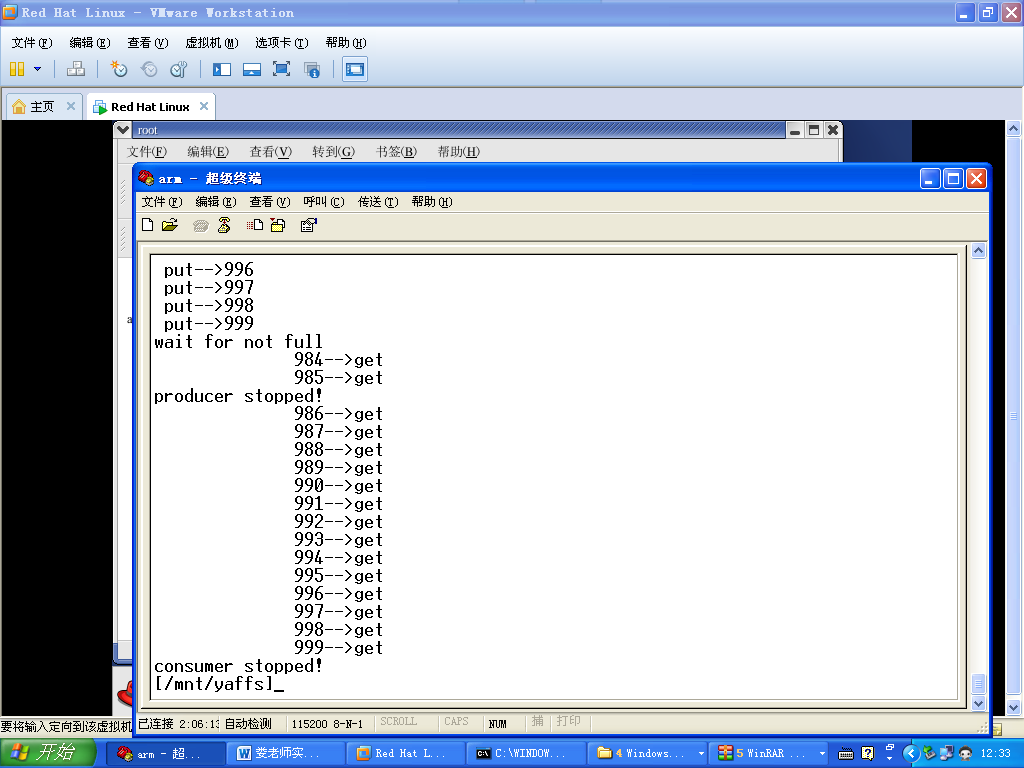
在超级终端中运行可执行文件pthread
三代码解析
- 这是一个生产者和消费者的LINUX多线程实现
1. pthread.c代码
.#include <stdio.h>
.#include <stdlib.h>
.#include <time.h>
.#include "pthread.h"
.#define BUFFER_SIZE 16
/* 设置一个整数的圆形缓冲区 */
struct prodcons {
int buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; /* 缓冲区数组 */
pthread_mutex_t lock; /* 互斥锁 */
int readpos, writepos; /* 读写的位置*/
pthread_cond_t notempty; /* 缓冲区非空信号 */
pthread_cond_t notfull; /*缓冲区非满信号 */
};
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
/*初始化缓冲区*/
void init(struct prodcons * b)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&b->lock, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&b->notempty, NULL); //条件变量初始化
pthread_cond_init(&b->notfull, NULL);
b->readpos = 0;
b->writepos = 0;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* 生产者写入共享的循环缓冲区函数 PUT,向缓冲区中写入一个整数*/
void put(struct prodcons * b, int data)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&b->lock); //获取互斥锁
/*等待缓冲区非满*/
while ((b->writepos + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE == b->readpos) {
printf("wait for not full
");
pthread_cond_wait(&b->notfull, &b->lock); //等待状态变量b->notfull,不满则跳出阻塞
}
/*写数据并且指针前移*/
b->buffer[b->writepos] = data; //写入数据
b->writepos++;
if (b->writepos >= BUFFER_SIZE) b->writepos = 0;
/*设置缓冲区非空信号*/
pthread_cond_signal(&b->notempty); //设置状态变量
pthread_mutex_unlock(&b->lock); //释放互斥锁
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
/*消费者读取共享的循环缓冲区函数 GET,从缓冲区中读出一个整数 */
int get(struct prodcons * b)
{
int data;
pthread_mutex_lock(&b->lock); //获取互斥锁
/* 等待缓冲区非空*/
while (b->writepos == b->readpos) { //如果读写位置相同
printf("wait for not empty
");
pthread_cond_wait(&b->notempty, &b->lock); //等待状态变量,不空则跳出阻塞。否则无数据可读。
}/* 读数据并且指针前移 */
data = b->buffer[b->readpos]; //读取数据
b->readpos++;
if (b->readpos >= BUFFER_SIZE) b->readpos = 0;
/* 设置缓冲区非满信号*/
pthread_cond_signal(&b->notfull); //设置状态变量
pthread_mutex_unlock(&b->lock); //释放互斥锁
return data;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
.#define OVER (-1)
struct prodcons buffer;
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
void * producer(void * data)
{
int n;
for (n = 0; n < 1000; n++) {
printf(" put-->%d
", n);
put(&buffer, n);
}
put(&buffer, OVER);
printf("producer stopped!
");
return NULL;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
void * consumer(void * data)
{
int d;
while (1) {
d = get(&buffer);
if (d == OVER ) break;
printf(" %d-->get
", d);
}
printf("consumer stopped!
");
return NULL;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
int main(void)
pthread_t th_a, th_b;
void * retval;
init(&buffer);
pthread_create(&th_a, NULL, producer, 0); //线程创建函数
pthread_create(&th_b, NULL, consumer, 0);
/* 等待生产者和消费者结束 */
pthread_join(th_a, &retval); //等待指定的线程结束
pthread_join(th_b, &retval);
return 0;
}
2.term.c代码
.#include <termios.h> /*PPSIX 终端控制定义*/
.#include <stdio.h> /*标准输入输出定义*/
.#include <unistd.h> /*linux 标准函数定义*/
.#include <fcntl.h> /*文件控制定义*/
.#include <sys/signal.h>
.#include <pthread.h> /*线程库定义*/
.#define BAUDRATE B115200
.#define COM1 "/dev/ttyS0"
.#define COM2 "/dev/ttyS1"
.#define ENDMINITERM1 27 /* ESC to quit miniterm */
.#define ENDMINITERM2 3 /*ctl +c to quit miniterm */
.#define FALSE 0
.#define TRUE 1
volatile int STOP=FALSE;
volatile int fd;
void child_handler(int s)
{
printf("stop!!!
");
STOP=TRUE;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
void* keyboard(void * data)
{
int c;
for (;;){
c=getchar();
// printf("getchar is :%d",c);
if( (c== ENDMINITERM1) | (c==ENDMINITERM2)){
STOP=TRUE;
break ;
}
}
return NULL;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* modem input handler */
void* receive(void * data)
{
int c;
printf("read modem
");
while (STOP==FALSE)
{
read(fd,&c,1); /* com port */
write(1,&c,1); /* stdout */
}
printf("exit from reading modem
");
return NULL;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
void* send(void * data)
{
int c='0';
printf("send data
");
while (STOP==FALSE)
{
c++;
c %= 255;
write(fd,&c,1); /* stdout */
usleep(100000);
}
return NULL; /* wait for child to die or it will become a zombie */
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
struct termios oldtio,newtio,oldstdtio,newstdtio;
struct sigaction sa;
int ok;
pthread_t th_a, th_b, th_c;
void * retval;
if( argc > 1)
fd = open(COM2, O_RDWR ); /*以读写方式打开串口*/
else
fd = open(COM1, O_RDWR ); //| O_NOCTTY |O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd <0) { /* 不能打开串口一*/
perror(COM1);
exit(-1);
}
tcgetattr(0,&oldstdtio);
tcgetattr(fd,&oldtio); /* save current modem settings */
tcgetattr(fd,&newstdtio); /* get working stdtio */
newtio.c_cflag = BAUDRATE | CRTSCTS | CS8 | CLOCAL | CREAD; /* 控制模式标志 */
newtio.c_iflag = IGNPAR; /* 输入模式标志 */
newtio.c_oflag = 0; /* 输出模式标志 */
newtio.c_lflag = 0; /* local mode flags */
newtio.c_cc[VMIN]=1;
newtio.c_cc[VTIME]=0;
/* now clean the modem line and activate the settings for modem */
tcflush(fd, TCIFLUSH);
tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio);/*set attrib */
sa.sa_handler = child_handler;
sa.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGCHLD,&sa,NULL); /* handle dying child */
pthread_create(&th_a, NULL, keyboard, 0);
pthread_create(&th_b, NULL, receive, 0);
pthread_create(&th_c, NULL, send, 0);
pthread_join(th_a, &retval);
pthread_join(th_b, &retval);
pthread_join(th_c, &retval);
tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&oldtio); /* restore old modem setings */
tcsetattr(0,TCSANOW,&oldstdtio); /* restore old tty setings */
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
3. tty.c代码
.#include <stdio.h> /*标准输入输出定义*/
.#include <unistd.h> /*linux 标准函数定义*/
.#include <fcntl.h> /*文件控制定义*/
.#include <errno.h> /*错误号定义*/
.#include <termios.h> /*PPSIX 终端控制定义*/
int main()
{
int fd,n;
char buf[256];
fd=open("/dev/ttyS1",O_NOCTTY|O_RDWR|O_NONBLOCK); /*以读写方式打开串口*/
if( fd < 0) /* 不能打开串口一*/
{
perror("Unable open /dev/ttyS0
");
return 1;
}
n = write( fd, "hello
", 6);
if ( n < 0 )
puts( "write() of 6 bytes failed!
");
puts( "write() of 6 bytes ok!
");
while(1)
{
read(fd,buf,256);
puts(buf);
if(strncmp(buf,"quit",4)==0)break;
}
return 0;
}
int set_port(int fd)
{
struct termios opt;
tcgetattr(fd,&opt);/*get current option setup*/
show_option(&opt);
// opt.c_cflags &=
tcsetattr(fd,&opt);/*get current option setup*/
}
三、遇到的问题及解决
这次实验和实验一一起完成的,基本没有遇到问题,只是由于这些指令平时没有用功,出现把命令敲错了情况,没有其他问题