快速排序
原理:
经过一趟排序 会把数组分成两段 一段比当前数大 一段比当前数小 左边以及右边的继续按照这种方式排序 直到完成所有排序。
稳定性:不稳定
时间复杂度:平均 O(nlogn) 最坏情况为O(n^2)
图解:
初始数组【49,38,65,97,76,13,27】
第一次排序流程如下:
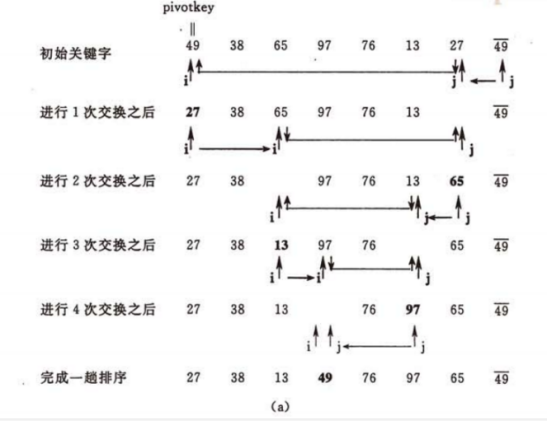
把整个序列看做一个数组,把第零个位置看做中轴,和最后一个比,如果比它小交换,比它大不做任何处理;交换了以后再和小的那端比,比它小不交换,比他大交换。这样循环往复,一趟排序完成,左边就是比中轴小的,右边就是比中轴大的,然后再用分治法,分别对这两个独立的数组进行排序。
public class QuickSort2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = { 49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27 };
quick(a);
for (int num : a) {
System.out.print(" " + num);
}
}
private static void quick(int[] a) {
if (a != null) {
quickSort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
}
private static void quickSort(int[] a, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int mid = getMid(a, low, high);
System.out.println(mid);
quickSort(a, low, mid - 1);
quickSort(a, mid + 1, high);
}
}
private static int getMid(int[] a, int low, int high) {
int temp = a[low];
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && a[high] >= temp) {
high--;
}
// 如果跳出循环 说明发现了比temp的小的值,移到左边去
a[low] = a[high];
while (low < high && a[low] <= temp) {
low++;
}
// 如果跳出循环 说明发现了比temp的大的值 ,移到右边去
a[high] = a[low];
}
a[low] = temp;
return low;
}
}