常见的字符串匹配算法有BF、KMP(教科书中非常经典的)、BM、Sunday算法
这里主要想介绍下性能比较好并且实现比较简单的Sunday算法 。
基本原理:
从前往后匹配,如果遇到不匹配情况判断母串参与匹配的最后一位的下一位字符
,如果该字符出现在模板串中,选择最右出现的位置进行对齐;
否则直接跳过该匹配区域。
画图说明:
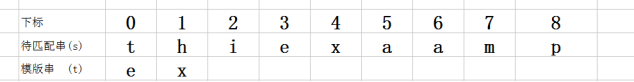
首先下标为0 的字符相互比较,发现并不相等,
然后查找 s 中参与匹配的最后一位字符的下一字符 ,即 i , 看 i 在是不是在t中(从右向左匹配) 发现i不在t中,
接下来 s后移2(即t.length())位,到i处,发现i不存在于t中,于是 s后移2(即t.length())位,到x处 发现x存在于t中
于是s在移动(t.length()-x在t中出现的下标) 在做比较
代码演示:
public class SundaySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "thiexaamp";
String t = "ex";
int rtn = sundaySearch(s, t);
System.out.println(rtn);
}
/**
* source 母串
* target 模板串
* 返回值 如果存在就返回target的第一个字符在source的下标
*
*/
private static int sundaySearch(String source, String target) {
int loc = 0;
int locSource = 0;
int locTarget = 0;
int count = 0; //用于记录有几个字符相同,如果与locTarget的长度相等就找到了
while (locSource < source.length() && locTarget < target.length()) {
if (target.charAt(locTarget) == source.charAt(locSource)) {
locTarget++;
locSource++;
count++;
} else {
count = 0;
if (locSource < source.length() - target.length()) {
//看原下标+target.length()位的元素是不是在target中,(从右往左匹配)
loc = target.lastIndexOf(source.charAt(locSource + target.length()));
} else {
break;
}
if (loc == -1) {//不存在 locSource 移动target.length()位
locSource = locSource + target.length();
} else {
//存在,右移(target.length() - loc) 位
locSource = locSource + target.length() - loc;
}
locTarget = 0;
}
}
if (loc != -1 && count == target.length()) {
return locSource - count;
}
return -1;
}
}
运行结果如下
