public class Example extends Thread{ @Override public void run(){ try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.print("run"); } public static void main(String[] args){ Example example=new Example(); example.run(); System.out.print("main"); } }
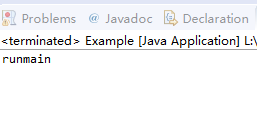
分析:这里调用run方法并不会启动子线程,而是直接当作普通函数调用,因此在执行run的时候,遇到Thread.sleep(1000)导致的是main线程休眠1s,因此效果是运行后,在1s后控制台输出“runmain",如果把example.run( )改成example.start( ),就会先输出main,1s后再输出run。