[抄题]:
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.

[暴力解法]:
时间分析:
空间分析:
[思维问题]:
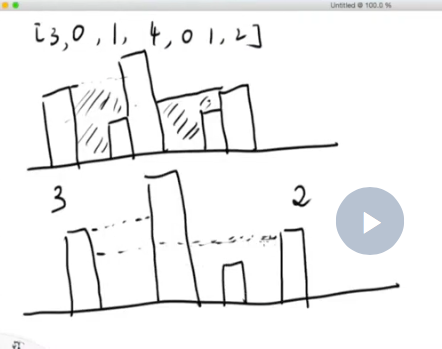
- 灌水的多少基本上由左右边界中较矮的一块木板开始,由相邻是否有较高的木板决定。第一次学灌水,算了
[一句话思路]:
[输入量]:空: 正常情况:特大:特小:程序里处理到的特殊情况:异常情况(不合法不合理的输入):
[画图]:
灌水的多少基本上由左右边界的木板决定。
[一刷]:
[二刷]:
[三刷]:
[四刷]:
[五刷]:
[五分钟肉眼debug的结果]:
[总结]:
[复杂度]:Time complexity: O(n) Space complexity: O(n)
[英文数据结构或算法,为什么不用别的数据结构或算法]:
[关键模板化代码]:

while (left < right) { if (heights[left] < heights[right]) { //start from left left++; if (left_max > heights[left]) { result += (left_max - heights[left]); }else { left_max = heights[left]; } }else { //start from right right--; if (right_max > heights[right]) { result += (right_max - heights[right]); }else { right_max = heights[right]; } } }
[其他解法]:
[Follow Up]:
[LC给出的题目变变变]:
装最多水的容器 · Container With Most Water 2指针
[代码风格] :

public class Solution { /** * @param heights: a list of integers * @return: a integer */ public int trapRainWater(int[] heights) { int result = 0; //corner case if (heights == null || heights.length == 0) { return 0; } int left = 0; int right = heights.length - 1; int left_max = heights[left]; int right_max = heights[right]; while (left < right) { if (heights[left] < heights[right]) { //start from left left++; if (left_max > heights[left]) { result += (left_max - heights[left]); }else { left_max = heights[left]; } }else { //start from right right--; if (right_max > heights[right]) { result += (right_max - heights[right]); }else { right_max = heights[right]; } } } return result; } }
[抄题]:
Given n x m non-negative integers representing an elevation map 2d where the area of each cell is 1 x 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.

Given 5*4 matrix
[12,13,0,12]
[13,4,13,12]
[13,8,10,12]
[12,13,12,12]
[13,13,13,13]
return 14.
[暴力解法]:
时间分析:
空间分析:
[思维问题]:
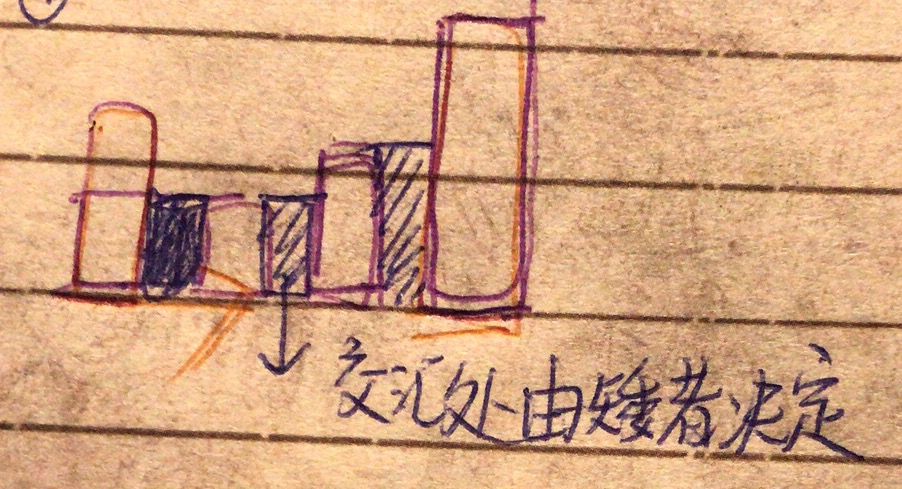
- 以为从四个角当作外围,朝中间过渡。应该把四堵墙当作外围,要能把中间都包起来才能做外围。
- 怎么想不到利用堆,要分析数据特点再选数据结构 而不是一个个套用数据结构:每次都是从q的顶点(最矮的点)从低往高注水,故用heap.
- q中放的是能向四周扩展的cell, 但是每次都是从q的顶点(最矮的点)从低往高注水。不是从高往低duang地一下往下倒,没想象出来。
[一句话思路]:
[输入量]:空: 正常情况:特大:特小:程序里处理到的特殊情况:异常情况(不合法不合理的输入):
[画图]:
[一刷]:
- PQ的括号里要传新建的引用new CellComparator(),体现参数的多态
- q中没有cell并往里头放时,新建即可
- 队列已经创建出对象,则不用null。再判断对象是否为零,因此用isempty()
- 从0 开始,取m个数,最后一个应该是m - 1,老是稍微理解了然后又忘了
- java int[] 未初始化时默认值是0,integer[]未初始化时默认值是null
- int[][] visit = new int[n][m]; 已经忘写好几次了
[二刷]:
[三刷]:
[四刷]:
[五刷]:
[五分钟肉眼debug的结果]:
[总结]:
灌水(扩展类)本质还是BFS,区区几个算法中的一种。要分析数据特点再选数据结构 而不是一个个套用数据结构
[复杂度]:Time complexity: O(m*n个元素*lg(m+n)每个元素在heap中取最小值) Space complexity: O(m*n个点保存在去重矩阵中)
[英文数据结构或算法,为什么不用别的数据结构或算法]:
- BFS,“扩展类”问题就应该想到,印象还不够深
- dp好用,可不要贪杯哦
- 重写@override是子类对父类的允许访问的方法的实现过程进行重新编写, 返回值和形参都不能改变。重载(overloading) 是在一个类里面,方法名字相同,而参数不同。
[关键模板化代码]:

class CellComparator implements Comparator<Cell> { public int compare(Cell a, Cell b) { if (a.h > b.h) { return 1; }else if (a.h == b.h) { return 0; }else { return -1; } } }
[其他解法]:
[Follow Up]:
[LC给出的题目变变变]:
542. 01 Matrix 所有点,用dfs
279. Perfect Squares dp
529. Minesweeper 扫雷 DFS BFS无疑了
[代码风格] :

class Cell { int x, y, h; Cell (int xx, int yy, int hh) { x = xx; y = yy; h = hh; } } class CellComparator implements Comparator<Cell> { public int compare(Cell a, Cell b) { if (a.h > b.h) { return 1; }else if (a.h == b.h) { return 0; }else { return -1; } } } public class Solution { /** * @param heights: a matrix of integers * @return: an integer */ public int trapRainWater(int[][] heightMap) { int result = 0; int n = heightMap.length; int m = heightMap[0].length; int[][] visit = new int[n][m]; int[] dx = {0, 1, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {1, 0, -1, 0}; //corner case if (heightMap == null || m == 0 || n == 0) { return 0; } PriorityQueue<Cell> q = new PriorityQueue<>(new CellComparator()); //get 4 edges into q for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { q.offer(new Cell(i, 0, heightMap[i][0])); q.offer(new Cell(i, m - 1, heightMap[i][m - 1])); visit[i][0] = 1; visit[i][m - 1] = 1; } for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { q.offer(new Cell(0, j, heightMap[0][j])); q.offer(new Cell(n - 1, j, heightMap[n - 1][j])); visit[0][j] = 1; visit[n - 1][j] = 1; } //bfs while (!q.isEmpty()) { Cell now = q.poll(); int cx = now.x; int cy = now.y; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int nx = cx + dx[i]; int ny = cy + dy[i]; if (0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < m && visit[nx][ny] == 0) { visit[nx][ny] = 1; q.offer(new Cell(nx, ny, Math.max(now.h, heightMap[nx][ny]))); result += Math.max(0, now.h - heightMap[nx][ny]); } } } return result; } }
