一、理论部分
1、泛型:也称参数化类型。就是定义类、接口和方法时,通过类型参数指示将要处理的对象类型。
2、泛型程序设计:编写代码可以被很多不同类型的对象所重用。
3、泛型方法:
a.除了泛型类外,还可以只单独定义一个方法作为泛型方法,用于指定方法参数或者返回值为泛型类型,留待方法调用时确定。
b.泛型方法可以申明在泛型类中,也可以申明在普通类中。
4、定义泛型变量的上界
public class NumberGeneric< T extends Number>
a.上述声明规定了NumberGeneric类所能处理的泛型变量类型需和Number有继承关系;
b.extends关键字所声明的上界既可以是一个类,也可以是一个接口。
5、<T extends Bounding Type>表示T应该是绑定类型的子类型。
6、一个类型变量或通配符可以有多个限定,限定类型用“&”分割。
7、泛型变量下界的说明
a.通过使用super关键字可以固定泛型参数的类型为某种类型或者其超类。
b.当程序希望为一个方法的参数限定类型时,通常可以使用下限通配符。
8、Java中的数组是协变的,但这一原理不适用于泛型类型。不允许这样做的理由:避免破坏要提供类型的安全泛型。
9、泛型类可扩展或实现其它的泛型类。
10、通配符
a. “?”符号表明参数的类型可以是任何一种类型,它和参数T的含义是有区别的。T表示一种未知类型,而“?”表示任何一种类型。这种通配符一般有以下三种用法:
(1)单独的?,用于表示任何类型。
(2)? extends type,表示带有上界。
(3) ? super type,表示带有下界。
11、无限定的通配符,例如,Pair<?>。Pair<?>与Pair的不同在于:可以用任意Object对象调用原始的Pair类的setObject方法。
二、实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解泛型概念;
(2) 掌握泛型类的定义与使用;
(3) 掌握泛型方法的声明与使用;
(4) 掌握泛型接口的定义与实现;
(5)了解泛型程序设计,理解其用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第8章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 编辑、调试、运行教材311、312页 代码,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型类定义及使用代码处添加注释;
l 掌握泛型类的定义及使用。
package pair1; /** * @version 1.01 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] words = { "Mary", "had", "a", "little", "lamb" };//初始化String对象数组 Pair<String> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(words);//通过类名调用minmax方法 System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst()); System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());//把打包的两个数据提取出来 } } class ArrayAlg { /** * Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of strings. * @param a an array of strings * @return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is null or empty */ public static Pair<String> minmax(String[] a)//实例化的一个Pair类对象 { if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null; String min = a[0]; String max = a[0]; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];//字符串对象比较,通过ASCII码比较 if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i]; } return new Pair<>(min, max);//泛型类作为返回值 } }
package pair1; /** * @version 1.00 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Pair<T> { private T first; private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; } public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; } public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; } public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; } }
实验结果如下: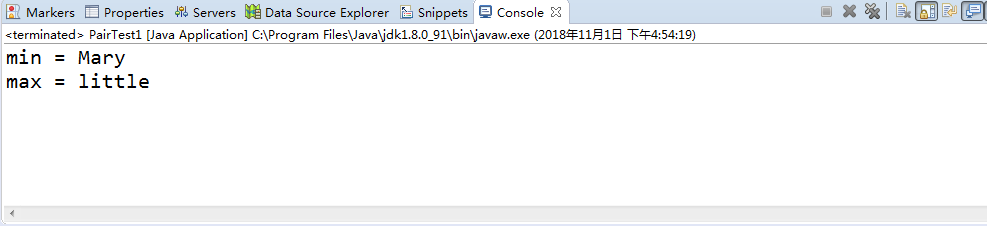
测试程序2:
l 编辑、调试运行教材315页 PairTest2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型程序设计代码处添加相关注释;
l 掌握泛型方法、泛型变量限定的定义及用途。
package pair2; import java.time.*; /** * @version 1.02 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //初始化LocalDate对象数组 LocalDate[] birthdays = { LocalDate.of(1906, 12, 9), // G. Hopper LocalDate.of(1815, 12, 10), // A. Lovelace LocalDate.of(1903, 12, 3), // J. von Neumann LocalDate.of(1910, 6, 22), // K. Zuse }; Pair<LocalDate> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(birthdays);//通过类名调用minmax方法 System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst()); System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond()); } } class ArrayAlg { /** Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of objects of type T. @param a an array of objects of type T @return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is null or empty */ public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a)//加了上界约束的泛型方法 { if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null; T min = a[0]; T max = a[0]; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i]; if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i]; } return new Pair<>(min, max); } }
package pair2; /** * @version 1.00 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Pair<T> { private T first; private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; } public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; } public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; } public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; } }
实验结果如下图所示: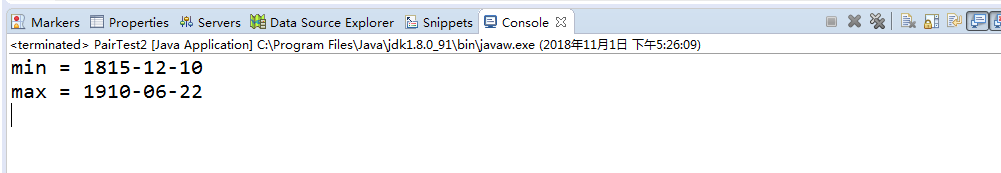
测试程序3:
l 用调试运行教材335页 PairTest3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解通配符类型的定义及用途。
package pair3; /** * @version 1.01 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Manager ceo = new Manager("Gus Greedy", 800000, 2003, 12, 15);//创建了一个Manager类对象 Manager cfo = new Manager("Sid Sneaky", 600000, 2003, 12, 15); Pair<Manager> buddies = new Pair<>(ceo, cfo); printBuddies(buddies); ceo.setBonus(1000000); cfo.setBonus(500000); Manager[] managers = { ceo, cfo }; Pair<Employee> result = new Pair<>(); minmaxBonus(managers, result); System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName() + ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName()); maxminBonus(managers, result); System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName() + ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName()); } public static void printBuddies(Pair<? extends Employee> p) { Employee first = p.getFirst(); Employee second = p.getSecond(); System.out.println(first.getName() + " and " + second.getName() + " are buddies."); } public static void minmaxBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result) { if (a.length == 0) return; Manager min = a[0]; Manager max = a[0]; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.getBonus() > a[i].getBonus()) min = a[i]; if (max.getBonus() < a[i].getBonus()) max = a[i]; } result.setFirst(min); result.setSecond(max); } public static void maxminBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result) { minmaxBonus(a, result); PairAlg.swapHelper(result); //swapHelper捕获通配符类型 } // 不能写公共静态 <T super manager> ... } class PairAlg { public static boolean hasNulls(Pair<?> p)//?表示:类型变量通配符 { return p.getFirst() == null || p.getSecond() == null; } public static void swap(Pair<?> p) { swapHelper(p); } public static <T> void swapHelper(Pair<T> p) { T t = p.getFirst(); p.setFirst(p.getSecond()); p.setSecond(t); } }
package pair3; public class Manager extends Employee { private double bonus; /** @param name the employee's name @param salary the salary @param year the hire year @param month the hire month @param day the hire day */ public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double b) { bonus = b; } public double getBonus() { return bonus; } }
package pair3; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
package pair3; /** * @version 1.00 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Pair<T> { private T first; private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; } public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; } public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; } public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; } }
实验结果如下图所示:
实验2:编程练习:
编程练习1:实验九编程题总结
l 实验九编程练习1总结(从程序总体结构说明、模块说明,目前程序设计存在的困难与问题三个方面阐述)。
程序总体结构说明:包括ID类和main类以及Comparable接口。
模块说明:ID类和main类
package IDcard; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Collections; public class ID { public static People findPeopleByname(String name) { People flag = null; for (People people : peoplelist) { if(people.getName().equals(name)) { flag = people; } } return flag; } public static People findPeopleByid(String id) { People flag = null; for (People people : peoplelist) { if(people.getnumber().equals(id)) { flag = people; } } return flag; } private static ArrayList<People> agenear(int yourage) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int j=0,min=53,d_value=0,k = 0; ArrayList<People> plist = new ArrayList<People>(); for (int i = 0; i < peoplelist.size(); i++) { d_value = peoplelist.get(i).getage() > yourage ? peoplelist.get(i).getage() - yourage : yourage - peoplelist.get(i).getage() ; k = d_value < min ? i : k; min = d_value < min ? d_value : min; } for(People people : peoplelist) { if(people.getage() == peoplelist.get(k).getage()) { plist.add(people); } } return plist; } private static ArrayList<People> peoplelist; public static void main(String[] args) { peoplelist = new ArrayList<People>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); File file = new File("D:\身份证号.txt"); try { FileInputStream files = new FileInputStream(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(files)); String temp = null; while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { String[] information = temp.split("[ ]+"); People people = new People(); people.setName(information[0]); people.setnumber(information[1]); int A = Integer.parseInt(information[3]); people.setage(A); people.setsex(information[2]); for(int j = 4; j<information.length;j++) { people.setplace(information[j]); } peoplelist.add(people); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("文件未找到"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("文件读取错误"); e.printStackTrace(); }//捕获异常 boolean isTrue = true; while (isTrue) { System.out.println("******************************************"); System.out.println(" 1.按姓名典序输出人员信息"); System.out.println(" 2.查询最大年龄人员信息"); System.out.println(" 3.查询最小年龄人员信息"); System.out.println(" 4.输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近的人"); System.out.println(" 5.查询人员中是否有你的同乡"); System.out.println(" 6.退出"); System.out.println("******************************************"); int nextInt = scanner.nextInt(); switch (nextInt) { case 1: Collections.sort(peoplelist); System.out.println(peoplelist.toString()); break; case 2: int max=0; int j,k1 = 0; for(int i=1;i<peoplelist.size();i++) { j = peoplelist.get(i).getage(); if(j>max) { max = j; k1 = i; } } System.out.println("年龄最大:"+peoplelist.get(k1)); break; case 3: int min = 100; int j1,k2 = 0; for(int i=1;i<peoplelist.size();i++) { j1 = peoplelist.get(i).getage(); if(j1<min) { min = j1; k2 = i; } } System.out.println("年龄最小:"+peoplelist.get(k2)); break; case 4: System.out.println("年龄:"); int input_age = scanner.nextInt(); ArrayList<People> plist = new ArrayList<People>(); plist = agenear(input_age); for(People people : plist) { System.out.println(people.toString()); } break; case 5: System.out.println("请输入省份"); String find = scanner.next(); for (int i = 0; i <peoplelist.size(); i++) { String [] place = peoplelist.get(i).getplace().split(" "); for(String temp : place) { if(find.equals(temp)) { System.out.println("你的同乡是 "+peoplelist.get(i)); break; } } } break; case 6: isTrue = false; System.out.println("byebye!"); break; default: System.out.println("输入有误"); } } } }
Comparable接口:
package IDcard; public class People implements Comparable<People> { private String name = null; private String number = null; private int age = 0; private String sex = null; private String place = null; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getnumber() { return number; } public void setnumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public int getage() { return age; } public void setage(int age ) { this.age = age; } public String getsex() { return sex; } public void setsex(String sex ) { this.sex = sex; } public String getplace() { return place; } public void setplace(String place) { if(this.place == null) { this.place = place; }else { this.place = this.place+ " " +place; } } public int compareTo(People o) { return this.name.compareTo(o.getName()); } public String toString() { return name+" "+sex+" "+age+" "+number+" "+place+" "; } }
目前程序设计存在的困难与问题:
(1) 对相关代码不熟悉,对有些代码的功能不会去运用,主要是由于编程练习较少导致。
(2)对问题分析不够透彻,很多代码放上去之后就会报错,对错误不能及时解决。
(3)对异常的出现处理之后还是不能使得编程问题得到解决,由于对问题的分析不够所导致。
l 实验九编程练习2总结(从程序总体结构说明、模块说明,目前程序设计存在的困难与问题三个方面阐述)。
程序总体结构说明:包括Suanshu1和main类以及Suanshu类
模块说明:Suanshu1和main类
package 练习2; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Scanner; public class Suanshu1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Suanshu Suanshu=new Suanshu(); PrintWriter output = null; try { output = new PrintWriter("ss.txt"); } catch (Exception e) { //e.printStackTrace(); } int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) { int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int s = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); switch(s) { case 1: System.out.println(i+": "+a+"/"+b+"="); while(b==0){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } double c = in.nextDouble(); output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c); if (c == Suanshu.chu_fa(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); } else { System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); } break; case 2: System.out.println(i+": "+a+"*"+b+"="); int c1 = in.nextInt(); output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1); if (c1 == Suanshu.chen_fa(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); } else { System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); } break; case 3: System.out.println(i+": "+a+"+"+b+"="); int c2 = in.nextInt(); output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2); if (c2 == Suanshu.jia_fa(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); } else { System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); } break ; case 4: System.out.println(i+": "+a+"-"+b+"="); int c3 = in.nextInt(); output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3); if (c3 == Suanshu.jian_fa(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); } else { System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); } break ; } } System.out.println("成绩"+sum); output.println("成绩:"+sum); output.close(); } }
Suanshu类:
package 练习2; public class Suanshu { private int a; private int b; public int jia_fa(int a,int b) { return a+b; } public int jian_fa(int a,int b) { if((a-b)<0) return 0; else return a-b; } public int chen_fa(int a,int b) { return a*b; } public int chu_fa(int a,int b) { if(b!=0) return a/b; else return 0; } }
目前程序设计存在的困难与问题:
(1)对问题的分析不够透彻,没有深入的去想小学的四则运算是整除的,生成的算术不完全是整除类型的。此外生成的减法运算结果可能为负,这也不符合题目要求。
(2)不知道生成文件名为test.txt的路径,是通过电脑搜索得到的。
(3)对程序的设计不够好,敲代码的能力也较差。
编程练习2:采用泛型程序设计技术改进实验九编程练习2,使之可处理实数四则运算,其他要求不变。
package 改进版; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; public class Suanshu1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Suanshu ss = new Suanshu(); PrintWriter out = null; try { out = new PrintWriter("test.txt"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("文件夹输出失败"); e.printStackTrace(); } int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int m; Random rand = new Random(); m = (int) rand.nextInt(4) + 1; System.out.println("随机生成的四则运算类型:" + m); switch (m) { case 1: a = b + (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); while(b == 0){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } while(a % b != 0){ a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } System.out.println(i + " " + a + "/" + b + "="); int c0 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + c0); if (c0 == ss.chufa(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("right!"); } else { System.out.println("error!"); } break; case 2: System.out.println(i + " " + a + "*" + b + "="); int c = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c); if (c == ss.chengfa(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("回答正确!"); } else { System.out.println("回答错误!"); } break; case 3: System.out.println(i + " " + a + "+" + b + "="); int c1 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c1); if (c1 == ss.jiafa(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("回答正确!"); } else { System.out.println("回答错误!"); } break; case 4: while (a < b) { b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } System.out.println(i + " " + a + "-" + b + "="); int c2 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c2); if (c2 == ss.jianfa(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("回答正确!"); } else { System.out.println("回答错误!"); } break; } } System.out.println("最后得分" + sum); out.println("最后得分" + sum); out.close(); } }
package 改进版; public class Suanshu<T> { private T a; private T b; public Suanshu() { a = null; b = null; } public Suanshu(T a, T b) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } public int jiafa(int a,int b) { return a + b; } public int jianfa(int a, int b) { return a - b; } public int chengfa(int a, int b) { return a * b; } public int chufa(int a, int b) { if (b != 0 && a%b==0) return a / b; else return 0; } }
实验结果如下图所示:
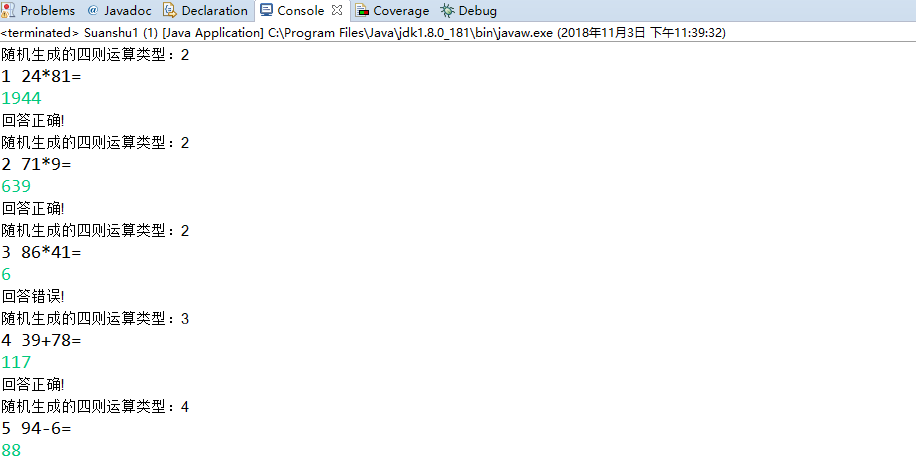
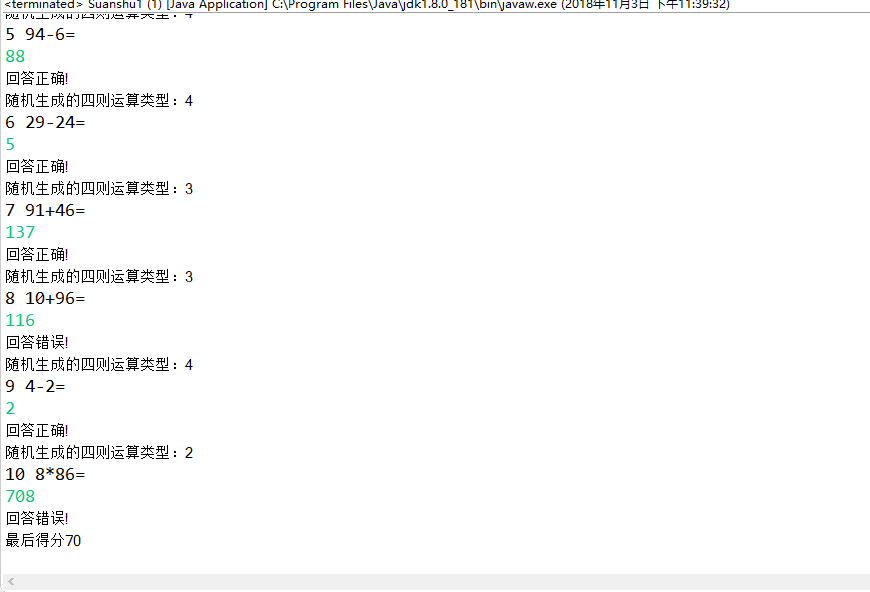
三、实验总结
通过本周对泛型程序设计的学习,我了解了运用泛型程序设计的代码可以被很多不同类型的对象所重用。这使得代码的重用性被提高,而且不用很麻烦的再去敲代码。这周的实验有对上周实验的总结,让我再次认识到了自己的不足,在今后的学习中仍需要很大的努力。