单层感知机

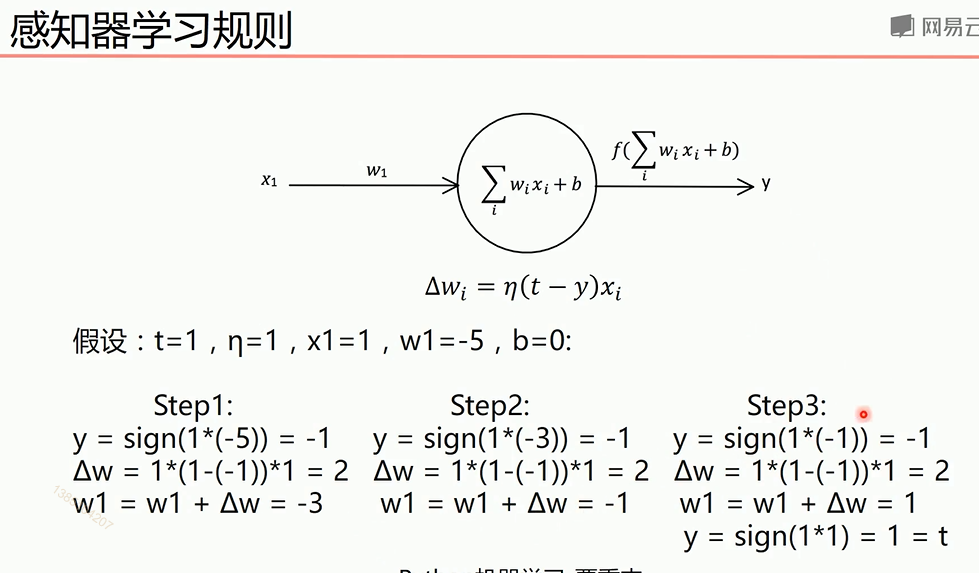
最终y=t,说明经过训练预测值和真实值一致。下面图是sign函数



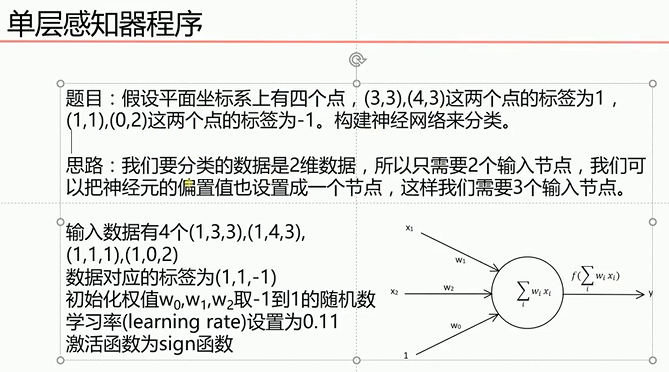
根据感知机规则实现的上述题目的代码
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 #输入数据 4 X = np.array([[1,3,3], 5 [1,4,3], 6 [1,1,1], 7 [1,0,2]]) 8 #标签 9 Y = np.array([[1], 10 [1], 11 [-1], 12 [-1]]) 13 #权值初始化,3行1列,取值范围-1到1 14 W = (np.random.random([3,1])-0.5)*2 15 print(W) 16 #学习率设置 17 lr = 0.11 18 #神经网络输出 19 O = 0 20 21 def update(): 22 global X,Y,W,lr 23 O = np.sign(np.dot(X,W)) 24 W_C = lr*(X.T.dot(Y-O))/int(X.shape[0])#除于样本个数目的是分子计算的误差是所有样本误差之和,所以要进行平均 25 W = W + W_C 26 for i in range(100): 27 update()#更新权值 28 print(W) 29 print(i) 30 O = np.sign(np.dot(X,W)) 31 if(O == Y).all(): 32 print('finished') 33 print('epoch:',i) 34 break 35 #正样本 36 x1 = [3,4] 37 y1 = [3,3] 38 #负样本 39 x2 = [1,0] 40 y2 = [1,2] 41 42 #计算分界线的斜率以及截距 43 k = -W[1]/W[2] 44 d = -W[0]/W[2] 45 print('k=',k) 46 print('d=',d) 47 48 xdata = (0,5) 49 50 plt.figure() 51 plt.plot(xdata,xdata*k+d,'r') 52 plt.scatter(x1,y1,c='b') 53 plt.scatter(x2,y2,c='y') 54 plt.show()
单层感知机解决异或问题
1 ''' 2 异或 3 0^0 = 0 4 0^1 = 1 5 1^0 = 1 6 1^1 = 0 7 ''' 8 import numpy as np 9 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 10 #输入数据 11 X = np.array([[1,0,0], 12 [1,0,1], 13 [1,1,0], 14 [1,1,1]]) 15 #标签 16 Y = np.array([[-1], 17 [1], 18 [1], 19 [-1]]) 20 21 #权值初始化,3行1列,取值范围-1到1 22 W = (np.random.random([3,1])-0.5)*2 23 24 print(W) 25 #学习率设置 26 lr = 0.11 27 #神经网络输出 28 O = 0 29 30 def update(): 31 global X,Y,W,lr 32 O = np.sign(np.dot(X,W)) # shape:(3,1) 33 W_C = lr*(X.T.dot(Y-O))/int(X.shape[0]) 34 W = W + W_C 35 for i in range(100): 36 update()#更新权值 37 print(W)#打印当前权值 38 print(i)#打印迭代次数 39 O = np.sign(np.dot(X,W))#计算当前输出 40 if(O == Y).all(): #如果实际输出等于期望输出,模型收敛,循环结束 41 print('Finished') 42 print('epoch:',i) 43 break 44 45 #正样本 46 x1 = [0,1] 47 y1 = [1,0] 48 #负样本 49 x2 = [0,1] 50 y2 = [0,1] 51 52 #计算分界线的斜率以及截距 53 k = -W[1]/W[2] 54 d = -W[0]/W[2] 55 print('k=',k) 56 print('d=',d) 57 58 xdata = (-2,3) 59 60 plt.figure() 61 plt.plot(xdata,xdata*k+d,'r') 62 plt.scatter(x1,y1,c='b') 63 plt.scatter(x2,y2,c='y') 64 plt.show()
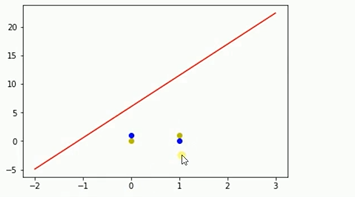
运行结果如上,可以知道单层感知机不适合解决如上类似的异或问题
线性神经网络

同时相比于感知机引入了Delta学习规则


解决感知机无法处理异或问题的方法
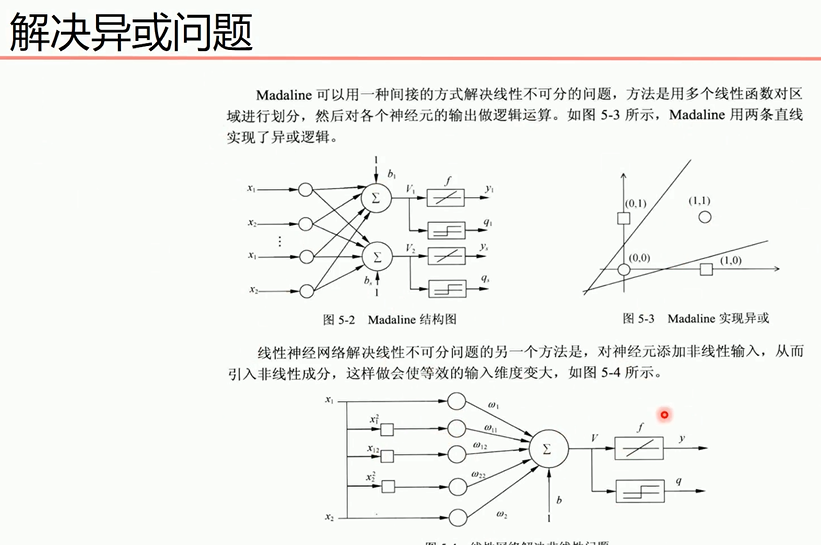
对于第二个方法

说明:X0是偏置值,值为1,X1,X2为线性输入,其它为添加的非线性输入,使用purelin激活函数(y=x)进行模型训练,再下面是y值的求法,用于图形绘制。
程序如下
1 #题目:异或运算 2 #0^0=0 3 #0^1=1 4 #1^0=1 5 #1^1=0 6 import numpy as np 7 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 8 #输入数据--这里偏置定为1 9 X = np.array([[1,0,0,0,0,0], 10 [1,0,1,0,0,1], 11 [1,1,0,1,0,0], 12 [1,1,1,1,1,1]]) 13 #标签--期望输出 14 Y = np.array([-1,1,1,-1]) 15 #权值初始化,1行6列,取-1到1的随机数 16 W = (np.random.random(6)-0.5)*2 17 print(W) 18 #学习率 19 lr = 0.11 20 #计算迭代次数 21 n = 0 22 #神经网络输出 23 o = 0 24 25 def update(): 26 global X,Y,W,lr,n 27 n+=1 28 o = np.dot(X,W.T) 29 W_C = lr*((Y-o.T).dot(X))/(X.shape[0])#权值改变数,这里除掉行数求平均值,因为行数多,权值改变就会很大。 30 W = W + W_C 31 for i in range(1000): 32 update()#更新权值 33 34 o = np.dot(X,W.T) 35 print("执行一千次后的输出结果:",o)#看下执行一千次之后的输出 36 37 #用图形表示出来 38 #正样本 39 x1 = [0,1] 40 y1 = [1,0] 41 #负样本 42 x2 = [0,1] 43 y2 = [0,1] 44 45 def calculate(x,root): 46 a = W[5] 47 b = W[2]+x*W[4] 48 c = W[0]+x*W[1]+x*x*W[3] 49 if root == 1:#第一个根 50 return (-b+np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a) 51 if root == 2:#第二个根 52 return (-b-np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a) 53 54 xdata = np.linspace(-1,2) 55 56 plt.figure() 57 plt.plot(xdata,calculate(xdata,1),'r')#用红色 58 plt.plot(xdata,calculate(xdata,2),'r')#用红色 59 plt.plot(x1,y1,'bo')#用蓝色 60 plt.plot(x2,y2,'yo')#用黄色 61 plt.show()
利用神经网络解决上述感知机题目
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 #输入数据 4 X = np.array([[1,3,3], 5 [1,4,3], 6 [1,1,1], 7 [1,0,2]]) 8 #标签 9 Y = np.array([[1], 10 [1], 11 [-1], 12 [-1]]) 13 14 #权值初始化,3行1列,取值范围-1到1 15 W = (np.random.random([3,1])-0.5)*2 16 17 print(W) 18 #学习率设置 19 lr = 0.11 20 #神经网络输出 21 O = 0 22 23 def update(): 24 global X,Y,W,lr 25 O = np.dot(X,W) 26 W_C = lr*(X.T.dot(Y-O))/int(X.shape[0]) 27 W = W + W_C 28 for i in range(100): 29 update()#更新权值 30 31 #正样本 32 x1 = [3,4] 33 y1 = [3,3] 34 #负样本 35 x2 = [1,0] 36 y2 = [1,2] 37 38 #计算分界线的斜率以及截距 39 k = -W[1]/W[2] 40 d = -W[0]/W[2] 41 print('k=',k) 42 print('d=',d) 43 44 xdata = (0,5) 45 if i % 10 == 0: 46 plt.figure() 47 plt.plot(xdata,xdata*k+d,'r') 48 plt.scatter(x1,y1,c='b') 49 plt.scatter(x2,y2,c='y') 50 plt.show()
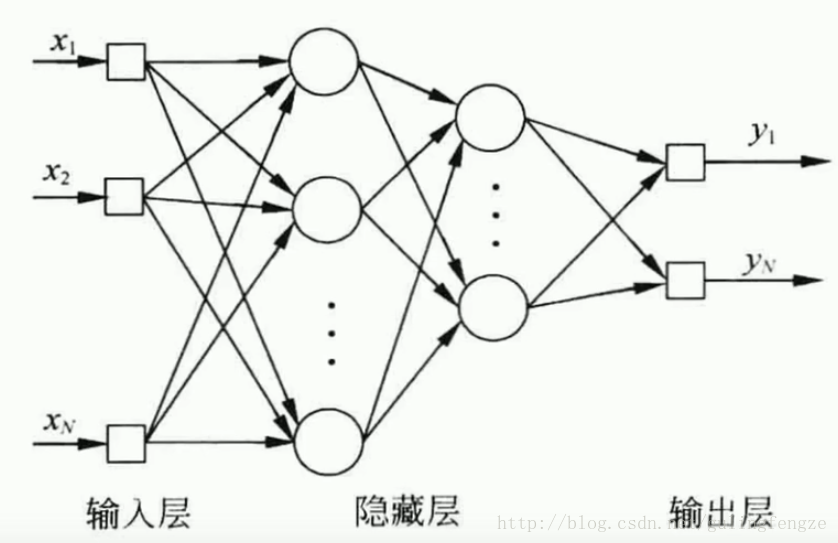
BP神经网络
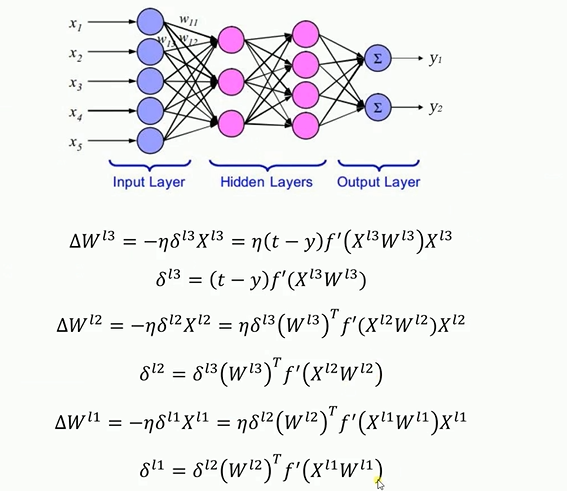
反向传播(Back Propagation,简称BP)神经网络解决了多层神经网络的学习问题,广泛应用于分类识别、图像识别、压缩、逼近以及回归等领域,其结构如下所示。
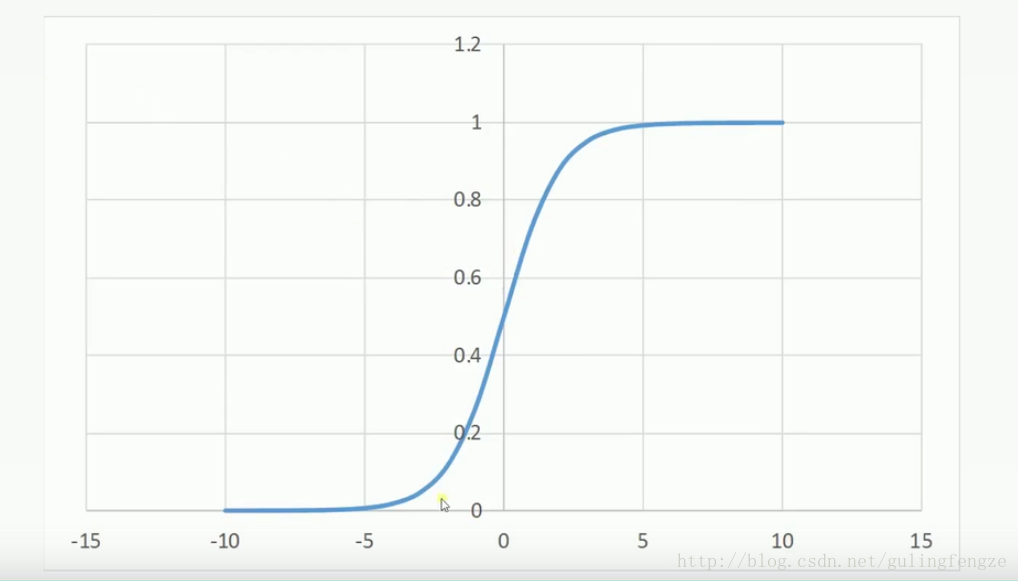
另外介绍及格激活函数:sigmoid、tanh和softsign。神经网络中的激活函数,其作用就是引入非线性。
Sigmoid:sigmoid的优点是输出范围有限,数据在传递的过程中不容易发散,求导很容易(y=sigmoid(x), y’=y(1-y))。缺点是饱和的时候梯度太小。其输出范围为(0, 1),所以可以用作输出层,输出表示概率。
公式:
Sigmoid:sigmoid的优点是输出范围有限,数据在传递的过程中不容易发散,求导很容易(y=sigmoid(x), y’=y(1-y))。缺点是饱和的时候梯度太小。其输出范围为(0, 1),所以可以用作输出层,输出表示概率。

公式:
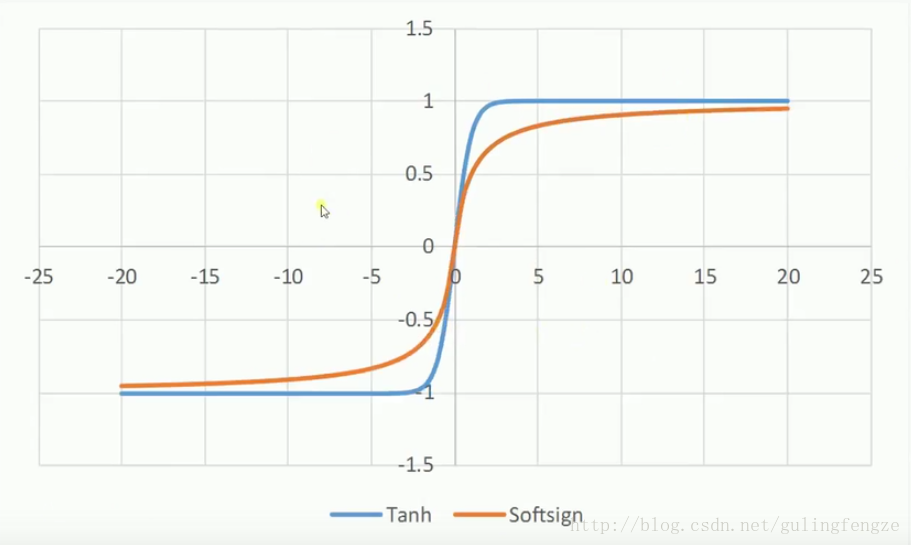
tanh和softsign:
要注意的是对多层神经元先对最后一层权重更新,其结果再更新前一层的权重

bp神经网络解决异或问题的程序如下
1 import numpy as np 2 3 # 输入数据 4 X = np.array([[1, 0, 0], 5 [1, 0, 1], 6 [1, 1, 0], 7 [1, 1, 1]]) 8 # 标签 9 Y = np.array([[0, 1, 1, 0]]) 10 # 权值初始化,取值范围-1到1 11 V = np.random.random((3, 4)) * 2 - 1 12 W = np.random.random((4, 1)) * 2 - 1 13 print(V) 14 print(W) 15 # 学习率设置 16 lr = 0.11 17 def sigmoid(x): 18 return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) 19 def dsigmoid(x): 20 return x * (1 - x)#激活函数的导数 21 def update(): 22 global X, Y, W, V, lr 23 24 L1 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, V)) # 隐藏层输出(4,4) 25 L2 = sigmoid(np.dot(L1, W)) # 输出层输出(4,1) 26 27 L2_delta = (Y.T - L2) * dsigmoid(L2) 28 L1_delta = L2_delta.dot(W.T) * dsigmoid(L1) 29 30 W_C = lr * L1.T.dot(L2_delta) 31 V_C = lr * X.T.dot(L1_delta) 32 33 W = W + W_C 34 V = V + V_C 35 36 37 for i in range(20000): 38 update() # 更新权值 39 if i % 500 == 0: 40 L1 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, V)) # 隐藏层输出(4,4) 41 L2 = sigmoid(np.dot(L1, W)) # 输出层输出(4,1) 42 print('Error:', np.mean(np.abs(Y.T - L2))) 43 44 L1 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, V)) # 隐藏层输出(4,4) 45 L2 = sigmoid(np.dot(L1, W)) # 输出层输出(4,1) 46 print(L2) 47 48 49 def judge(x): 50 if x >= 0.5: 51 return 1 52 else: 53 return 0 54 55 56 for i in map(judge, L2): 57 print(i)