一:代理模式
1 根据名字我们就可以理解为:代替别人管理
2 什么情况下使用代理模式呢?
在软件系统中,有些对象有时候由于跨越网络或者其他的障碍,而不能够或者不想直接访问另一个对象,如果直接访问会给系统带来不必要的复杂性,这时候可以在客户程序和目标对象之间增加一层中间层,让代理对象来代替目标对象打点一切。
结构图:
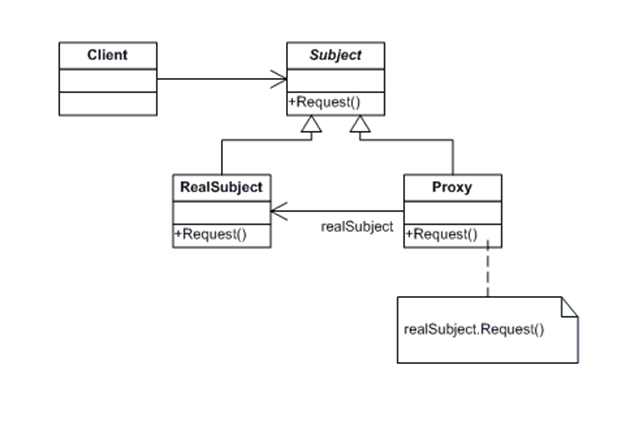
3 我们一卖书为例:
1 package com.lovo.Proxy; 2 /** 3 * 4 * @author acer 5 * 6 */ 7 public interface IBook { 8 public void sailBook(); 9 10 }
1 package com.lovo.Proxy; 2 /** 3 * 4 * @author acer 5 * 6 */ 7 public class RealSubject implements IBook { 8 9 @Override 10 public void sailBook() { 11 System.out.println("卖书了"); 12 } 13 14 }
1 package com.lovo.Proxy; 2 /** 3 * 4 * @author acer 5 * 6 */ 7 public class MyProxy implements IBook { 8 private RealSubject realSubject; 9 10 11 public MyProxy(RealSubject realSubject) { 12 super(); 13 this.realSubject = realSubject; 14 } 15 16 17 @Override 18 public void sailBook() { 19 realSubject.sailBook(); 20 21 } 22 23 }
1 package com.lovo.Proxy; 2 /** 3 * 4 * @author acer 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Test { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 MyProxy myProxy=new MyProxy(new RealSubject()); 11 myProxy.sailBook(); 12 13 } 14 15 }
二:桥梁模式
主要的一句话就是 :将抽象部分与他的实现部分分离,使他们都可以独立的变化!现实指的是抽象类和他派生的类用来实现自己的对象!
我们来举个例子吧!
结构图:
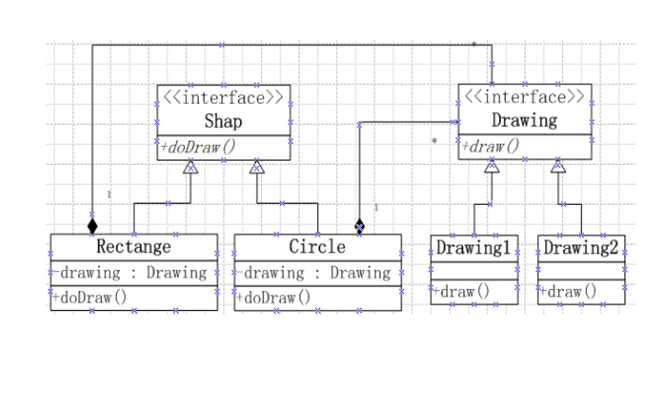
比如:客户需要我们画出多种图形,并且可以用多种线条来画这些图形;
这里面变化的是图形,线条,那么我们就可以使用两个接口,让子类来实现这两个接!让子类来实现画出怎样的图像来!
首先我们写个画线条的接口:
1 package com.lovo.Bridge.two; 2 3 public interface IDraw { 4 public void doDraw(); 5 6 }
画图形接口:
1 package com.lovo.Bridge.two; 2 3 public interface IShape { 4 public void myDraw(); 5 6 }
各种图形的类:// 矩形 圆
1 package com.lovo.Bridge.two; 2 3 public class Rectangular implements IShape { 4 private int width; 5 private int height; 6 private IDraw draw; 7 8 public Rectangular(int width, int height, IDraw draw) { 9 super(); 10 this.width = width; 11 this.height = height; 12 this.draw = draw; 13 } 14 15 16 public int getWidth() { 17 return width; 18 } 19 20 21 public void setWidth(int width) { 22 this.width = width; 23 } 24 25 26 public int getHeight() { 27 return height; 28 } 29 30 31 public void setHeight(int height) { 32 this.height = height; 33 } 34 35 36 public IDraw getDraw() { 37 return draw; 38 } 39 40 41 public void setDraw(IDraw draw) { 42 this.draw = draw; 43 } 44 45 @Override 46 public void myDraw() { 47 System.out.println("画矩形:长:"+this.width+"高:"+this.height); 48 draw.doDraw(); 49 50 } 51 52 }
1 package com.lovo.Bridge.two; 2 3 public class Round implements IShape{ 4 private int r; 5 private int x; 6 private int y; 7 private IDraw draw; 8 9 10 public Round(int r, int x, int y, IDraw draw) { 11 super(); 12 this.r = r; 13 this.x = x; 14 this.y = y; 15 this.draw = draw; 16 } 17 18 19 public int getR() { 20 return r; 21 } 22 23 24 public void setR(int r) { 25 this.r = r; 26 } 27 28 29 public int getX() { 30 return x; 31 } 32 33 34 public void setX(int x) { 35 this.x = x; 36 } 37 38 39 public int getY() { 40 return y; 41 } 42 43 44 public void setY(int y) { 45 this.y = y; 46 } 47 48 49 public IDraw getDraw() { 50 return draw; 51 } 52 53 54 public void setDraw(IDraw draw) { 55 this.draw = draw; 56 } 57 58 59 60 61 62 @Override 63 public void myDraw() { 64 System.out.println("画圆:半径:"+this.r +"圆心在("+this.x+","+this.y+")"); 65 draw.doDraw(); 66 67 } 68 69 }
在写两个线条的类://实线 虚线
1 package com.lovo.Bridge.two; 2 3 public class Dotted implements IDraw{ 4 5 @Override 6 public void doDraw() { 7 System.out.println("画虚线"); 8 } 9 10 }
1 package com.lovo.Bridge.two; 2 3 public class Solid implements IDraw{ 4 5 @Override 6 public void doDraw() { 7 System.out.println("画实线"); 8 } 9 10 }
最后来个测试类:
1 package com.lovo.Bridge.two; 2 3 public class Test { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 IDraw d=new Solid(); 7 IShape s=new Rectangular(100, 50, d); 8 s.myDraw(); 9 } 10 11 }
对于这些设计模式 其实我自己也不太搞得清楚的,只是因为最近在学这个!算是做一些记录吧!