题目大意
一只蜜蜂在下图所示的数字蜂房上爬动,已知它只能从标号小的蜂房爬到标号大的相邻蜂房,现在问你:蜜蜂从蜂房M开始爬到蜂房N,M<N,有多少种爬行路线?M,N<=1000
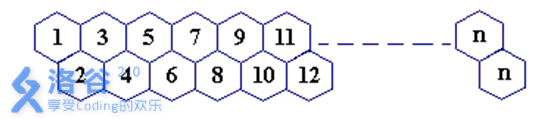
题解
看到M,N<=1000,我们不能寻求通项解。我们从动规的角度看,令f(i)为从1到达编号为i的蜂房爬行路线总数,则f(i)=f(i-1)+f(i-2)。这就是斐波那契数的定义呀!求f(n-m)即可。注意斐波那契数很大,要用到高精度。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_LEN = 1001, BASE = 10000, CARRY = 4;
struct BigInt
{
private:
int A[MAX_LEN];
int Len;
public:
BigInt()
{
memset(A, 0, sizeof(A));
Len = 0;
}
BigInt& operator += (const BigInt& a)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= max(Len, a.Len); i++)
{
A[i] += a.A[i];
A[i + 1] += A[i] / BASE;
A[i] %= BASE;
}
if (A[Len + 1])
Len++;
return *this;
}
BigInt& operator = (const BigInt& a)
{
memcpy(A, a.A, sizeof(A));
Len = a.Len;
return *this;
}
BigInt& operator = (int x)
{
memset(A, 0, sizeof(A));
Len = 0;
while (x)
{
A[Len++] = x%BASE;
x /= BASE;
}
while (Len > 0 && A[Len] == 0)
Len--;
return *this;
}
BigInt operator +(const BigInt& a)
{
BigInt ans = *this;
return ans += a;
}
void Print()
{
printf("%d", A[Len]);
for (int i = Len - 1; i >= 0; i--)
printf("%0*d", CARRY, A[i]);
}
};
BigInt& GetF(int n)
{
static BigInt F[3];
F[0] = 1;
F[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
F[i % 3] = F[(i - 1) % 3] + F[(i - 2) % 3];
return F[n % 3];
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &m, &n);
GetF(n - m).Print();
return 0;
}