原文:https://blog.csdn.net/a909301740/article/details/78379720
Spring感觉复杂多了,不知道后面读源码会不会困难很多,先摘抄别人的文章复习下使用
web监听器先安上,监听ServletContext,设置好配置文件

Spring注入的常用三种方式
一、构造器注入,类型匹配
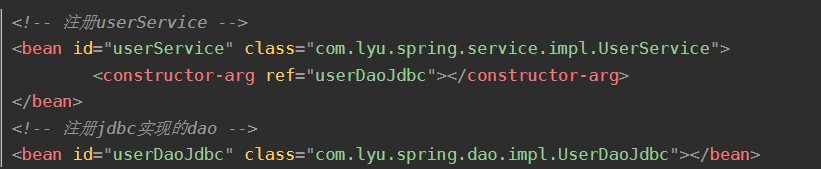
二、setter注入,set方法名相关

三、注解注入,用注解(注解分为constructor、byName、byType)
@Resource 默认byName找不到就用byType
@Autowired 默认byType
Spring Aop配置
代码来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Mister_yang/article/details/80652190
AOP概念上是方法增强,用动态代理实现。
我不怎么用这玩意,但这东西功能很强,一直记一直不用,一直忘,但很多概念我都记得,概括下别人的文章。
切面(Aspect):切入点的集合
连接点:满足切入点的方法
切入点:切面李想去切入的点(方法)
通知:想增强的内容,方式的类型,直接看名字理解
- 前置通知(Before advice)
- 返回后通知(After returning advice):
- 抛出异常后通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知
两种方式使用Aop,xml方式和注解方式(我只用过前者)
一、xml方式
<bean id="aspect" class="x.x.x.x.x"></bean> <aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* x.x.x.class.method(..))" id="pointcut"/>
<aop:aspect ref="aspect">
<aop:before method="A" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after-returning method="B" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:around method="C" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>二、注解方式
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />//在配置中开启动态代理@Component
@Aspect
public class Aspect {
//方式1:
@Before(value="execution(* x.x.x.x.*(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("前置通知。。。。。。");
}
//方式二:先编写切点在将切点加到加强上。
@Pointcut("execution(* x.x.x.*.*(..))")
public void after() {}
@AfterReturning("after()")
public void after1() {
System.out.println("....后置通知....");
}
}Spring事务管理
这个还能用到,因为要用到Aop把我给弄混淆了,一直用的乱七八糟, 现在脑子清楚很多了,事务针对service层
JDBC的事务大家应该有印象,其实就是关闭语句的自动提交,setAutoCommit(false);这应该是事务的底层了
Spring 定义了如下七中传播行为,这里以A、B个业务之间如何传播事务为例:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED :required ,需要事务。如果A有事务存在,B就在同一个事务中否则新建事务
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:supports ,支持事务。如果A有事务存在,B就在同一个事务中否则非事务运行
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:mandatory ,强制事务。A没事务就抛出异常
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW :requires_new,需要新建事务。无论原本A有没有事务,B都创建新事务运行
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED :not_supported ,不支持。A有本来没有事务B都以非事务运行
PROPAGATION_NEVER :never,从不。如果A有事务,B将抛异常;如果A没有事务,B将以非事务执行。
PROPAGATION_NESTED :nested ,嵌套。有点复杂,我不明白
基于Aop的两种方式都使用事务管理,分别是声明式和注解式
//都先将数据源交给事务管理器
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>
一、声明式
//配置事务方法和事务传播级别,还可以配置数据库隔离级别,但建议看深入的文章
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 传播行为 -->
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="get*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="query*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
//用Aop处理请求
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice"
pointcut="execution(* com.taotao.service.*.*(..))" />
</aop:config>
二、注解式
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
在类(代表所有方法都加上)或方法上单独加 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)