Spring boot 的@Value只能用于bean中,在bean的实例化时,会给@Value的属性赋值:如下面的例子:
@SpringBootApplication @Slf4j public class DemoApplication { @Value(value = "${server.port}") private String config; public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
下面的类显示了bean的实例化方法:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // 实例化方法 Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
bean的具体实例过过程,就不在这里说了,具体可以看前面的文章Spring boot IOC源码解析.
这个方法中:org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata#inject 会遍历bean中所有的成员:
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
这个方法会读取出要取值的Vaule:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
@Nullable public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException { InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor); try { Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this); if (shortcut != null) { return shortcut; } Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType(); Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor); // 取出server.port if (value != null) { if (value instanceof String) { String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);//解析出具体的value BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ? getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null); value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd); } TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter()); try { return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor()); } catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) { // A custom TypeConverter which does not support TypeDescriptor resolution... return (descriptor.getField() != null ? converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) : converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter())); } } Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter); if (multipleBeans != null) { return multipleBeans; } Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor); if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { if (isRequired(descriptor)) { raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor); } return null; } String autowiredBeanName; Object instanceCandidate; if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) { autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor); if (autowiredBeanName == null) { if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) { return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans); } else { // In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case: // possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans // (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans). return null; } } instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName); } else { // We have exactly one match. Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next(); autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey(); instanceCandidate = entry.getValue(); } if (autowiredBeanNames != null) { autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName); } if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) { instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this); } Object result = instanceCandidate; if (result instanceof NullBean) { if (isRequired(descriptor)) { raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor); } result = null; } if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) { throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass()); } return result; } finally { ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint); } }
最终解析的代码如下:org.springframework.core.env.PropertySourcesPropertyResolver#getProperty(java.lang.String, java.lang.Class<T>, boolean)
@Nullable protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) { if (this.propertySources != null) { for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" + propertySource.getName() + "'"); } Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key); if (value != null) { if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) { value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value); } logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value); return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType); } } } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source"); } return null; }
propertySource的内容,可以看上篇博客,里面记录了spring boot是如何读取配置文件信息的。
详细的调用堆栈信息如下:
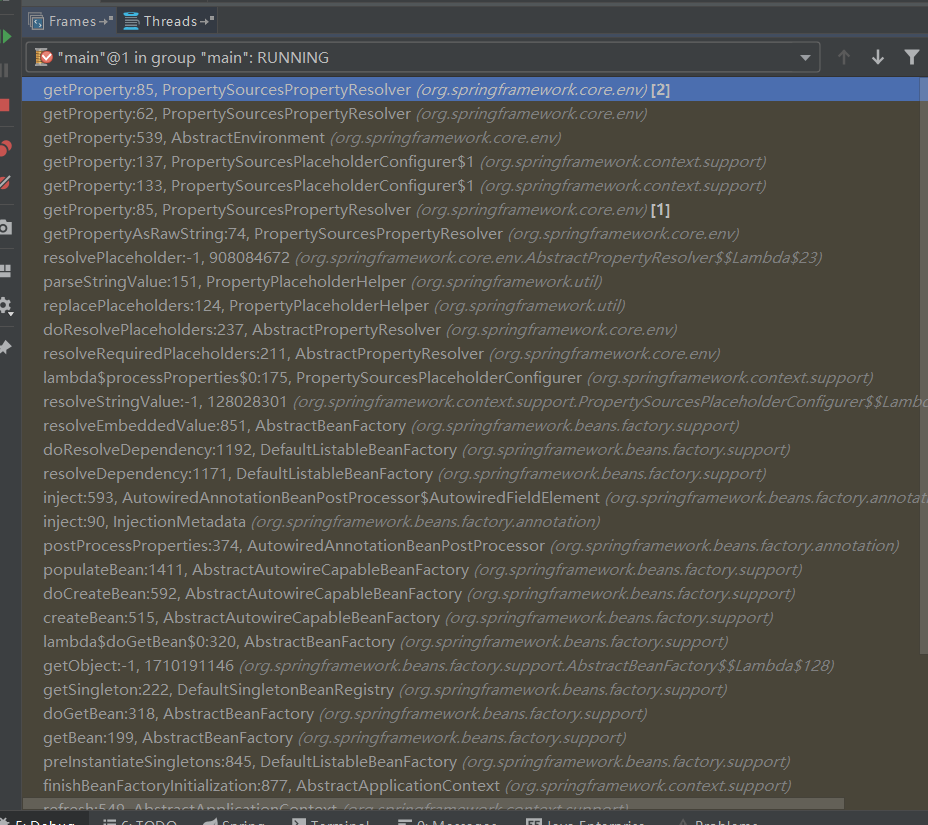
这里还有一个顺序的问题:
比如:有三个配置文件:
系统加载出来是这个样子的
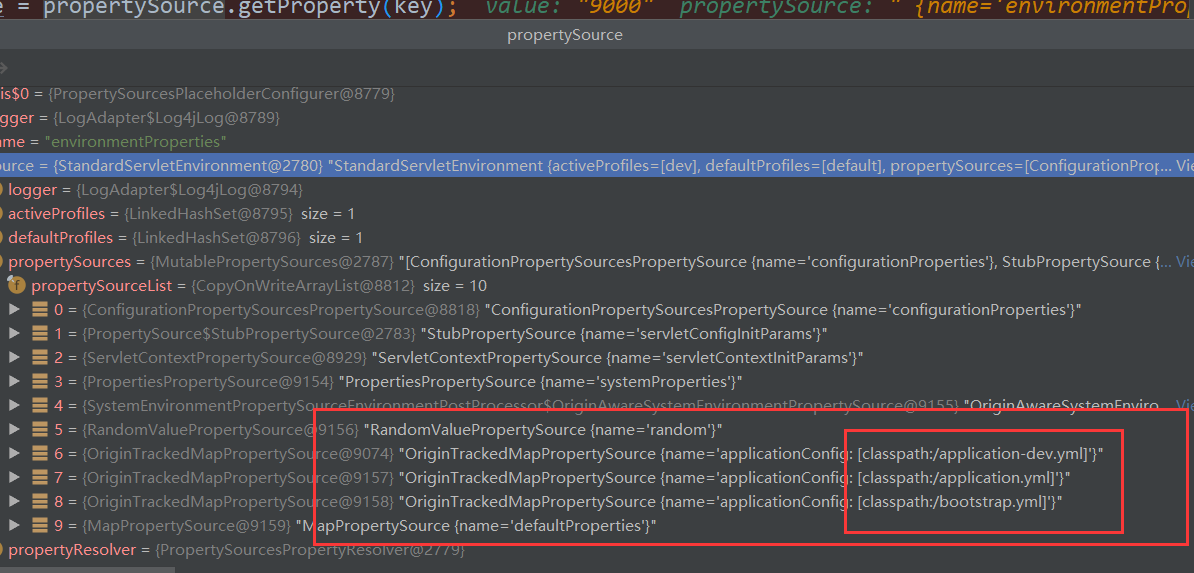
每个配置文件,我都配置了:
server:
port: ****
那它会最终读取哪个配置文件的端口呢?
答案就是加上面的顺序,找到了第一个就返回了,后面的不管了。
也就是说dev的优先,(加了profile的) 然后是不加的,最后是bootstrap的。