博客搬家:初版发布于 2014/07/04
定义:
所谓链表就是指在某节点存储数据的过程中还要有一个属性用来指向下一个链表节点,这样的数据存储方式叫做链表
链表优缺点:
优点:易于存储和删除
缺点:查询起来较麻烦
下面我们用java来实现如下链表结构:
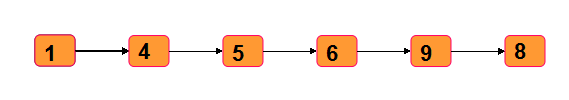
首先定义节点类:
package LinkTest;
/**
* 链表节点类
* @author admin
*
*/
public class Node {
private int value;//存储数据
private Node next;//下一个节点
/**
* 定义构造器
* @param vlaue
* @param value
*/
public Node(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
然后定义一个链表类:
* 注意:遍历链表定义了两个方法,一个是普通方法,一个是递归方法,都可以遍历出来
package LinkTest;
/**
* 链表
* @author admin
*
*/
public class Link {
private Node current;
private Node root;
public void insert(int vlaue){
Node newNode=new Node(vlaue);
if(this.current==null){
this.current=newNode;
this.root=this.current;
}else{
this.current.setNext(newNode);
this.current=this.current.getNext();
}
}
//普通遍历
public void getList(){
this.current=this.root;
while(this.current!=null){
System.out.print(this.current.getValue());
this.current=this.current.getNext();
if(this.current!=null){
System.out.print("------->");
}
}
}
//递归遍历
public void getList2(){
DG(this.root);
}
//递归方法
public void DG(Node node){
System.out.print(node.getValue()+"----->");
if(node.getNext()!=null){
DG(node.getNext());
}else{
return;
}
}
}
测试类:
package LinkTest;
/**
* 测试类
* @author admin
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Link l=new Link();
l.insert(1);
l.insert(4);
l.insert(5);
l.insert(6);
l.insert(9);
l.insert(8);
l.getList();
}
}
测试类运行结果:
1------->4------->5------->6------->9------->8
这样我们就用java实现了一个简单的链表结构。