
上面这样的数据,想要的结果是:如果matchResult为2的话,代表是黑名单。同一个softId,version,pcInfoId的代表是同一个软件,需要去重;同时,如果相同软件里面只要有一个matchResult为2的话,那么同一个softId,version,pcInfoId的数据全部不要。
思路:
1、先找出matchResult为2的softId,version,pcInfoId
select softId,version,pcInfoId from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic where matchResult=2 and softId=7
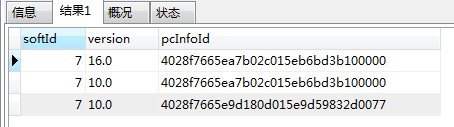
2、考虑查出来的数据的 softId,version,pcInfoId 不在这个子查询结果集里面:(softId,version,pcInfoId) not in(select softId,version,pcInfoId from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic where matchResult=2 and softId=7)
注意此处(softId,version,pcInfoId)需要加括号,否则会报错。
3、和其他条件拼接找出matchResult为1,且不在上面子查询结果集里面的数据
select * from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic
where softId=7 and matchResult=1
and (softId,version,pcInfoId) not in(select softId,version,pcInfoId from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic where matchResult=2 and softId=7)

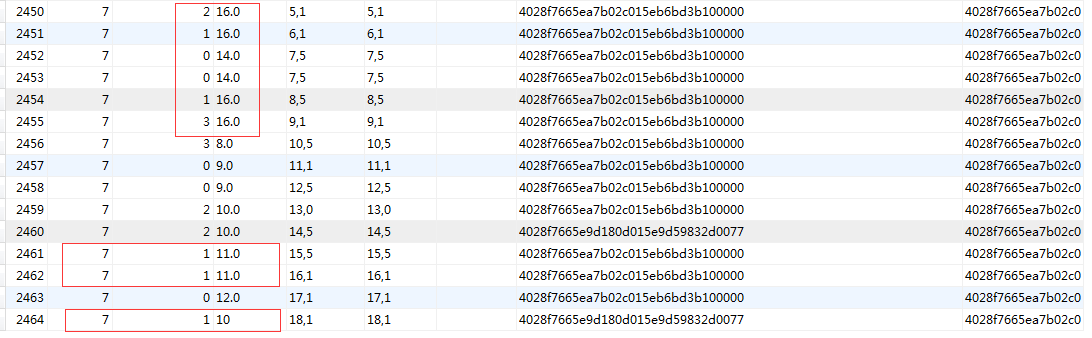
在这里发现一个问题,就是2460和2464应该算一个软件,但是有2,应该去除,但是为什么没去除呢?这里就是造数据的时候粗心导致:version:10和10.0是不一样的,数据改为如下即正常了。这样也启发我们:当查询有误的时候,一定要先保证数据是正确的。这样才好去排查问题。

select * from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic
where (softId,version,pcInfoId) not in(select softId,version,pcInfoId from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic where matchResult=2 and softId=7)
and softId=7
and matchResult=1

这样结果就正确了。
4、最后需要去重下
select count(distinct softId,version,pcInfoId) from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic
where (softId,version,pcInfoId) not in(select softId,version,pcInfoId from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic where matchResult=2 and softId=7)
and softId=7
and matchResult=1
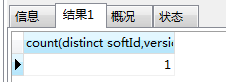
结果就为1。
//新的正版数逻辑
@Override
public Integer queryGenuineNumNew(Integer matchResult, Integer genuine, Integer softId) {
return Integer.parseInt(getSession().createSQLQuery(" select count(distinct softId,version,pcInfoId) from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic "
+ "where (softId,version,pcInfoId) not in(select softId,version,pcInfoId from vrv_paw_genuineManagementStatic where matchResult=:matchResult and softId=:softId)"
+ "and matchResult=:genuine "
+ "and softId=:softId ")
.setParameter("matchResult", matchResult)
.setParameter("genuine", genuine)
.setParameter("softId", softId)
.list().get(0).toString());
}
一、mysql查询的五种子句:
where(条件查询)、having(筛选)、group by(分组)、order by(排序)、limit(限制结果数)
1、where常用运算符:
(1)比较运算符:
> , < ,= , != (< >),>= , <=
in(v1,v2..vn)
between v1 and v2 在v1至v2之间(包含v1,v2)
(2) 逻辑运算符:
not ( ! ) 逻辑非
or ( || ) 逻辑或
and ( && ) 逻辑与
实例:
where price>=3000 and price <= 5000 or price >=500 and price <=1000
取500-1000或者3000-5000的值
where price not between 3000 and 5000
不在3000与5000之间的值
(3)模糊查询
like 像
通配符:
% 任意字符
_ 单个字符
where goods_name like '诺基亚%'
where goods_name like '诺基亚N__'
2、group by 分组
一般情况下group需与统计函数(聚合函数)一起使用才有意义
如:select goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,max(shop_price) from goods group by cat_id;
这里取出来的结果中的good_name是错误的!因为shop_price使用了max函数,那么它是取最大的,而语句中使用了group by 分组,那么goods_name并没有使用聚合函数,它只是cat_id下的第一个商品,并不会因为shop_price改变而改变
mysql中的五种统计函数:
(1)max:求最大值
select max(goods_price) from goods
这里会取出最大的价格的值,只有值
#查询每个栏目下价格最高的
select cat_id,max(goods_price) from goos group by cat_id;(根据cat_id分组取cat_id下价格最高的)
#查出价格最高的商品编号
select goods_id,max(goods_price) from goods group by goods_id;
(2)min:求最小值
(3)sum:求总数和
#求商品库存总和
select sum(goods_number) from goods;
(4)avg:求平均值
#求每个栏目的商品平均价格
select cat_id,avg(goods_price) from goods group by cat_id;
(5)count:求总行数
#求每个栏目下商品种类
select cat_id,count(*) from goods group by cat_id;
###要把每个字段名当成变量来理解,它可以进行运算###(字段可当变量进行计算)
例:查询本店每个商品价格比市场价低多少;
select goods_id,goods_name,goods_price-market_price from goods;
查询每个栏目下面积压的货款
select cat_id,sum(goods_price*goods_number) from goods group by cat_id;
###可以用as来给计算结果取个别名###
select cat_id,sum(goods_price * goods_number) as hk from goods group by cat_id
不仅列名可以取别名,表单也可以取别名
3、having 与where 的异同点(where对表中的列,having对结果中的列)
having与where类似,可以筛选数据,where后的表达式怎么写,having后就怎么写
where针对表中的列发挥作用,查询数据
having对查询结果中的列发挥作用,筛选数据
#查询本店商品价格比市场价低多少钱,输出低200元以上的商品
select goods_id,good_name,market_price - shop_price as s from goods having s>200 ;
//这里不能用where因为s是查询结果,而where只能对表中的字段名筛选
如果用where的话则是:
select goods_id,goods_name from goods where market_price - shop_price > 200;(注意这种转换有助于更好的理解)
#同时使用where与having
select cat_id,goods_name,market_price - shop_price as s from goods where cat_id = 3 having s > 200;
#查询积压货款超过2万元的栏目,以及该栏目积压的货款
select cat_id,sum(shop_price * goods_number) as t from goods group by cat_id having s > 20000
#查询两门及两门以上科目不及格的学生的平均分
思路:
#先计算所有学生的平均分
select name,avg(score) as pj from stu group by name;
#查出所有学生的挂科情况
select name,score<60 from stu;
#这里score<60是判断语句,所以结果为真或假,mysql中真为1假为0
#查出两门及两门以上不及格的学生
select name,sum(score<60) as gk from stu group by name having gk > 1;
#综合结果
select name,sum(score<60) as gk,avg(score) as pj from stu group by name having gk >1;
4、order by
(1) order by price //默认升序排列
(2)order by price desc //降序排列
(3)order by price asc //升序排列,与默认一样
(4)order by rand() //随机排列,效率不高
#按栏目号升序排列,每个栏目下的商品价格降序排列
select * from goods where cat_id !=2 order by cat_id,price desc;
5、limit
limit [offset,] N
offset 偏移量,可选,不写则相当于limit 0,N
N 取出条目
#取价格第4-6高的商品
select good_id,goods_name,goods_price from goods order by good_price desc limit 3,3;
###查询每个栏目下最贵的商品
思路:
#先对每个栏目下的商品价格排序
select cat_id,goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from goods order by cat_id,shop_price desc;
#上面的查询结果中每个栏目的第一行的商品就是最贵的商品
#把上面的查询结果理解为一个临时表[存在于内存中]【子查询】
#再从临时表中选出每个栏目最贵的商品
select * from (select goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price from goods order by cat_id,shop_price desc) as t group by cat_id;
#这里使用group by cat_id是因为临时表中每个栏目的第一个商品就是最贵的商品,而group by前面没有使用聚合函数,所以默认就取每个分组的第一行数据,这里以cat_id分组
良好的理解模型:
1、where后面的表达式,把表达式放在每一行中,看是否成立
2、字段(列),理解为变量,可以进行运算(算术运算和逻辑运算)
3、 取出结果可以理解成一张临时表
二、mysql子查询:
1、where型子查询:(把内层查询结果当作外层查询的比较条件)
#不用order by 来查询最新的商品
select goods_id,goods_name from goods where goods_id = (select max(goods_id) from goods);
#取出每个栏目下最新的产品(goods_id唯一)
select cat_id,goods_id,goods_name from goods where goods_id in(select max(goods_id) from goods group by cat_id);
2、from型子查询:(把内层的查询结果供外层再次查询)
#用子查询查出挂科两门及以上的同学的平均成绩
思路:
#先查出哪些同学挂科两门以上
select name,count(*) as gk from stu where score < 60 having gk >=2;
#以上查询结果,我们只要名字就可以了,所以再取一次名字
select name from (select name,count(*) as gk from stu having gk >=2) as t;
#找出这些同学了,那么再计算他们的平均分
select name,avg(score) from stu where name in (select name from (select name,count(*) as gk from stu having gk >=2) as t) group by name;
3、exists型子查询:(把外层查询结果拿到内层,看内层的查询是否成立)
#查询哪些栏目下有商品,栏目表category,商品表goods
select cat_id,cat_name from category where exists(select * from goods where goods.cat_id = category.cat_id);
三、union的用法:
(把两次或多次的查询结果合并起来,要求查询的列数一致,推荐查询的对应的列类型一致,可以查询多张表,多次查询语句时如果列名不一样,则取第一次的列名!如果不同的语句中取出的行的每个列的值都一样,那么结果将自动会去重复,如果不想去重复则要加all来声明,即union all)
## 现有表a如下
id num
a 5
b 10
c 15
d 10
表b如下
id num
b 5
c 10
d 20
e 99
#求两个表中id相同的和
select id,sum(num) from (select * from ta union select * from tb) as tmp group by id;
//以上查询结果在本例中的确能正确输出结果,但是,如果把tb中的b的值改为10,则查询结果的b的值就是10了,因为ta中的b也是10,所以union后会被过滤掉一个重复的结果,这时就要用union all
select id,sum(num) from (select * from ta union all select * from tb) as tmp group by id;
#取第4、5栏目的商品,按栏目升序排列,每个栏目的商品价格降序排列,用union完成
select goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price from goods where cat_id=4 union select goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price from goods where cat_id=5 order by cat_id,shop_price desc;
【如果子句中有order by 需要用( ) 包起来,但是推荐在最后使用order by,即对最终合并后的结果来排序】
#取第3、4个栏目,每个栏目价格最高的前3个商品,结果按价格降序排列
(select goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price from goods where cat_id=3 order by shop_price desc limit 3) union (select goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price from goods where cat_id=4 order by shop_price desc limit 3) order by shop_price desc;
四、左连接,右连接,内连接:
现有表a有10条数据,表b有8条数据,那么表a与表b的笛尔卡积是多少?
select * from ta,tb //输出结果为8*10=80条
1、左连接
以左表为准,去右表找数据,如果没有匹配的数据,则以null补空位,所以输出结果数>=左表原数据数
语法:select n1,n2,n3 from ta left join tb on ta.n1= ta.n2 [这里on后面的表达式,不一定为=,也可以>,<等算术、逻辑运算符]
【连接完成后,可以当成一张新表来看待,运用where等查询】
#取出价格最高的五个商品,并显示商品的分类名称
select goods_id,goods_name,goods.cat_id,cat_name,shop_price from goods left join category on goods.cat_id = category.cat_id order by shop_price desc limit 5;
2、右连接
a left join b 等价于 b right join a,推荐使用左连接代替右连接
语法:select n1,n2,n3 from ta right join tb on ta.n1= ta.n2
3、内连接
查询结果是左右连接的交集,【即左右连接的结果去除null项后的并集(去除了重复项)】
mysql目前还不支持 外连接(即左右连接结果的并集,不去除null项)
语法:select n1,n2,n3 from ta inner join tb on ta.n1= ta.n2
#########
例:现有表a
name hot
a 12
b 10
c 15
表b:
name hot
d 12
e 10
f 10
g 8
(1)表a左连接表b,查询hot相同的数据
select a.*,b.* from a left join b on a.hot = b.hot
查询结果:
name hot name hot
a 12 d 12
b 10 e 10
b 10 f 10
c 15 null null
从上面可以看出,查询结果表a的列都存在,表b的数据只显示符合条件的项目
(2)再如表b左连接表a,查询hot相同的数据
select a.*,b.* from b left join a on a.hot = b.hot
查询结果为:
name hot name hot
d 12 a 12
e 10 b 10
f 10 b 10
g 8 null null
(3)再如表a右连接表b,查询hot相同的数据
select a.*,b.* from a right join b on a.hot = b.hot
查询结果和上面的b left join a一样
###练习,查询商品的名称,所属分类,所属品牌
select goods_id,goods_name,goods.cat_id,goods.brand_id,category.cat_name,brand.brand_name from goods left join category on goods.cat_id = category.cat_id left join brand on goods.brand_id = brand.brand_id limit 5;
理解:每一次连接之后的结果都可以看作是一张新表
###练习,现创建如下表
create table m(
id int,
zid int,
kid int,
res varchar(10),
mtime date
) charset utf8;
insert into m values
(1,1,2,'2:0','2006-05-21'),
(2,3,2,'2:1','2006-06-21'),
(3,1,3,'2:2','2006-06-11'),
(4,2,1,'2:4','2006-07-01');
create table t
(tid int,tname varchar(10)) charset utf8;
insert into t values
(1,'申花'),
(2,'红牛'),
(3,'火箭');
要求按下面样式打印2006-0601至2006-07-01期间的比赛结果
样式:
火箭 2:0 红牛 2006-06-11
查询语句为:
select zid,t1.tname as t1name,res,kid,t2.tname as t2name,mtime from m left join t as t1 on m.zid = t1.tid
left join t as t2 on m.kid = t2.tid where mtime between '2006-06-01' and '2006-07-01';
总结:可以对同一张表连接多次,以分别取多次数据