Mike has a frog and a flower. His frog is named Xaniar and his flower is named Abol. Initially(at time 0), height of Xaniar is h1 and height of Abol is h2. Each second, Mike waters Abol and Xaniar.

So, if height of Xaniar is h1 and height of Abol is h2, after one second height of Xaniar will become  and height of Abol will become
and height of Abol will become  where x1, y1, x2 and y2 are some integer numbers and
where x1, y1, x2 and y2 are some integer numbers and  denotes the remainder of amodulo b.
denotes the remainder of amodulo b.
Mike is a competitive programmer fan. He wants to know the minimum time it takes until height of Xania is a1 and height of Abol is a2.
Mike has asked you for your help. Calculate the minimum time or say it will never happen.
The first line of input contains integer m (2 ≤ m ≤ 106).
The second line of input contains integers h1 and a1 (0 ≤ h1, a1 < m).
The third line of input contains integers x1 and y1 (0 ≤ x1, y1 < m).
The fourth line of input contains integers h2 and a2 (0 ≤ h2, a2 < m).
The fifth line of input contains integers x2 and y2 (0 ≤ x2, y2 < m).
It is guaranteed that h1 ≠ a1 and h2 ≠ a2.
Print the minimum number of seconds until Xaniar reaches height a1 and Abol reaches height a2 or print -1 otherwise.
5
4 2
1 1
0 1
2 3
3
1023
1 2
1 0
1 2
1 1
-1
题解:
In this editorial, consider p = m, a = h1, a′ = a1, b = h2 and b′ = a2.
First of all, find the number of seconds it takes until height of Xaniar becomes a′ (starting from a) and call it q. Please note that q ≤ pand if we don't reach a′ after p seconds, then answer is - 1.
If after q seconds also height of Abol will become equal to b′ then answer if q.
Otherwise, find the height of Abdol after q seconds and call it e.
Then find the number of seconds it takes until height of Xaniar becomes a′ (starting from a′) and call it c. Please note that c ≤ p and if we don't reach a′ after p seconds, then answer is - 1.
if g(x) = Xx + Y, then find f(x) = g(g(...(g(x)))) (c times). It is really easy:
c = 1, d = 0
for i = 1 to c
c = (cX) % p
d = (dX + Y) % pThen,
f(x)
return (cx + d) % p
Actually, if height of Abol is x then, after c seconds it will be f(x).
Then, starting from e, find the minimum number of steps of performing e = f(e) it takes to reach b′ and call it o. Please note thato ≤ p and if we don't reach b′ after p seconds, then answer is - 1.
Then answer is x + c × o.
Time Complexity: 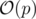

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 typedef long long ll ; 5 ll mod ; 6 ll a , a1 ; 7 ll x , y ; 8 ll b , b1 ; 9 ll _x , _y ; 10 ll A , T ; 11 ll B , _T ; 12 13 ll exgcd (ll a,ll b,ll& x,ll &y) 14 { 15 if(b==0){ 16 x=1; 17 y=0; 18 return a; 19 } 20 ll d = exgcd ( b , a % b , x , y ) ; 21 ll tmp = x ; 22 x = y ; 23 y = tmp - a / b * y ; 24 return d; 25 } 26 //用扩展欧几里得算法解线性方程ax+by=c; 27 void __exgcd(ll a , ll b , ll c ) 28 { 29 ll x , y ; 30 ll d = exgcd ( a , b , x , y ) ; 31 if(c % d) { 32 puts ("-1") ; 33 return ; 34 } 35 36 ll k = c / d ; 37 x *= k ; y *= k ;//求的只是其中一个解 38 if (d < 0) d = -d ; 39 ll t1 = T / d , t2 = _T / d ; 40 // printf ("t1 = %I64d , t2 = %I64d " , t1 , t2 ) ; 41 //printf ("x = %I64d , y = %I64d " , x , y ) ; 42 if (x < 0 || y < 0) { 43 while (x < 0 || y < 0) { 44 x += t1 ; 45 y += t2 ; 46 } 47 } 48 else { 49 while (x >= 0 && y >= 0) { 50 x -= t1 ; 51 y -= t2 ; 52 } 53 x += t1 ; 54 y += t2 ; 55 } 56 //printf ("x = %I64d , y = %I64d " , x , y ) ; 57 printf ("%I64d " , A + T * y) ; 58 } 59 60 bool workA () 61 { 62 ll cnt = 0 ; 63 ll c = a ; 64 while (1) { 65 cnt ++ ; 66 c = (c * x + y) % mod ; 67 if (c == a1) { 68 A = cnt ; 69 return true ; 70 } 71 if (cnt > mod) break ; 72 } 73 return false ; 74 } 75 76 bool workB () 77 { 78 ll cnt = 0 ; 79 ll c = b ; 80 while (1) { 81 cnt ++ ; 82 c = (c * _x + _y) % mod ; 83 if (c == b1) { 84 B = cnt ; 85 return true ; 86 } 87 if (cnt > mod) break ; 88 } 89 return false ; 90 } 91 92 bool workT () 93 { 94 T = 0 ; 95 ll cnt = 0 ; 96 ll c = a1 ; 97 while (1) { 98 cnt ++ ; 99 c = (c * x + y) % mod ; 100 if (c == a1) { 101 T = cnt ; 102 return true ; 103 } 104 if (cnt > mod) break ; 105 } 106 return false ; 107 } 108 109 bool work_T () 110 { 111 _T = 0 ; 112 ll cnt = 0 ; 113 ll c = b1 ; 114 while (1) { 115 cnt ++ ; 116 c = (c * _x + _y) % mod ; 117 if (c == b1) { 118 _T = cnt ; 119 return true ; 120 } 121 if (cnt > mod) break ; 122 } 123 return false ; 124 } 125 126 int main () 127 { 128 //freopen ("a.txt" , "r" , stdin ) ; 129 while (~ scanf ("%I64d" , &mod)) { 130 scanf ("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d" , &a , &a1 , &x , &y) ; 131 scanf ("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d" , &b , &b1 , &_x , &_y) ; 132 if (!workA ()) puts ("-1") ; 133 else { 134 if (!workB ()) puts ("-1") ; 135 else if (A == B) printf ("%I64d " , A) ; 136 else { 137 workT () ; 138 work_T () ; 139 if (T == 0 || _T == 0) { 140 if (T == 0 && _T == 0) puts ("-1") ; 141 else if (T == 0 ) { 142 if (A - B >= 0 && (A - B) % _T == 0) printf ("%I64d " , A) ; 143 else puts ("-1") ; 144 } 145 else if (_T == 0) { 146 if (B - A >= 0 && (B - A) % T == 0) printf ("%I64d " , B) ; 147 else puts ("-1") ; 148 } 149 } else { 150 ll a = _T , b = -T , c = A - B ; 151 __exgcd (a , b , c) ; 152 } 153 } 154 } 155 } 156 return 0 ; 157 }
题解:
一般情况:我们能用暴力求出a-->a1所需时间A , b-->b1所需时间B,a1-->a1时间Ta , b1-->b1时间Tb;
注意:A , B , Ta , Tb 都会在 “mod 时间”内完成,若没在这段时间内找到,则不存在。
所以为了达到目标显然需要满足一下等式:A + x * Ta = B + y * Tb ---- ①---> A - B = - Ta * x + Tb * y ----②;
那么问题就转变成了求该方程是否有整数解(这道题有整数解,就必有正整数解)。
根据扩展欧几里得算法:
c = a * x + b * y ;
只要满足gcd (a , b) | c (及a,b的gcd为c的约数)时,该方程必有解,我们令 d = gcd (a , b) ;
则存在解时:(下面的_x , _y都假定为执行完 exgcd(a , b , x , y)后产生的 _x , _y)
其中一组特解:x' = _x * c / d ;(c = A - B)
y' = _y * c / d ;
递推式:
x = x' + Ta / fabs (d) * k ;( k 为 参数)
y = y' + Tb / fabs (d) * k ;
然后我们只要暴力求出可行解(x , y)中与0最接近的即可 , A + x * Ta 及为答案。
暴力枚举:(简洁,大神的)

1 #include <cstring> 2 #include <map> 3 #include <deque> 4 #include <queue> 5 #include <stack> 6 #include <sstream> 7 #include <iostream> 8 #include <cstdio> 9 #include <cmath> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <ctime> 12 #include <algorithm> 13 #include <vector> 14 #include <set> 15 #include <list> 16 #include <climits> 17 #include <cctype> 18 #include <bitset> 19 #include <iostream> 20 #include <complex> 21 22 using namespace std; 23 24 typedef stringstream ss; 25 typedef long long ll; 26 typedef pair<ll, ll> ii; 27 typedef vector<vector<ii> > vii; 28 typedef vector<string> vs; 29 typedef vector<ll> vi; 30 typedef vector<double> vd; 31 typedef long double ld; 32 typedef vector<vector<ll> > matrix; 33 typedef complex<double> point; 34 35 #define all(v) v.begin(), v.end() 36 #define rall(v) v.rbegin(), v.rend() 37 #define sz(v) ((ll)v.size()) 38 #define clr(v, d) memset(v, d, sizeof(v)) 39 #define polar(r,t) ((r)*exp(point(0,(t)))) 40 #define length(a) hypot((a).real(),(a).imag()) 41 #define angle(a) atan2((a).imag() , (a).real()) 42 #define vec(a,b) ((b)-(a)) 43 #define dot(a,b) ((conj(a)*(b)).real()) 44 #define cross(a,b) ((conj(a)*(b)).imag()) 45 #define lengthSqr(a) dot(a,a) 46 #define rotate(v,t) ((v)*exp(point(0,t))) 47 #define rotateAbout(v,t,a) (rotate(vec(a,v),t)+(a)) 48 #define reflect(v,m) (conj((v)/(m))*m) 49 #define dist(a,b) (sqrt(pow((a).real()-(b).real(),2.0)+pow((a).imag()-(b).imag(),2.0))) 50 #define normalize(a) ((a)/length(a)) 51 52 int dx[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 }; 53 int dy[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 }; 54 double PI = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795; 55 56 const ll oo = (ll) 1e9 + 1; 57 const double eps = 1e-9; 58 const ll mod = 1000000007; 59 60 int main() { 61 //freopen("a.txt", "r", stdin); 62 ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); 63 ll m, h1, a1, x1, y1, h2, a2, x2, y2; 64 cin >> m >> h1 >> a1 >> x1 >> y1 >> h2 >> a2 >> x2 >> y2; 65 ll idx1 = -1, idx2 = -1; 66 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 67 h1 = (x1 * h1 + y1) % m; 68 if (h1 == a1) { 69 idx1 = i; 70 break; 71 } 72 } 73 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 74 h2 = (x2 * h2 + y2) % m; 75 if (h2 == a2) { 76 idx2 = i; 77 break; 78 } 79 } 80 81 if (idx1 == -1 || idx2 == -1) { 82 cout << "-1" << endl; 83 return 0; 84 } 85 86 ll step1, step2; 87 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 88 h1 = (x1 * h1 + y1) % m; 89 if (h1 == a1) { 90 step1 = i; 91 break; 92 } 93 } 94 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 95 h2 = (x2 * h2 + y2) % m; 96 if (h2 == a2) { 97 step2 = i; 98 break; 99 } 100 } 101 //printf ("idx1 = %I64d , idx2 = %I64d , step1 = %I64d, step2 = %I64d " , idx1 , idx2 , step1 , step2 ) ; 102 for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * m; i++) { 103 if (idx1 == idx2) { 104 cout << idx1 << endl; 105 return 0; 106 } 107 if (idx1 > idx2) { 108 idx2 += step2; 109 } else { 110 idx1 += step1; 111 } 112 } 113 cout << "-1" << endl; 114 return 0; 115 }
