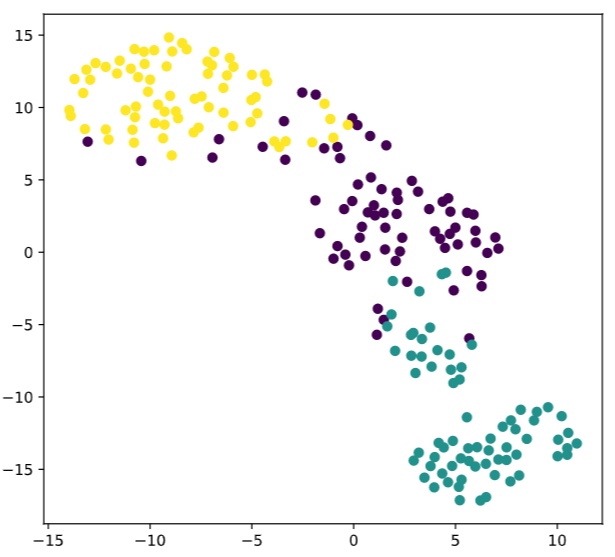
1.t-SNE
- t-分布领域嵌入算法
- 虽然主打非线性高维数据降维,但是很少用,因为
- 比较适合应用于可视化,测试模型的效果
- 保证在低维上数据的分布与原始特征空间分布的相似性高
因此用来查看分类器的效果更加
1.1 复现demo
# Import TSNE
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
# Create a TSNE instance: model
model = TSNE(learning_rate=200)
# Apply fit_transform to samples: tsne_features
tsne_features = model.fit_transform(samples)
# Select the 0th feature: xs
xs = tsne_features[:,0]
# Select the 1st feature: ys
ys = tsne_features[:,1]
# Scatter plot, coloring by variety_numbers
plt.scatter(xs,ys,c=variety_numbers)
plt.show()
2.PCA
主成分分析是进行特征提取,会在原有的特征的基础上产生新的特征,新特征是原有特征的线性组合,因此会达到降维的目的,但是降维不仅仅只有主成分分析一种
- 当特征变量很多的时候,变量之间往往存在多重共线性。
- 主成分分析,用于高维数据降维,提取数据的主要特征分量
- PCA能“一箭双雕”的地方在于
- 既可以选择具有代表性的特征,
- 每个特征之间线性无关
- 总结一下就是原始特征空间的最佳线性组合
有一个非常易懂的栗子知乎
2.1 数学推理
可以参考【机器学习】降维——PCA(非常详细)
Making sense of principal component analysis, eigenvectors & eigenvalues
2.2栗子
sklearn里面有直接写好的方法可以直接使用
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# Perform the necessary imports
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import pearsonr
# Assign the 0th column of grains: width
width = grains[:,0]
# Assign the 1st column of grains: length
length = grains[:,1]
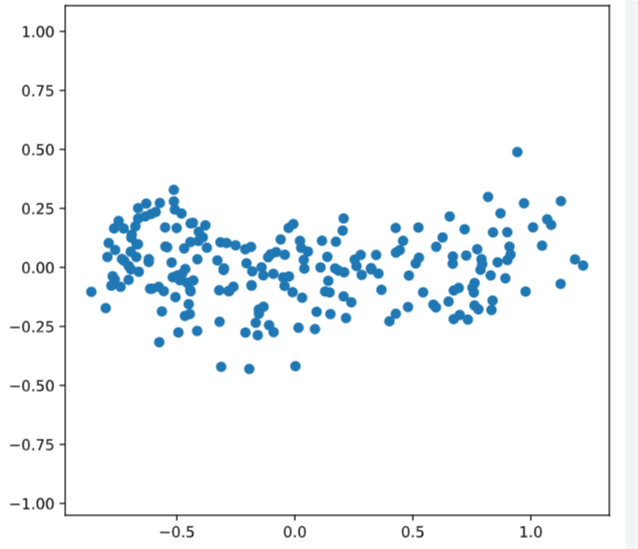
# Scatter plot width vs length
plt.scatter(width, length)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.show()
# Calculate the Pearson correlation
correlation, pvalue = pearsonr(width, length)
# Display the correlation
print(correlation)

# Import PCA
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# Create PCA instance: model
model = PCA()
# Apply the fit_transform method of model to grains: pca_features
pca_features = model.fit_transform(grains)
# Assign 0th column of pca_features: xs
xs = pca_features[:,0]
# Assign 1st column of pca_features: ys
ys = pca_features[:,1]
# Scatter plot xs vs ys
plt.scatter(xs, ys)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.show()
# Calculate the Pearson correlation of xs and ys
correlation, pvalue = pearsonr(xs, ys)
# Display the correlation
print(correlation)
<script.py> output:
2.5478751053409354e-17
2.3intrinsic dimension
主成分的固有维度,其实就是提取主成分,得到最佳线性组合
2.3.1 提取主成分
.n_components_
提取主成分一般占总的80%以上,不过具体问题还得具体分析
# Perform the necessary imports
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create scaler: scaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
# Create a PCA instance: pca
pca = PCA()
# Create pipeline: pipeline
pipeline = make_pipeline(scaler,pca)
# Fit the pipeline to 'samples'
pipeline.fit(samples)
# Plot the explained variances
features =range( pca.n_components_)
plt.bar(features, pca.explained_variance_)
plt.xlabel('PCA feature')
plt.ylabel('variance')
plt.xticks(features)
plt.show()

2.3.2Dimension reduction with PCA
主成分降维
给一个文本特征提取的小例子
虽然我还不知道这个是啥,以后学完补充啊
# Import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
# Create a TfidfVectorizer: tfidf
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer()
# Apply fit_transform to document: csr_mat
csr_mat = tfidf.fit_transform(documents)
# Print result of toarray() method
print(csr_mat.toarray())
# Get the words: words
words = tfidf.get_feature_names()
# Print words
print(words)
['cats say meow', 'dogs say woof', 'dogs chase cats']
<script.py> output:
[[0.51785612 0. 0. 0.68091856 0.51785612 0. ]
[0. 0. 0.51785612 0. 0.51785612 0.68091856]
[0.51785612 0.68091856 0.51785612 0. 0. 0. ]]
['cats', 'chase', 'dogs', 'meow', 'say', 'woof']
<script.py> output:
[[0.51785612 0. 0. 0.68091856 0.51785612 0. ]
[0. 0. 0.51785612 0. 0.51785612 0.68091856]
[0.51785612 0.68091856 0.51785612 0. 0. 0. ]]
['cats', 'chase', 'dogs', 'meow', 'say', 'woof']