1、运行代码
class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { //super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); //super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { public static void main(String args[]) { Child c = new Child(); } } TestInherits.java
运行结果:

总结:Java构造函数的调用是按照顺序来的,如果不先构造父类,又何来子类,子类是继承父类的,首先得知道父类里面有什么,才能继承,其次,父类只有自己的东西,子类的元素父类是不知道的,所以,先构造子类是不和语法的。
2.运行代码
1 package Test; 2 public class ExplorationJDKSource { 3 4 /** 5 * @param args 6 */ 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 System.out.println(new A()); 9 } 10 11 } 12 13 class A{} 14 15 ExplorationJDKSource.java
运行结果:
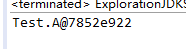
总结:其实类可以做到输出,是因为我们的写每一个类,都是默认继承Object类!所以Object类里的方法名称都得到了继承!而System.out实际上是Object的一个子类PrintStream,而这个子类内部定义了一个public static void println(String ...);的方法传进来的大类参数就会调用父类的toString方法,改成String类型并输出。而该方法如下: public String toString() { return getClass().getName() +"@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()); } hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现: public native int hashCode();所以出现上述结果。
3.运行代码
1 package Test; 2 public class TestInstanceof 3 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) 5 { 6 //声明hello时使用Object类,则hello的编译类型是Object,Object是所有类的父类 7 //但hello变量的实际类型是String 8 Object hello = "Hello"; 9 //String是Object类的子类,所以返回true。 10 System.out.println("字符串是否是Object类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Object)); 11 //返回true。 12 System.out.println("字符串是否是String类的实例:" + (hello instanceof String)); 13 //返回false。 14 System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Math)); 15 //String实现了Comparable接口,所以返回true。 16 System.out.println("字符串是否是Comparable接口的实例:" + (hello instanceof Comparable)); 17 String a = "Hello"; 18 //String类既不是Math类,也不是Math类的父类,所以下面代码编译无法通过 19 //System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (a instanceof Math)); 20 } 21 }
运行结果:

4.运行代码
1 public class ParentChildTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Parent parent=new Parent(); 4 parent.printValue();//Parent.printValue(),myValue=100 5 Child child=new Child(); 6 child.printValue();//Child.printValue(),myValue=200 7 8 parent=child; 9 parent.printValue();//Child.printValue(),myValue=200 10 11 parent.myValue++; 12 parent.printValue();//Child.printValue(),myValue=200 13 14 ((Child)parent).myValue++; 15 parent.printValue();//Child.printValue(),myValue=201 16 17 } 18 } 19 20 class Parent{ 21 public int myValue=100; 22 public void printValue() { 23 System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); 24 } 25 } 26 class Child extends Parent{ 27 public int myValue=200; 28 public void printValue() { 29 System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); 30 } 31 } 32 33 ParentChildTest.java
运行结果:

结论:
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。这个特性实际上就是面向对象“多态”特性的具体表现。如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的!
5.代码验证
1 package second; 2 3 class Parent 4 5 { 6 7 public int value=100; 8 9 public void Introduce() 10 { 11 12 System.out.println("I'm father"); 13 14 } 15 16 17 } 18 19 class Son extends Parent 20 { 21 22 public int value=101; 23 24 public void Introduce() 25 { 26 27 System.out.println("I'm son"); 28 29 } 30 31 } 32 33 34 class Daughter extends Parent 35 { 36 37 public int value=102; 38 public void Introduce() 39 { 40 41 System.out.println("I'm daughter"); 42 43 } 44 45 } 46 47 public class TestPolymorphism 48 { 49 50 51 public static void main(String args[]) 52 { 53 54 Parent p=new Parent(); 55 56 p.Introduce(); 57 58 System.out.println(p.value); 59 60 p=new Son(); 61 62 p.Introduce(); 63 64 System.out.println(p.value); 65 66 p=new Daughter(); 67 68 p.Introduce(); 69 70 System.out.println(p.value); 71 72 73 } 74 75 76 }
运行结果:
