一.json模块
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于人阅读和编写。


JSON函数:
使用JSON之前必须导入json库: import json

json.dumps 用于将 Python 对象编码成 JSON 字符串
例子:
import json data={'a':1,'2':1,'c':3} j=json.dumps(data) #将一个python字典转换为json对象 print(j) #{"a": 1, "2": 1, "c": 3} 输出
这里需要注意的是字典中的键(字符串)可以用单引号也可以用双引号,而json对象只能用双引号
json.loads 用于解码 JSON 数据。该函数返回 Python 字段的数据类型
例子:
#json.loads jsondata='{"a": 1, "2": 1, "c": 3}' j=json.loads(jsondata) #将一个json对象转换为python字典 print(j) #输出 #{'a': 1, '2': 1, 'c': 3}
注意:json对象必须应‘ ’包着,如jsondata,否则会报错。
二.OS模块
os 模块提供了非常丰富的方法用来处理文件和目录。
使用os之前,首先需要导入os模块: import os
具体使用方法:
1 os.getcwd() #返回当前路径 2 os.listdir() #返回当前文件中所有文件名 3 os.makedirs('a') #创建一个文件夹 4 os.removedirs('a') #删除一个文件夹 5 os.remove() #删除文件 6 os.rename('test1.py','test11.py') #重命名 7 os.path.basename('test11.py') #返回文件名 8 os.path.abspath('test11.py') #返回绝对路径 9 path.relpath('test11.py') #返回相对路径 10 os.path.getsize('test11.py') #返回文件大小 单位字节 11 os.path.exists('test11.py') #返回文件存在与否 12 os.path.isfile('test1.py') #判断是不是文件夹 13 os.path.isabs('test/11.py') #判断是否为绝对路径
以上列举出了常用的部分,更具体的见http://www.runoob.com/python/os-file-methods.html
三.time 模块
Python 提供了一个 time 和 calendar 模块可以用于格式化日期和时间。
时间间隔是以秒为单位的浮点小数。
每个时间戳都以自从1970年1月1日午夜(历元)经过了多长时间来表示。
使用time模块之前首先导入time模块: import time
time.time()获取时间戳
1 #获取当前时间 2 d=time.time() 3 print(d) 4 #输出 1523037104.4448636(时间戳) 5 ''' 6 时间戳单位最适于做日期运算。但是1970年之前的日期就无法以此表示了。太遥远的日期也不行,UNIX和Windows只支持到2038年 7 '''
时间元组
Python函数用一个元组装起来的9组数字处理时间:

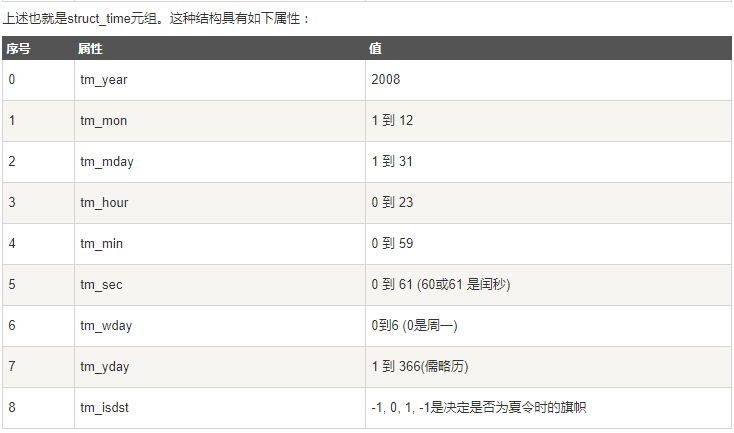
将时间戳转化为时间元组: localtime()
1 d=time.localtime(time.time()) 2 print(d) 3 ''' 4 输出: 5 time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=7, tm_hour=2, tm_min=8, tm_sec=44, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=97, tm_isdst=0) 6 7 '''
获取格式化时间:
你可以根据需求选取各种格式,但是最简单的获取可读的时间模式的函数是asctime():
将时间元组转化为可读时间:asctime()
1 localtime = time.asctime( time.localtime(time.time()) ) 2 print(localtime) 3 #输出 Sat Apr 7 09:30:14 2018
格式化日期:strftime() time.strftime(format[, t])
1 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())) 2 #输出 2018-04-07 09:38:12
print(time.strftime("%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y", time.localtime()))
#输出 Sat Apr 07 09:46:54 2018
# 将格式字符串转换为时间戳
a = "Sat Mar 28 22:24:24 2016"
print(time.mktime(time.strptime(a,"%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y")))
#输出 1459175064.0


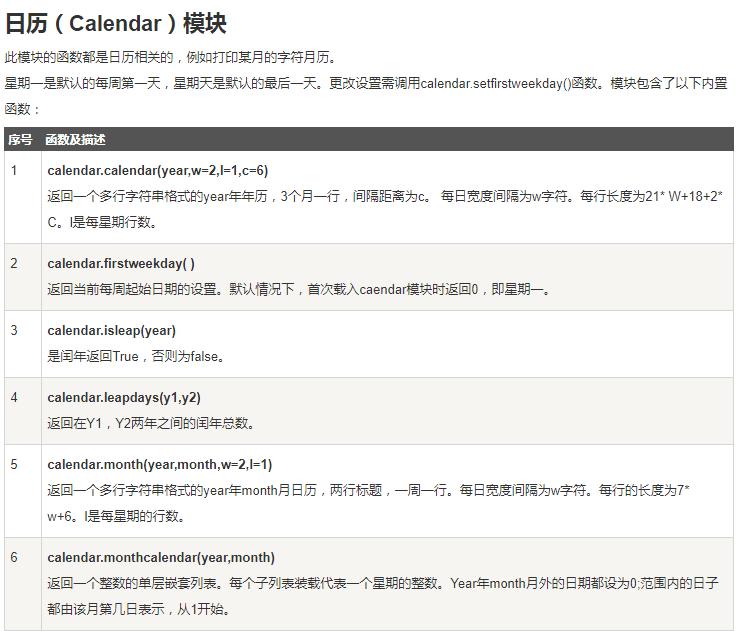
获取某月日历
Calendar模块有很广泛的方法用来处理年历和月历
用calendar首先要导入calendar包 : import calendar
1 import calendar 2 cal = calendar.month(2018, 4) 3 print("以下输出2018年4月份的日历:") 4 print (cal) 5
输出
''' 6 以下输出2018年4月份的日历: 7 April 2018 8 Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su 9 1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 11 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 12 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 13 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 14 30 15 '''
总结:




---恢复内容结束---