一,介绍SVN
SVN是Subversion的简称,是一个开放源代码的版本控制系统,相较于RCS、CVS,它采用了分支管理系统,它的设计目标就是取代CVS。互联网上很多版本控制服务已从CVS迁移到Subversion。说得简单一点SVN就是用于多个人共同开发同一个项目,共用资源的目的。
二、安装svn
[root@test188 ~]# yum install subversion
1.新建一个目录用于存储SVN目录
[root@test188 ~]# mkdir /svn
2.新建一个测试仓库
[root@test188 ~]# svnadmin create /svn/test/
[root@test188 ~]# ll /svn/test/
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 18 11:41 conf
drwxr-sr-x 6 root root 4096 Jun 18 11:17 db
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 2 Jun 18 11:17 format
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 18 11:17 hooks
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 18 11:17 locks
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 229 Jun 18 11:17 README.txt
以
3.下关于目录的说明:
hooks目录:放置hook脚步文件的目录
locks目录:用来放置subversion的db锁文件和db_logs锁文件的目录,用来追踪存取文件库的客户端
format目录:是一个文本文件,里边只放了一个整数,表示当前文件库配置的版本号
conf目录:是这个仓库配置文件(仓库用户访问账户,权限)
4.配置SVN服务的配置文件svnserver.conf:
[root@test188 conf]# vim svnserve.conf
anon-access = none
auth-access = write
password-db = passwd
authz-db = authz
realm = This is My First Test Repository
5.配置访问用户及密码
[root@test188 conf]# cat passwd
### This file is an example password file for svnserve.
### Its format is similar to that of svnserve.conf. As shown in the
### example below it contains one section labelled [users].
### The name and password for each user follow, one account per line.
[users]
# harry = harryssecret
# sally = sallyssecret
admin = admin
6.配置用户权限
[root@test188 conf]# cat passwd
### This file is an example password file for svnserve.
### Its format is similar to that of svnserve.conf. As shown in the
### example below it contains one section labelled [users].
### The name and password for each user follow, one account per line.
[users]
# harry = harryssecret
# sally = sallyssecret
admin = admin
[root@test188 conf]# cat authz
### This file is an example authorization file for svnserve.
### Its format is identical to that of mod_authz_svn authorization
### files.
### As shown below each section defines authorizations for the path and
### (optional) repository specified by the section name.
### The authorizations follow. An authorization line can refer to:
### - a single user,
### - a group of users defined in a special [groups] section,
### - an alias defined in a special [aliases] section,
### - all authenticated users, using the '$authenticated' token,
### - only anonymous users, using the '$anonymous' token,
### - anyone, using the '*' wildcard.
###
### A match can be inverted by prefixing the rule with '~'. Rules can
### grant read ('r') access, read-write ('rw') access, or no access
### ('').
[aliases]
# joe = /C=XZ/ST=Dessert/L=Snake City/O=Snake Oil, Ltd./OU=Research Institute/CN=Joe Average
[groups]
# harry_and_sally = harry,sally
# harry_sally_and_joe = harry,sally,&joe
# [/foo/bar]
# harry = rw
# &joe = r
# * =
# [repository:/baz/fuz]
# @harry_and_sally = rw
# * = r
[/]
admin = rw
7.启动服务
[root@test188 conf]# svnserve -d -r /svn/
####注意:更改svnserver.conf时需要重启SVN服务,更改authz,passwd文件时则不需要重启服务
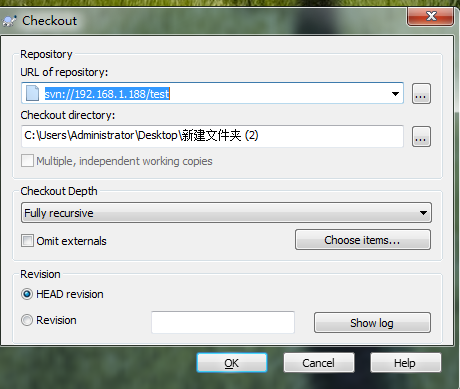
.在Linux使用如下命令行:
[root@test188 conf]# svn co svn://192.168.1.188/test