Dive deep into Basic HTML
表table
tabular data in tables:
table:<table></table>
table row:<tr></tr>
Question
What is a “cell”?
Answer
A cell is a grouping within our table which will contain either heading labels or information pertaining to the associated row and column headings. In the next exercise, you will create table cells – bear with us!
基本元素 cell(理解为基本表格单元元素)
table data:<td></td>
table heading:<th></th>
<th scope=“row”>
<th scope=“col”>
形式里table heading 和data 一样,以行填充
column span:<td colspan=“2”></td>作用于cell
row span:<td rowspan=“3”></td>同样作用于cell
table head:<thead></thead>表头字段项
table body:<tbody></tbody>表内容体
table footer:<tfoot></tfoot>一般是放一些total、count之类的在table footer中
一切都是为了semantic,可读性高
————————————————
表单form
HTTP:hypertext transfer protocol
forms:computer need an HTTP request to know how to comunicate
<form>是很棒的收集数据的工具,可以有子元素
POST:the action attribute determines where the information is sent and the method attribute is assigned a HTTP verb that is included in the HTTP request
类似的HTTP动作不要求大小写,可以是post、get
<input>:input标签没有关闭的/,功能非常强大,拥有很多type,如checkboc,calendar等
<label>:配合其他标签使用,如input id=“jas”,label for=“jas”,就是为input tag提供的label
for属性为label提供了一个功能:点击label后会高亮/选择对应的input
这里有两种写法,一种是label和input分开,一种是label包裹着(wrapping)input,如下:
<label><input type="checkbox" name="personality" checked> Loving</label>
看实际应用场景,因为表现一样,一切为了高可读性
<input type=“text”>:简单文本输入框
<input type=“password”>:简单密码输入框,会用dot或者asterisk遮盖输入
<input type=“number” step=1>:简单数字输入,右边会有两个按钮提供加或者减,step的值代表按一次加号加几、减号减几
<input type=“range” min=“0” max=“5” step=“0.5”>:简单横向滑动条,可通过min、max、step规定滑动的顺滑程度以及节点涩度
<input type="checkbox" id="lettuce" name="topping" value="lettuce”>:简单选择框,注意这里的value是对于客户端不可见但是服务器可以获取的,如果不写value,那么默认值是“on“
<input type=“radio” id=“selectionA” name=“answer” value=“1”>
<input type=“radio” id=“selectionB” name=“answer” value=“3”>
简单单选按钮:name是一样的时候只能选一个,称name一样的radiobox为一个radio group,同组内的value值只能唯一
很多tag带有name和value的属性,反映到代码里就是name=value,为的是能获取这个tag的动作,将tag的变化变成变量
<select id=“bun” name=“content”>
<option value=“beef”>Beef</option>
……
</select>
dropdown list: 利用select标签实现下拉菜单,类似radiobox的操作,select包裹住的每个option带有一个属性用于传入select的name属性对应的变量,只能选一个option
<input list=“sauces” name=“choice”>
<datalist id=“sauces”>
<option value=“yy”>yy</option>
……
</datalist>
datalist做到了给value固定范围,适配很多input type,这里省略了type,default type=“text”,显示效果是用户输入时会根据字符匹配value list中的值。如果没有一个和option匹配的,那么value仍会和用户输入的值进行配对。相当于option的选项只是prefered result,用户仍然可以自行输入值
<textarea id=“extra” name=“extra” cols=“40” rows=“3”>
textarea本身是自带一个resize button在右下角的,要想关闭需要在style里加入resize:none
其余的基本都类似<input type=“text”>,更细的标签需要时查询MDN即可。
这里注意placeholder的用法和text不一样,如果想要textarea里有default值,直接在tag中写就好
<input type=“submit” value=“done”>
简单提交按钮:如果这里value不写在按钮上默认是Submit的字样
—————————————————
Form Validations:
required属性返回一个boolean值,有值为true,反之为false,支持绝大多数input类型除color和range
这是因为color和range本身具有default值
max、min属性针对于type=“number”,约束给定值的最大最小值
maxlength、minlength针对输入字符个数
required pattern接受一个正则表达式约束regular expression(regex)
—————————————————
Semantic HTML: relating to meaning 语义HTML网页
单纯的div和span并非可读性很高,于是我们利用不同的标签去区分块以及功能
有三点优点:
Accessibility
SEO-Search Engine Optimization
Easy to Understand
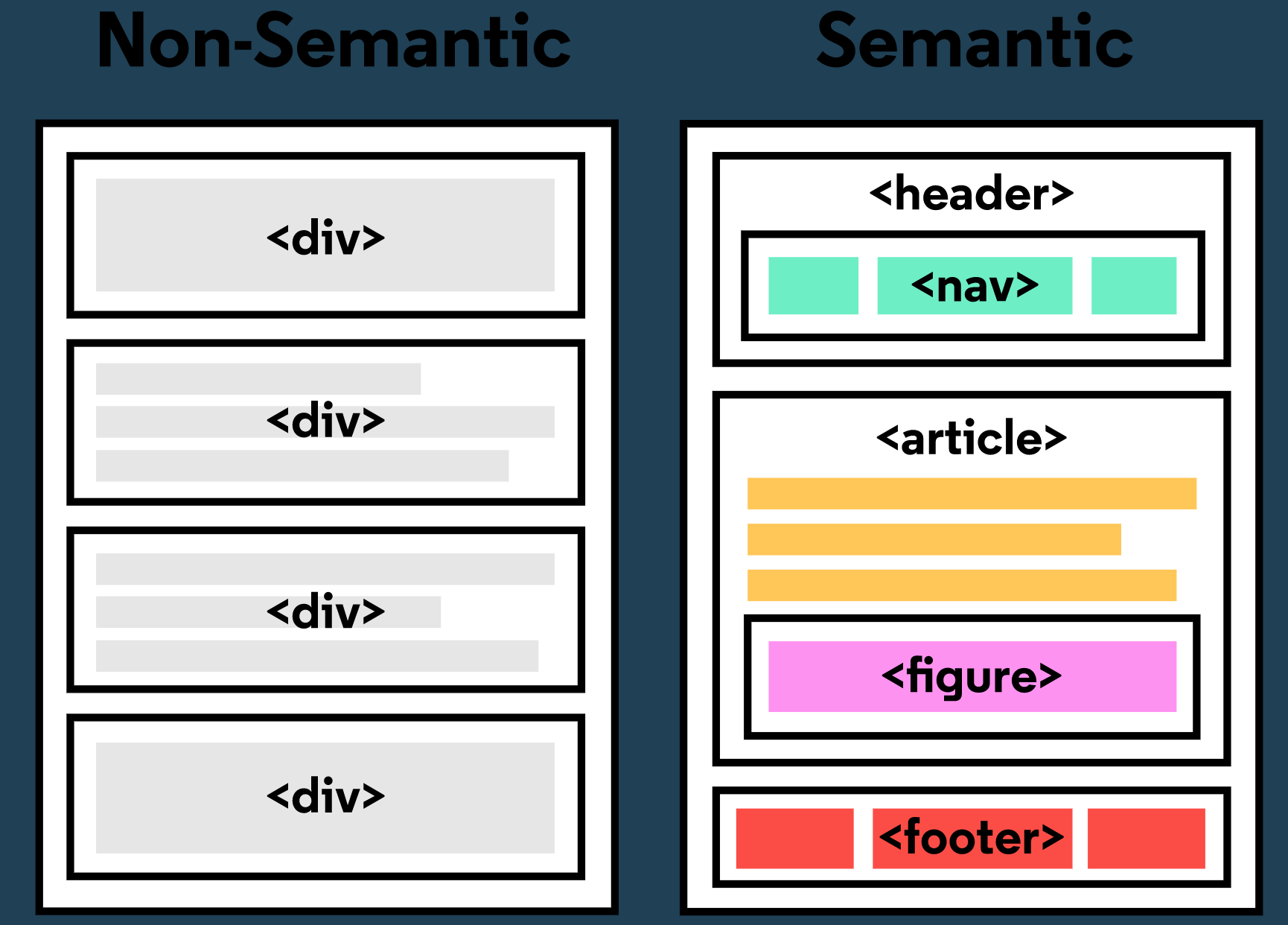
structural elements:
<header>
<nav>
<main>
<footer>
为的是主次分明,条理清晰
在main中:
<section>
<article>
<aside>
<figure>,<figcaption>
<audio><source src=“”></audio>
<video>注意是self-closing tag
<embed>同样是self-closing tag