一个java程序从main()方法开始执行,然后按照既定的代码逻辑执行,看似没有其他线程参与,但实际上java程序天生就是一个多线程程序,包含了:(1)分发处理发送给给JVM信号的线程;(2)调用对象的finalize方法的线程;(3)清除Reference的线程;(4)main线程,用户程序的入口。那么,如何在用户程序中新建一个线程了,只要有三种方式:
1.通过继承Thread类,重写run方法;
2.通过实现runable接口;
3.通过实现callable接口这三种方式,下面看具体demo。
public class CreateThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.继承Thread Thread thread = new Thread() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("继承Thread"); super.run(); } }; thread.start();
Thread thread11 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("lambda方式创建线程");
});
thread11.start(); //2.实现runable接口 Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("实现runable接口"); } }); thread1.start(); //3.实现callable接口 ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); Future<String> future = service.submit(new Callable() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { return "通过实现Callable接口"; } }); try { String result = future.get(); System.out.println(result); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
三种新建线程的方式具体看以上注释,需要主要的是:
- 由于java不能多继承可以实现多个接口,因此,在创建线程的时候尽量多考虑采用实现接口的形式;
- 实现callable接口,提交给ExecutorService返回的是异步执行的结果,另外,通常也可以利用
FutureTask(Callable<V> callable)将callable进行包装然后FeatureTask提交给ExecutorsService。如图
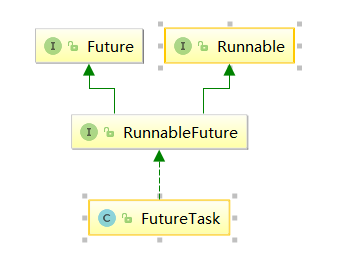
另外由于FeatureTask也实现了Runable接口也可以利用上面第二种方式(实现Runable接口)来新建线程;
- 可以通过Executors将Runable转换成Callable,具体方法是:
Callable callable(Runnable task, T result), Callable<Object> callable(Runnable task)。