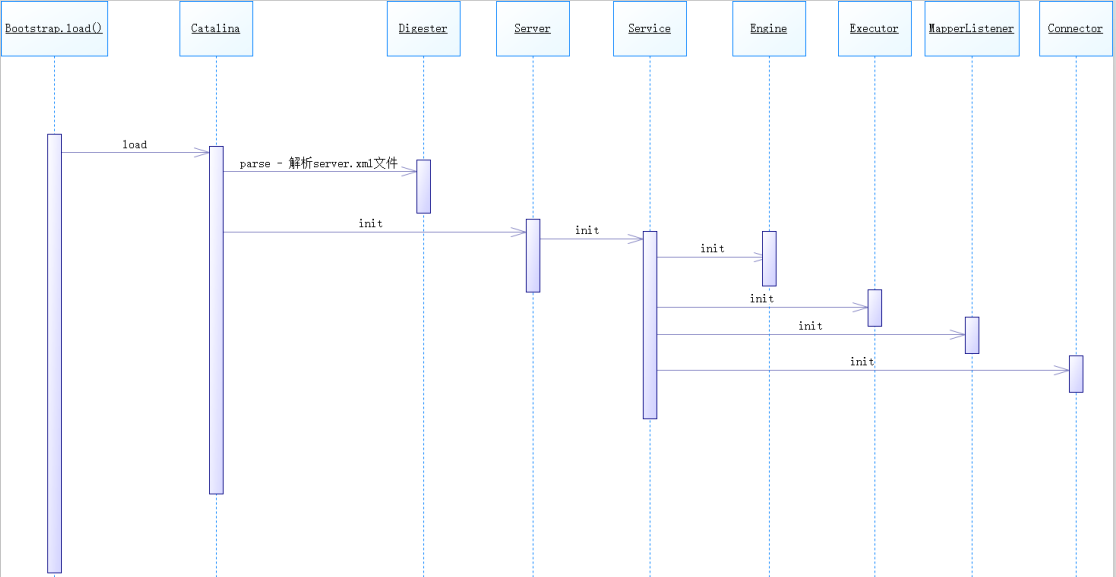
Bootstrap#load()
daemon.load(args) 调用的, 其实就是 bootstrap.load(args)
main方法中执行了 daemon = bootstrap;
org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#load():
private void load(String[] arguments) throws Exception { // Call the load() method String methodName = "load"; Object param[]; Class<?> paramTypes[]; if (arguments == null || arguments.length == 0) { paramTypes = null; param = null; } else { paramTypes = new Class[1]; paramTypes[0] = arguments.getClass(); param = new Object[1]; param[0] = arguments; } // 拿到 Catalina 的 load 方法 Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Calling startup class " + method); } // 调用 Catalina#load(args)方法, 最终会调用Catalina#load() 方法 method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param); }
反射调用了 Catalina.load(args)方法. 然后在方法中对args做了个验证, 最终调用的,是 Catalina.load() 无参方法.
Catalina#load()
//org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina#load() public void load() { if (loaded) { return; } loaded = true; //获取当前纳秒数, 1纳秒=0.00000 0001秒 long t1 = System.nanoTime(); //初始化目录 - 过时方法, 内部为空 initDirs(); //初始化 jmx 的环境变量 initNaming(); // Create and execute our Digester //创建解析器, 用于解析 conf/Server.xml 文件,告诉Digester哪个xml标签应该解析成什么类 Digester digester = createStartDigester(); InputSource inputSource = null; InputStream inputStream = null; File file = null; try { try { //file -> conf/server.xml 文件 file = configFile(); inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString()); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail", file), e); } } //region conf/Server.xml文件不存在时的处理 ...... //endregion try { inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream); //把 Catalina 作为一个顶级实例 digester.push(this); //解析 conf/server.xml 文件 //解析过程中, 会实例化各个组件, 如 Server Container Connector等 digester.parse(inputSource); } catch (SAXParseException spe) { ...... } catch (Exception e) { ...... } } finally { if (inputStream != null) { try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore } } } //解析Server.xml的时候, 会创建 Server = StandardServer, 然后调用了 Catalina#setServer()方法 getServer().setCatalina(this); getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile()); getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile()); // Stream redirection initStreams(); // Start the new server try { //初始化服务器 StandardServer#init(), 最终调用的是 StandardServer.initInternal() 方法 getServer().init(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { ...... } long t2 = System.nanoTime(); if(log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("Initialization processed in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms"); } }
1. digester.parse(inputSource) 是对 conf/server.xml 进行解析, 具体解析过程比较复杂, 其中还加入了很多变量的设置和创建. 目前可以不看, 可以通过调试来查看变量的值.
2. getServer().init() : server 是在解析server.xml时候, 创建的. 这里调用的是 StandardServer.init() 方法.
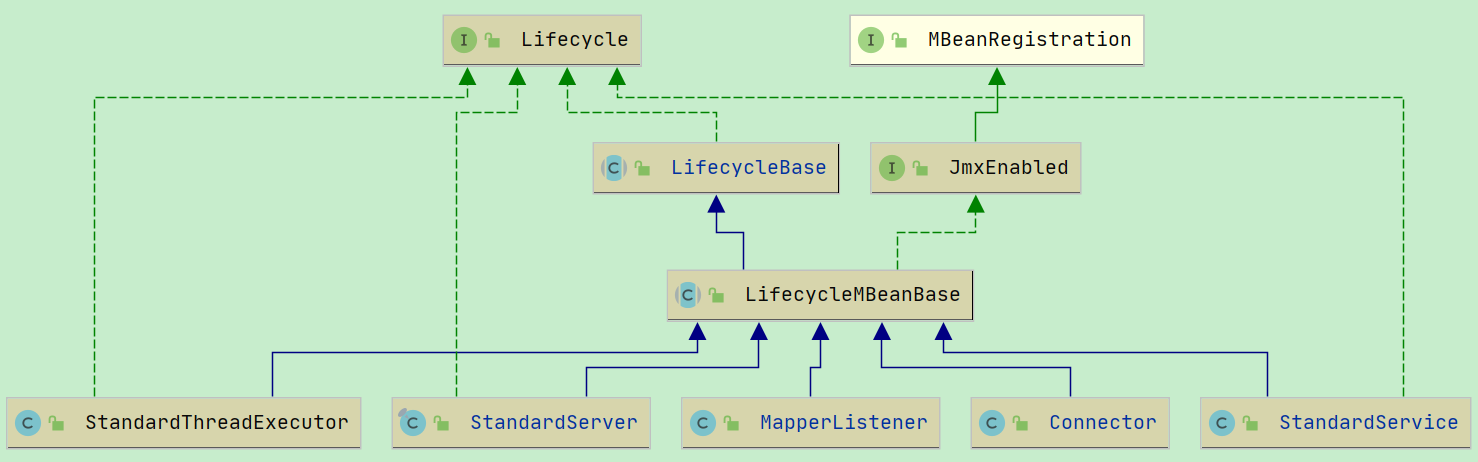
StandardServer本身没有 init() 方法, init() 是父类 LifecycleBase 中的方法.
在此方法中, 调用了抽象方法 initInternal(). 其实就是 StandardServer#initInternal() 方法.
StandardServer#initInternal()
@Override protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); // Register global String cache // Note although the cache is global, if there are multiple Servers // present in the JVM (may happen when embedding) then the same cache // will be registered under multiple names // 往 jmx 中注册全局的 String cache,尽管这个 cache 是全局的,但是如果在同一个 jvm 中存在多个 Server, // 那么则会注册多个不同名字的 StringCache,这种情况在内嵌的tomcat中可能会出现 onameStringCache = register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache"); // Register the MBeanFactory JMX // 注册MBeanFactory,用来管理Server MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory(); factory.setContainer(this); onameMBeanFactory = register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory"); // Register the naming resources //往 jmx 中注册全局的 NamingResources, NamingResourcesImpl#initInternal() globalNamingResources.init(); // Populate the extension validator with JARs from common and shared // class loaders if (getCatalina() != null) { ClassLoader cl = getCatalina().getParentClassLoader(); // Walk the class loader hierarchy. Stop at the system class loader. // This will add the shared (if present) and common class loaders while (cl != null && cl != ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()) { if (cl instanceof URLClassLoader) { URL[] urls = ((URLClassLoader) cl).getURLs(); for (URL url : urls) { if (url.getProtocol().equals("file")) { try { File f = new File (url.toURI()); if (f.isFile() && f.getName().endsWith(".jar")) { ExtensionValidator.addSystemResource(f); } } catch (URISyntaxException e) { // Ignore } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore } } } } cl = cl.getParent(); } } //一个 Server 可以有多个 Service(服务) // Initialize our defined Services for (Service service : services) { //StandardService#init(), 最终会调用 StandardService#initInternal() service.init(); } }
这里的 service 是通过 server.xml 解析得来的. service = StandardService. 同样的, init()方法是 LifecycleBase 里的. 最终调用到 StandardService#initInternal().
StandardService#startInternal()
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); // 1. 初始化 engine, 一个 Service 只有一个 engine if (engine != null) { //此处最终会调用 StandardEngine#initInternal() engine.init(); } // Initialize any Executors // 2. 初始化线程池, 默认为空, 配置 server.xml 的 tomcatThreadPool 可以改变 for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) { if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) { ((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain()); } executor.init(); } // Initialize mapper listener // 3. 初始化 MapperListener, MapperListener用于注册 Host Context Wrapper mapperListener.init(); // Initialize our defined Connectors // 4. 初始化连接器, 用来接收客户端请求 synchronized (connectorsLock) { for (Connector connector : connectors) { try { //最终执行的是 Connector.initInternal() connector.init(); } catch (Exception e) { String message = sm.getString( "standardService.connector.initFailed", connector); log.error(message, e); if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) throw new LifecycleException(message); } } } }
这里执行了4个init()方法.
1. engine也是通过解析 server.xml 来得到的. engine.init() 最终执行的是 StandardEngine#initInternal()
2. executor.init() 是初始化线程池的, server.xml 中, 有配置 tomcatThreadPool, 但是注释掉了, 把它注释回来, 然后在Connector标签上设置 executor="tomcatThreadPool" 就可以了.
所以线程池默认是空
3. mapperListener.init() 是对 MapperListener 监听器进行初始化的. 这里的init()是调用的父类 LifecycleBase#init() 方法. MapperListener 没有重写 init() 或 initInternal()
MapperListener是用来注册 Host Context Wrapper 的.
4. connector.init() 是初始化连接器的.
StandardEngine#initInternal()
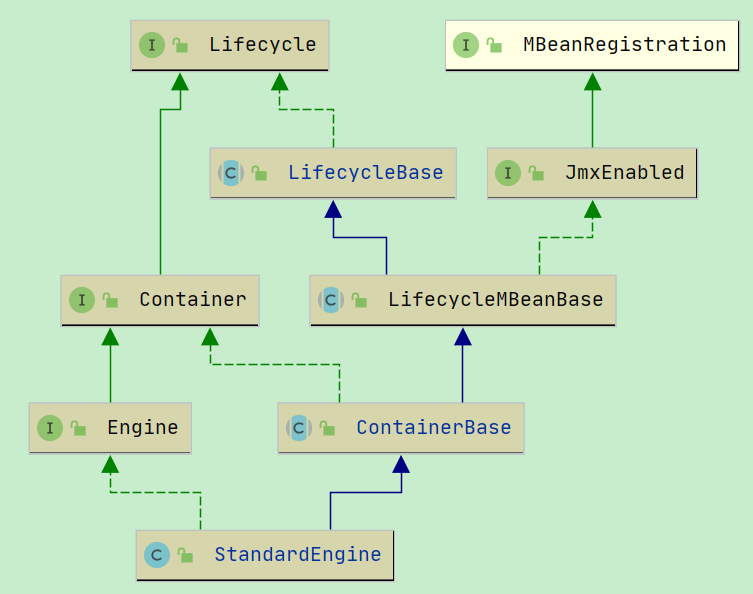
@Override protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Ensure that a Realm is present before any attempt is made to start // one. This will create the default NullRealm if necessary. getRealm(); super.initInternal(); }
1. getRealm 是域的一些设置, 可以不管.
2. super.initInternal() 调用的是父类中的方法:
//org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase#initInternal @Override protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { BlockingQueue<Runnable> startStopQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(); startStopExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( getStartStopThreadsInternal(), getStartStopThreadsInternal(), 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, startStopQueue, new StartStopThreadFactory(getName() + "-startStop-")); startStopExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true); super.initInternal(); }
这里创建了一个阻塞队列的线程池, 然后继续调用父类中的 initInternal 方法:
//org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleMBeanBase#initInternal protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { // If oname is not null then registration has already happened via // preRegister(). if (oname == null) { mserver = Registry.getRegistry(null, null).getMBeanServer(); oname = register(this, getObjectNameKeyProperties()); } }
注意到, 这里并没有去接着往下一层初始化了, 也就是说, Host Context Wrapper 的初始化, 不是在这里完成的.
Connector#initInternal()
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); // Initialize adapter // 初始化一个适配器, 用于Coyote的Request、Response与HttpServlet的Request、Response适配的 adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this); protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter); // Make sure parseBodyMethodsSet has a default if (null == parseBodyMethodsSet) { setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods()); } if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprLifecycleListener.isInstanceCreated()) { throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprListener", getProtocolHandlerClassName())); } if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable()) { throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprLibrary", getProtocolHandlerClassName())); } if (AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() && AprLifecycleListener.getUseOpenSSL() && protocolHandler instanceof AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol) { AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?> jsseProtocolHandler = (AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?>) protocolHandler; if (jsseProtocolHandler.isSSLEnabled() && jsseProtocolHandler.getSslImplementationName() == null) { // OpenSSL is compatible with the JSSE configuration, so use it if APR is available jsseProtocolHandler.setSslImplementationName(OpenSSLImplementation.class.getName()); } } try { // 初始化ProtocolHandler,这个init不是Lifecycle定义的init,而是ProtocolHandler接口的init // protocolHandler = Http11NioProtocol,其实调用的是 AbstractProtocol#init() protocolHandler.init(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new LifecycleException( sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e); } }
protocolHandler 是解析 server.xml 时确定的, 对应 protocol.
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" connectionTimeout="20000" redirectPort="8443" />
HTTP/1.1解析出来, 就是 Http11NioProtocol
如果没有配置 protocol, 则默认使用 Http11NioProtocol
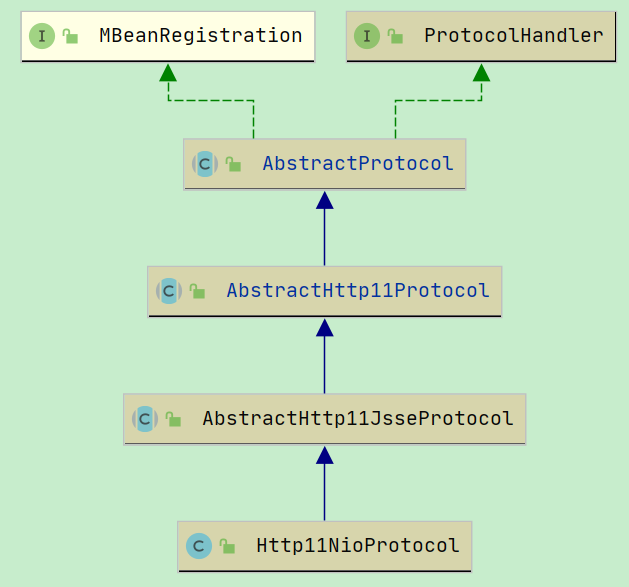
这里实际调用的是 org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol#init()
public void init() throws Exception { if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) { getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.init", getName())); } if (oname == null) { // Component not pre-registered so register it oname = createObjectName(); if (oname != null) { Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null); } } if (this.domain != null) { rgOname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=GlobalRequestProcessor,name=" + getName()); Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent( getHandler().getGlobal(), rgOname, null); } String endpointName = getName(); endpoint.setName(endpointName.substring(1, endpointName.length()-1)); endpoint.setDomain(domain); //NioEndpoint#init(), 调用的是 AbstractEndpoint#init() endpoint.init(); }
这个 NioEndpoint 是在创建 Http11NipProtocol 的时候, 创建的, 所以这里调用的是 NioEndpoint#init()方法.
public Http11NioProtocol() { super(new NioEndpoint()); }
NioEndpoint#init() 调用的是父类 org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint#init()
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint#init public void init() throws Exception { if (bindOnInit) { // NioEndpoint#bind() bind(); bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_INIT; } if (this.domain != null) { // Register endpoint (as ThreadPool - historical name) oname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=ThreadPool,name="" + getName() + """); Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null); ObjectName socketPropertiesOname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=SocketProperties,name="" + getName() + """); socketProperties.setObjectName(socketPropertiesOname); Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(socketProperties, socketPropertiesOname, null); for (SSLHostConfig sslHostConfig : findSslHostConfigs()) { registerJmx(sslHostConfig); } } }
bind()方法是个抽象方法, 实际调用的是 NipEndpoint 中的bind() 方法
//org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint#bind public void bind() throws Exception { if (!getUseInheritedChannel()) { // 实例化ServerSocketChannel,并且绑定端口和地址 serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open(); socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket()); InetSocketAddress addr = (getAddress()!=null?new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(),getPort()):new InetSocketAddress(getPort())); // 设置最大连接数,原来是在这里设置的 serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount()); } else { // Retrieve the channel provided by the OS Channel ic = System.inheritedChannel(); if (ic instanceof ServerSocketChannel) { serverSock = (ServerSocketChannel) ic; } if (serverSock == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("endpoint.init.bind.inherited")); } } serverSock.configureBlocking(true); //mimic APR behavior // Initialize thread count defaults for acceptor, poller // 初始化acceptor、poller线程的数量 if (acceptorThreadCount == 0) { // FIXME: Doesn't seem to work that well with multiple accept threads acceptorThreadCount = 1; } if (pollerThreadCount <= 0) { //minimum one poller thread pollerThreadCount = 1; } setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(pollerThreadCount)); // Initialize SSL if needed // 如果有必要的话初始化ssl initialiseSsl(); // 初始化selector selectorPool.open(); }
总结:
Bootstrap#load() 主体调用过程: