第二篇里面, 看到容器创建的是 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 类型.
一 .类图
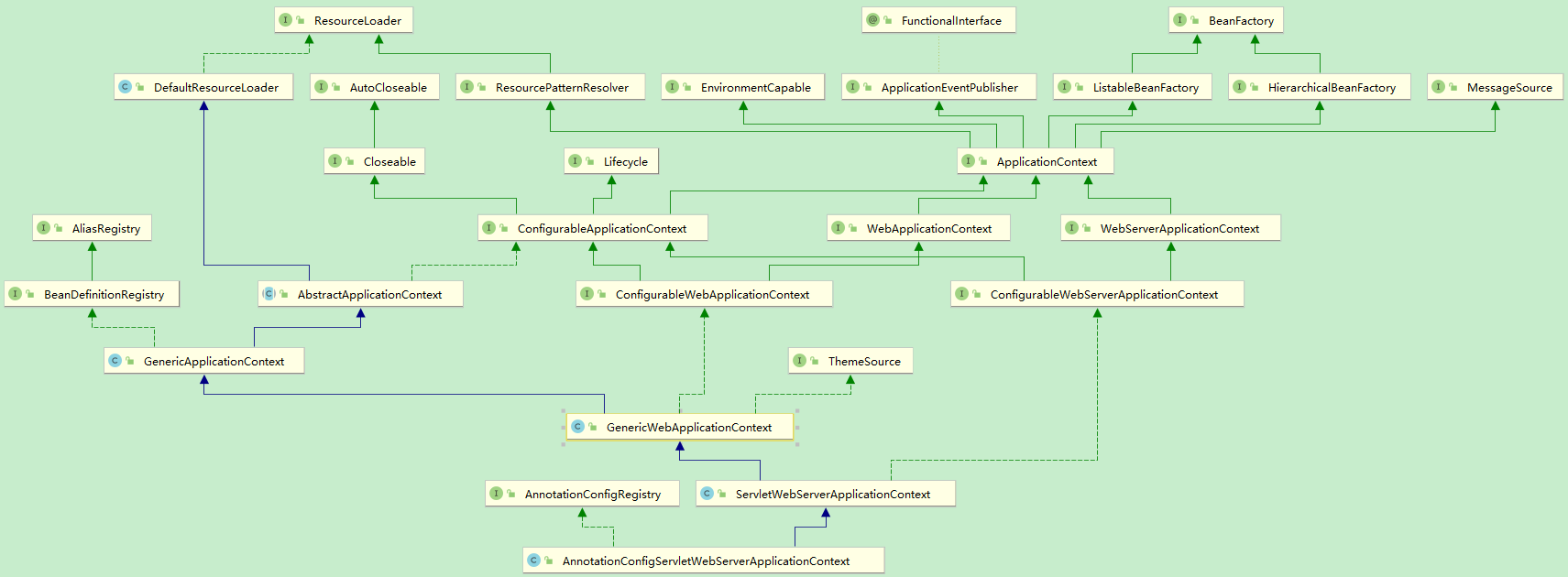
二. 构造
public GenericApplicationContext() {
//创建 bean 工厂 this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); } public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
//创建读取器 this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//创建扫描器 this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); }
构造函数中, 创建了三个类, 并赋值给相应的属性.
三. 启动 tomcat
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
这里我主要是想要了解tomcat启动, 所以一些方法, 就先不看.
1. onRefresh()
onRefresh() 方法执行的是 ServletWebServerApplicationContext 的方法.
@Override protected void onRefresh() { super.onRefresh(); try { createWebServer(); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex); } }
createWebServer() 方法中, 会创建 Tomcat 类.
private void createWebServer() { WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
//当前进来, servletContext 为null ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//创建了 TomcatServletWebServerFactory 类 ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
//创建 Tomcat this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer()); } else if (servletContext != null) { try { getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext); } catch (ServletException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex); } } initPropertySources(); }
getWebServer方法里面, 就创建了 Tomcat 类, 并对其进行一些配置操作.
@Override public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//创建 Tomcat Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat")); tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath()); Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol); tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector); customizeConnector(connector); tomcat.setConnector(connector); tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false); configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine()); for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) { tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector); } prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//这里会创建 TomcatWebServer 实例, 并返回 return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat); }
这里的 protocol 是有一个默认值的:
public static final String DEFAULT_PROTOCOL = "org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"; private String protocol = DEFAULT_PROTOCOL;
可以看到, 这里默认使用的是 同步非阻塞io协议. 需要注意的是, 在 new Connector() 的时候 对 Http11NioProtocol 进行了反射实例化.
public Http11NioProtocol() { super(new NioEndpoint()); }
在实例化的时候, new 了一个 NioEndpoint. 这个东西很重要, 后面会看到.
getTomcatWebServer()
protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) { return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0); }
在创建 TomcatWebServer 的时候, 就会启动 Tomcat
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart) { Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null"); this.tomcat = tomcat; this.autoStart = autoStart; initialize(); } private void initialize() throws WebServerException { TomcatWebServer.logger .info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false)); synchronized (this.monitor) { try { addInstanceIdToEngineName(); Context context = findContext(); context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> { if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) { // Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't // happen when the service is started. removeServiceConnectors(); } }); // Start the server to trigger initialization listeners this.tomcat.start(); // We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions(); try { ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader()); } catch (NamingException ex) { // Naming is not enabled. Continue } // Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a // blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown startDaemonAwaitThread(); } catch (Exception ex) { stopSilently(); throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex); } } }
2. finishRefresh()
ServletWebServerApplicationContext 重写了该方法.
@Override protected void finishRefresh() {
//调用父类的 finishedRefresh 方法, 保证处理完整性 super.finishRefresh();
//启动 TomcatWebServer WebServer webServer = startWebServer(); if (webServer != null) { publishEvent(new ServletWebServerInitializedEvent(webServer, this)); } }
startWebServer()
private WebServer startWebServer() { WebServer webServer = this.webServer; if (webServer != null) { webServer.start(); } return webServer; } @Override public void start() throws WebServerException { synchronized (this.monitor) { if (this.started) { return; } try {
//遍历service, 拿到service, 然后绑定 Connector addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors(); Connector connector = this.tomcat.getConnector(); if (connector != null && this.autoStart) { performDeferredLoadOnStartup(); } checkThatConnectorsHaveStarted(); this.started = true; TomcatWebServer.logger .info("Tomcat started on port(s): " + getPortsDescription(true) + " with context path '" + getContextPath() + "'"); ...... }
addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors()
private void addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors() { Service[] services = this.tomcat.getServer().findServices(); for (Service service : services) { Connector[] connectors = this.serviceConnectors.get(service); if (connectors != null) { for (Connector connector : connectors) { service.addConnector(connector); if (!this.autoStart) { stopProtocolHandler(connector); } } this.serviceConnectors.remove(service); } } }
service 在绑定 Connector 的时候, 会启动 Connector
@Override public void addConnector(Connector connector) { synchronized (connectorsLock) { connector.setService(this); Connector results[] = new Connector[connectors.length + 1]; System.arraycopy(connectors, 0, results, 0, connectors.length); results[connectors.length] = connector; connectors = results; if (getState().isAvailable()) { try { connector.start(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.error(sm.getString( "standardService.connector.startFailed", connector), e); } } // Report this property change to interested listeners support.firePropertyChange("connector", null, connector); } }
看一下 connector.start() 方法.
@Override public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException { ......try { setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false); startInternal(); if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) { // This is a 'controlled' failure. The component put itself into the // FAILED state so call stop() to complete the clean-up. stop(); } else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.STARTING)) { // Shouldn't be necessary but acts as a check that sub-classes are // doing what they are supposed to. invalidTransition(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT); } else { setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTED, null, false); } } catch (Throwable t) { // This is an 'uncontrolled' failure so put the component into the // FAILED state and throw an exception. ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); setStateInternal(LifecycleState.FAILED, null, false); throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.startFail", toString()), t); } }
startInternal() 是一个抽象方法, 其中的一个实现类 Connector
@Override protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Validate settings before starting if (getPort() < 0) { throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString( "coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPort()))); } setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); try { protocolHandler.start(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new LifecycleException( sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e); } }
接着进 start() 方法
@Override public void start() throws Exception { if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) { getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", getName())); } endpoint.start(); // Start async timeout thread asyncTimeout = new AsyncTimeout(); Thread timeoutThread = new Thread(asyncTimeout, getNameInternal() + "-AsyncTimeout"); int priority = endpoint.getThreadPriority(); if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) { priority = Thread.NORM_PRIORITY; } timeoutThread.setPriority(priority); timeoutThread.setDaemon(true); timeoutThread.start(); }
endPoint.start() 方法:
public final void start() throws Exception { if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) { bind(); bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START; } startInternal(); }
这个bind() 执行的是NioEndpoint 中的方法, 进行端口绑定监听.
@Override public void bind() throws Exception { serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open(); socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket()); InetSocketAddress addr = (getAddress()!=null?new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(),getPort()):new InetSocketAddress(getPort())); serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount()); serverSock.configureBlocking(true); //mimic APR behavior // Initialize thread count defaults for acceptor, poller if (acceptorThreadCount == 0) { // FIXME: Doesn't seem to work that well with multiple accept threads acceptorThreadCount = 1; } if (pollerThreadCount <= 0) { //minimum one poller thread pollerThreadCount = 1; } setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(pollerThreadCount)); // Initialize SSL if needed initialiseSsl(); selectorPool.open(); }
总结:
从执行流程上来看,
1. 在onRefresh() 中, 启动Tomcat
2. 在 finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 中进行了后台方法的路由映射(待续)
3. 在finishRefresh()中进行了端口绑定监听