1. low level vision: 图像数字化处理,包括:
sensing: 图像捕获以及数字化
pre-processing: 提高图像质量(去除干扰点,增强对象特征,边缘提取即将对象与背景分离)
description: 特征提取
classification: 为图像片段分配标签
2. high level vision: 有关知识的构造表示及推论
recognition+interpretation+scene analysis
3. pinhole camera
成像与物体大小之比为小孔到成像屏的举例除以小孔到物体的距离
成像与物体大小比例相同
成像为倒立的且左右颠倒,即与原物体成中心对称
小孔越小,成像越清晰,但亮度会较小
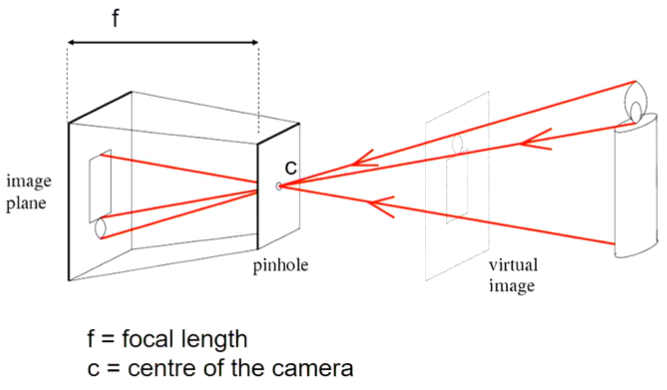
上面的图中,因为是中心对称的所以可以把成像反过来移到前面,如virtual image所示
4. projection: 3D to 2D
length,angle会改变但是形状会保留,如直线依然是直线
5. vanishing point: 线性透视中,两条或多条代表平行线线条向远处地平线(HORIZON LINE)伸展直至聚合的那一点
vertical vanishing point: at infinity因为垂直于图像的点不会相交,所以我们说它们的vanishing point在无穷远处
6. projection
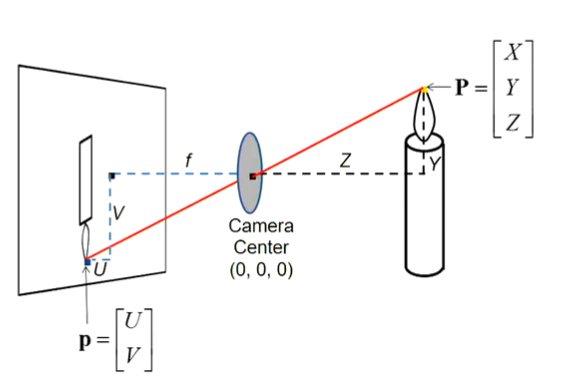
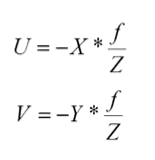
7. 其他projection: affine projection
suitable when scene depth is small relative to the average distance from the camera
增加一个系数,使相机始终与场景保持大致恒定的距离
8. 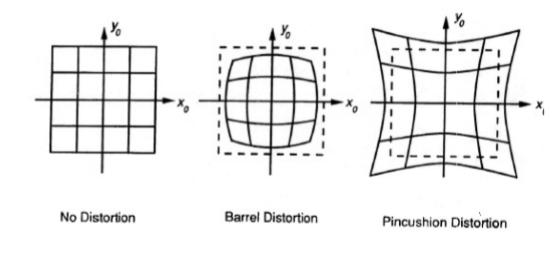 need to be corrected
need to be corrected
9. images respresented
high value: light
low value: dark
如对应蓝色的时候,天空会变成白色
10. spatial resolution: 空间分辨率,每单位长度的像素数
too little resolution, poor recognition
too much resolution, slow and wastes memory
11. quantisation: 将强度或者幅度数字化