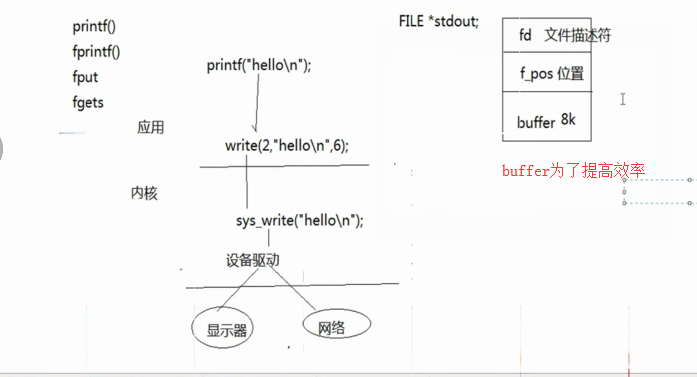
1. 系统api与库函数的关系

man 2 open
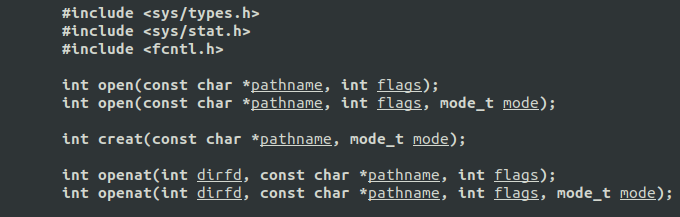
1.1 open

1.2 read/write

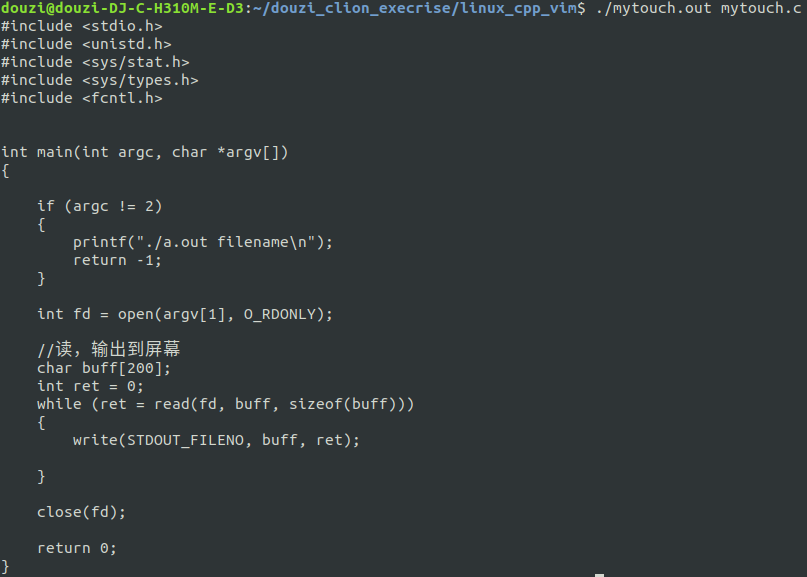
实现cat功能
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 2) { printf("./a.out filename "); return -1; } int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY); //读,输出到屏幕 char buff[200]; int ret = 0; while (ret = read(fd, buff, sizeof(buff))) { write(STDOUT_FILENO, buff, ret); } close(fd); return 0; }
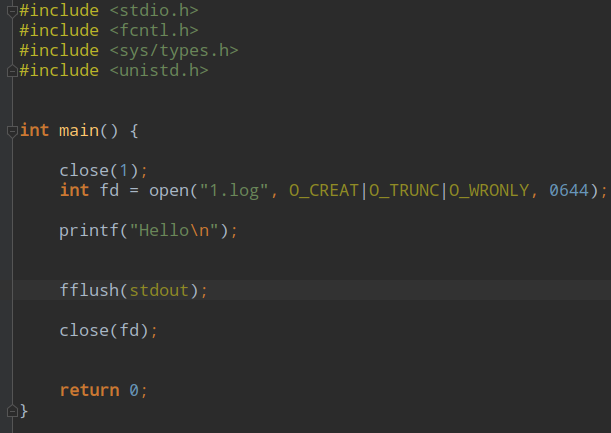
1.3 lseek

#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 2) { printf("./a.out filename "); return -1; } int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0666); write(fd, "helloword", 11); //文件读写的位置此时到末尾 //需要移动读写的位置 lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET); char buf[256] = {0}; int ret = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)); if (ret) { write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, ret); } close(fd); return 0; }
计算大小
int fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY); int ret = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END); printf("file size is %d ", ret); close(fd);
拓展文件
//1. open int fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 0666); int ret = lseek(fd, 1024, SEEK_END); printf("file size is %d ", ret); //需要至少写一次,否则不能保存 write(fd, "a", 1); close(fd);
1.4 阻塞
- read函数在读设备或者的读管道,或者读网络的时候。
- 输入输出设备对应 /dev/tty
int fd = open("/dev/tty", O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_NONBLOCK);
1.5 fcntl函数--设置非阻塞
#include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );
int flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL); flags |= O_NONBLOCK;