
1. 写在前面
个人主页: https://gzh.readthedocs.io
关注容器技术、关注
Kubernetes。问题或建议,请公众号(
double12gzh)留言。
在本系列教程的第一篇中,我们已经对如下这张图作了简单介绍。这张图非常重要,理解这张图对我们正确理解client-go及Controller非常有帮助(出处)。
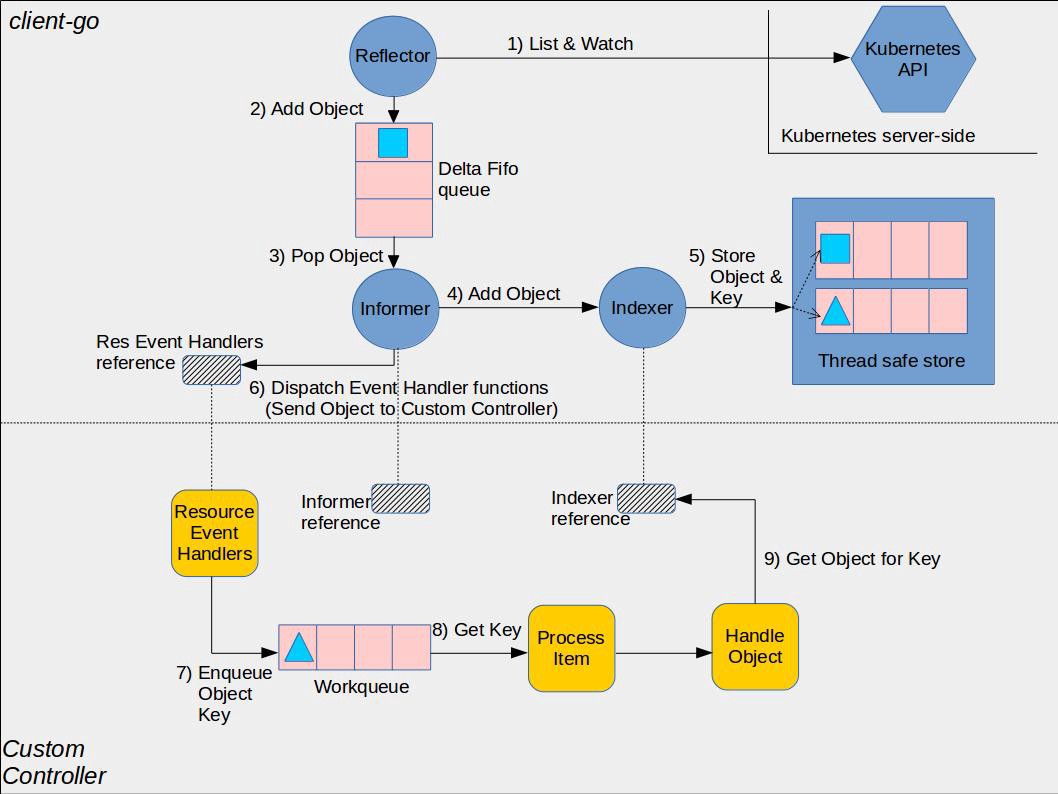
client-go中对其实现的代码位于tools/cache,如下图:

除了上图中展示的Indexer的定义比较重要外,我们还需要关注Indexer比较重要的数据结构:
[root@xxxx-wsl /ACode/client-go] cat tools/cache/index.go| grep -B 1 -A 1 type
// IndexFunc knows how to compute the set of indexed values for an object.
type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
--
// Index maps the indexed value to a set of keys in the store that match on that value
type Index map[string]sets.String
// Indexers maps a name to a IndexFunc
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// Indices maps a name to an Index
type Indices map[string]Index
- IndexFunc: 从接收的资源对象中,根据一系列的key来获取相应的值。
- Index: 建立key与被索引值的对应关系并存储到
Store中,即它里面的数据都是Key/Value的形式。 - Indexers: 存储的是索引器的名字与索引器的实现函数。
- Indices: 存储缓存数据,形式
Key/Value,其中Key为缓存器的字,Value为缓存数据。
2. Custom Controller中的组件
如图中所示,Custom Controller是位于下半部分的内容。从图中可以很容易的看到,一个Custom Controller主要包含以下内容:
Indexer ReferenceInformer ReferenceResource Event HandlerWorkQueueProcessItem
2.1 Indexer
2.1.1 简单介绍
它是一个知道如何使用CRD对象的 Indexer 实例的引用(reference)。当我们写自定义控制器(Custom Controller)代码时,将使用这个reference去做对象检索。
Indexer是client-go中实现的一个本地存储,它可以建立索引并存储Resource的对象。Reflector通过Delta FIFO Queue将资源对象存储到Indexer中。
需要注意的是,Indexer中的数据与etcd中的数据是完全一致的,这样client-go需要数据时,无须每次都从api-server获取,从而减少了请求过多造成对api-server的压力。
一句话总结:Indexer是用于存储+快速查找资源,即它的目的就是为了能够进行快速查找。
Indexer是如何实现“存储+快速查找资源”的呢?我们来看一下下面这张图,通过这张图方便我们理解一下Indexer的存储结构:

说明: 图中的
Indexers与Indices虽然都指向了相同的IndexFunc,这并不是说二者的数据是相同的,而是说二者使用的IndexFunc是相同的。
根据上面这个图,我们可以简单的规纳出与之对应的数据结构:
// 包含的所有索引器/分类以及对应的实现
Indexers: {
"namespace": NamespaceIndexFunc,
"nodeName": NodeNameIndexFunc,
}
// 包含的所有索引分类中所有的索引数据
Indices: {
//namespace 这个索引分类下的所有索引数据
"namespace": {
// Index 就是一个索引键下所有的对象键列表
"default": ["pod-1", "pod-2"],
// Index
"kube-system": ["pod-3"]
},
//nodeName 这个索引分类下的所有索引数据(对象键列表)
"nodeName": {
// Index
"node1": ["pod-1"],
// Index
"node2": ["pod-2", "pod-3"]
}
}
Indexers和Indices都是按照IndexFunc(名字)分组, 每个IndexFunc输出多个IndexKey,产生相同IndexKey的多个对象存储在一个集合中。
IndexKey主要是用于快速查找ObjectKey; 而ObjectKey是对象存储时唯一命名的key(这个key方便在存储中快速找到相应的对象)。
2.1.2 代码位置
$GOPATH/pkg/mod/k8s.io/client-go@v0.19.0/tools/cache/index.go
2.1.3 类图展示
从下图我们可以很容易的看到Indexer与cache、Store及ThreadSafeStore之间的调用关系。

上图如果长时间无法显示,请参考这里
-
Store: 是一个通用对象存储和处理接口。
26 // Store is a generic object storage and processing interface. A 27 // Store holds a map from string keys to accumulators, and has 28 // operations to add, update, and delete a given object to/from the 29 // accumulator currently associated with a given key. A Store also 30 // knows how to extract the key from a given object, so many operations 31 // are given only the object. 32 // 33 // In the simplest Store implementations each accumulator is simply 34 // the last given object, or empty after Delete, and thus the Store's 35 // behavior is simple storage. 36 // 37 // Reflector knows how to watch a server and update a Store. This 38 // package provides a variety of implementations of Store. 39 type Store interface { 40 41 // Add adds the given object to the accumulator associated with the given object's key 42 Add(obj interface{}) error 43 44 // Update updates the given object in the accumulator associated with the given object's key 45 Update(obj interface{}) error 46 47 // Delete deletes the given object from the accumulator associated with the given object's key 48 Delete(obj interface{}) error 49 50 // List returns a list of all the currently non-empty accumulators 51 List() []interface{} 52 53 // ListKeys returns a list of all the keys currently associated with non-empty accumulators 54 ListKeys() []string 55 56 // Get returns the accumulator associated with the given object's key 57 Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) 58 59 // GetByKey returns the accumulator associated with the given key 60 GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) 61 62 // Replace will delete the contents of the store, using instead the 63 // given list. Store takes ownership of the list, you should not reference 64 // it after calling this function. 65 Replace([]interface{}, string) error 66 67 // Resync is meaningless in the terms appearing here but has 68 // meaning in some implementations that have non-trivial 69 // additional behavior (e.g., DeltaFIFO). 70 Resync() error 71 } -
Indexer: 扩展了多个索引的
Store,并限制每个累加器只保存当前对象(删除后为空)。 -
ThreadSafeStore: 与
Indexer类似,是一个允许对存储后端进行并发索引访问的接口 -
cache: 根据
ThreadSafeStore和关联的KeyFunc实现的Indexer。所有的对象都缓存在内存中,这不是一个外部可以调用的对象,在包的外部不能直接调用cache。它的定义也比较简单, 如下:131 // 代码位置:client-go/tools/cache/store.go 132 // `*cache` implements Indexer in terms of a ThreadSafeStore and an 133 // associated KeyFunc. 134 type cache struct { 135 // cacheStorage bears the burden of thread safety for the cache 136 cacheStorage ThreadSafeStore 137 // keyFunc is used to make the key for objects stored in and retrieved from items, and 138 // should be deterministic. 139 keyFunc KeyFunc 140 }我们可以使用
NewStore或NewIndexer来实例化一个Store或Indexer。 -
threadSafeMap : 是
ThreadSafeStore的实现,它实现了并发安全的存储(它是一个内存中的存储),具备CRUD等操作。它其中包含了三个比较重要的属性,见代码:61 // 代码位置:client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go 62 // threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore 63 type threadSafeMap struct { 64 lock sync.RWMutex 65 items map[string]interface{} //用于保存数据 66 67 // indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc 68 indexers Indexers 69 // indices maps a name to an Index 70 indices Indices 71 }对于
threadSafeMap中各种索引的关系,我们可以用下图来表示:
threadSafeMap其实只会做两件事情:存储, 索引。存储即存储runtime.object到items这个Map中; 索引即为items这个Map建立三层索引:indices的Map类型的索引(如:namespace, nodeName等);index Map的类型索引(如: namespace1, namespace2, ...); runtime.object的索引。如果我们需要向
threadSafeMap中添加一个对象,只需要调用下以代码即可:72 // 代码位置:client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go 73 func (c *threadSafeMap) Add(key string, obj interface{}) { 74 c.lock.Lock() 75 defer c.lock.Unlock() 76 oldObject := c.items[key] 77 c.items[key] = obj 78 c.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key) 79 }如果想了解更多的细节,请查看
updateIndices()另外,从图中我们也可以看出,
Indexer实际上是对threadSafeMap的封装,它继承了后者的所有方法,同时也实现了IndexFunc。
2.2 Indexer索引器实现
在kubernetes中使用的比较多的索引函数是MetaNamespaceIndexFunc()(代码位置: client-go/tools/cache/index.go)。
Indexer索引的实现是通过index.ByIndex来完成的,index.ByIndex的代码如下:
178 // 代码位置:client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
179 // ByIndex returns a list of the items whose indexed values in the given index include the given indexed value
180 func (c *threadSafeMap) ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error) {
181 c.lock.RLock()
182 defer c.lock.RUnlock()
183
184 indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName] // 关键代码。获取索引器函数。
185 if indexFunc == nil {
186 return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)
187 }
188
189 index := c.indices[indexName] // 关键代码。获取缓存器函数。
190
191 set := index[indexedValue] // 关键代码。Index中的数据以Set类型存储在缓存中。
192 list := make([]interface{}, 0, set.Len())
193 for key := range set {
194 list = append(list, c.items[key])
195 }
196
197 return list, nil
198 }
上述方法接收两个参数:
- indexName: 索引器的名字
- indexedValue: 需要索引的key
此方法的基本思路如下:
- 根据索引器名字查找指定的索引器函数(
c.indexers[indexName]) - 根据索引器名字查找相应的缓存器函数(
c.indices[indexName]) - 根据索引key(即:
indexedValue)从缓存中进行数据查询,并返回查询结果