1、什么是p-value
p值用于假设检验,以帮助您支持或拒绝零假设。p值是反对零假设的证据。p值越小,拒绝原假设的证据就越强p
A p value is used in hypothesis testing to help you support or reject the null hypothesis. The p value is the evidence against a null hypothesis. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis.
P值用小数表示,不过如果把它们转换成百分数可能更容易理解。例如,p值0.0254是2.54%。这意味着有2.54%的可能性你的结果可能是随机的(即偶然发生)。这是很微小的。另一方面,一个大的p值为。0.9(90%)意味着你的结果有90%的可能性是完全随机的,而不是由于你的实验中的任何东西。因此,p值越小,结果越重要(“significant”)。
P values are expressed as decimals although it may be easier to understand what they are if you convert them to a percentage. For example, a p value of 0.0254 is 2.54%. This means there is a 2.54% chance your results could be random (i.e. happened by chance). That’s pretty tiny. On the other hand, a large p-value of .9(90%) means your results have a 90% probability of being completely random and not due to anything in your experiment. Therefore, the smaller the p-value, the more important (“significant”) your results.
当您运行一个假设测试时,您将测试中的p值与您在运行测试时选择的alpha级别进行比较。Alpha等级也可以写成百分比。
When you run a hypothesis test, you compare the p value from your test to the alpha level you selected when you ran the test. Alpha levels can also be written as percentages.
从图形上看,p值是概率分布尾部的面积。它是在运行假设测试时计算出来的,是测试统计量右侧的面积(如果运行双尾测试,它是左侧和右侧的面积)
Graphically, the p value is the area in the tail of a probability distribution. It’s calculated when you run hypothesis test and is the area to the right of the test statistic (if you’re running a two-tailed test, it’s the area to the left and to the right).
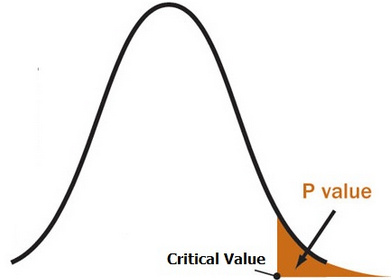
2、P Value vs Alpha level
Alpha水平由研究人员控制,并与自信水平相关。从100%减去你的自信水平,你就得到了alpha水平。例如,如果你想对你的研究有98%的信心,alpha水平应该是2%(100% - 98%)。当你运行假设测试时,测试会给你一个p的值。例如,假设你选择了5%(0.05)的水平。如果测试结果给你:
一个小p(≤0.05),拒绝零假设。这是零假设无效的有力证据。大p(> 0.05)表示备选假设较弱,因此不拒绝null。
Alpha levels are controlled by the researcher and are related to confidence levels. You get an alpha level by subtracting your confidence level from 100%. For example, if you want to be 98 percent confident in your research, the alpha level would be 2% (100% – 98%). When you run the hypothesis test, the test will give you a value for p. Compare that value to your chosen alpha level. For example, let’s say you chose an alpha level of 5% (0.05). If the results from the test give you:
A small p (≤ 0.05), reject the null hypothesis. This is strong evidence that the null hypothesis is invalid.
A large p (> 0.05) means the alternate hypothesis is weak, so you do not reject the null.
3、What if I Don’t Have an Alpha Level?
在理想世界中,你会有一个alpha级别。但如果你没有,你仍然可以使用以下粗略的准则来决定是否支持或拒绝原假设:
If p > .10 → “not significant”
If p ≤ .10 → “marginally significant”
If p ≤ .05 → “significant”
If p ≤ .01 → “highly significant.”
参考文献
https://www.statisticshowto.datasciencecentral.com/p-value/
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/statistical-significance.asp