参考:https://www.runoob.com/python/python-files-io.html
1.open()函数
用于打开一个文件,创建一个 file 对象,相关的方法才可以调用它进行读写。
1 f = open('C:/Users/LKX/Desktop/first.txt') 2 f.read()
>>>'hello world! why are you so cute? '
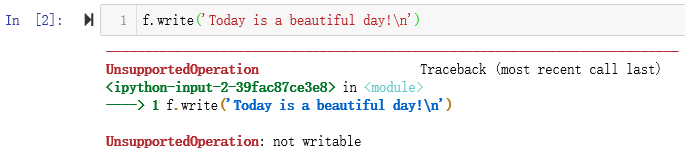
默认是只读,所以并不能写入。
1 f = open('C:/Users/LKX/Desktop/first.txt','a+') 2 f.write('Today is a beautiful day! ') 3 f.close()
2.write()方法
1 #打开一个文件 2 fo = open('foo.txt','w') 3 fo.write('www.runoob.com Very good site! ') 4 #关闭打开的文件 5 fo.close()
www.runoob.com
Very good site!
如果该文件不存在,会创建新文件。
1 file = open('C:/Users/LKX/Desktop/third.txt','w') 2 file.write('This is a better world') 3 file.close()
桌面上就会出现一个 third.txt 文本文件。
3.read()方法
1 fo = open('foo.txt','r+') 2 str = fo.read(10) 3 print('读取的字符串是:',str) 4 fo.close()
>>>读取的字符串是: www.runoob
但要及时关闭(close)文件!
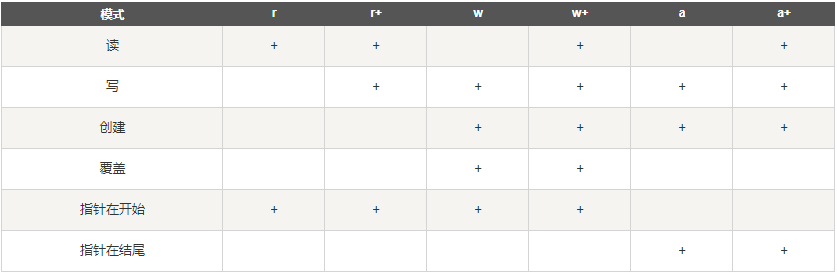
4.#coding:utf-8
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-
ascii码:8位(英文。没有中文情况)(在python2中就为ascii码编码)
万国码:unicode(至少16位,用不到16位时就会浪费内存)
utf-8:能用多少位表示就用多少位表示(节省空间)
使用utf-8编码,代码里出现了中文,就不会报错了。python3为utf-8编码,头部可不加。
5.字符串的方法replace()、find()、format()
replace() 方法把字符串中的 old(旧字符串)替换成 new(新字符串),如果指定第三个参数max,则替换不超过 max 次。
需要注意 replace 不会改变原 string 的内容。
1 msg = 'this is string example...wow!!!this is really string' 2 print(msg.replace('is','was')) 3 print(msg.replace('is','was',3)) 4 print(msg)
>>>thwas was string example...wow!!!thwas was really string >>>thwas was string example...wow!!!thwas is really string >>>this is string example...wow!!!this is really string
eg.hiding_num
1 phone_num = '13099932221' 2 hiding_num = phone_num.replace(phone_num[3:7],'*'* 4) 3 print(hiding_num)
>>>130****2221
find()方法:
str.find(str, beg=0, end=len(string))
- str -- 指定检索的字符串
- beg -- 开始索引,默认为0。
- end -- 结束索引,默认为字符串的长度。
返回:如果包含子字符串返回开始的索引值,否则返回-1。
1 info = 'abca' 2 print(info.find('a')) 3 print(info.find('a',1)) 4 print(info.find('3'))
>>>0
>>>3
>>>-1
eg.find()
1 search = '168' 2 num_a = '13861680006' 3 num_b = '16812220006' 4 print(search + ' is at ' + str(num_a.find(search)) + ' to ' + str(num_a.find(search) + len(search)) + ' of num_a') 5 print(search + ' is at ' + str(num_b.find(search)) + ' to ' + str(num_b.find(search) + len(search)) + ' of num_b')
>>>168 is at 4 to 7 of num_a >>>168 is at 0 to 3 of num_b
字符串格式化函数format():
1 '{} {}'.format('hello','world') #不设置指定位置,按默认顺序
>>>'hello world'
2 '{0} {1}'.format('hello','world') #设置指定位置
3 '{1} {0} {1}'.format('hello','world') #设置指定位置
>>>'world hello world'
4 print('网站名:{name},地址:{url}'.format(name='菜鸟教程',url='www.runoob.com'))
>>>网站名:菜鸟教程,地址:www.runoob.com
5 #通过字典设置参数 6 site = {'name':'菜鸟教程','url':'www.runoob.com'} 7 print('网站名:{name},地址:{url}'.format(**site))
8#通过列表索引设置参数 9 my_list = ['菜鸟教程','www.runoob.com'] 10 print('网站名:{0[0]},地址:{0[1]}'.format(my_list))
6.input()
1 city = input('write down the name of city:') 2 url = 'http://apistore.baidu.com/microservice/weather?citypinyin={}'.format(city) 3 print(url)
>>>write down the name of city:shanghai
>>>http://apistore.baidu.com/microservice/weather?citypinyin=shanghai
7.求幂运算符**,而不是^
1 a = 3 2 b = 5 3 print(b**a)
>>>125