缓存机制一直是性能优化的重要方式,LevelDB在读取SSTable、Block中均采用了缓存。
LevelDB的缓存机制可谓“白手起家”,由最下层的Hash类到最上层的TableCache都由作者编写完成。先来看下类图:
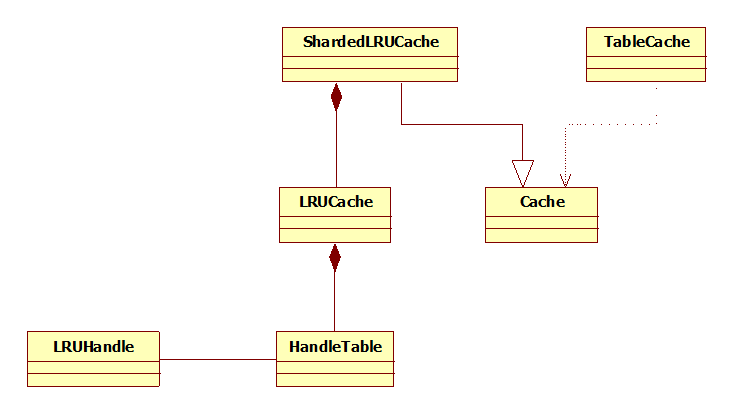
LRUHandle代表缓存记录,
HandleTable是专门用于存储LRUHandle的哈希表,
LRUCache则是基于HandleTable实现的LRU缓存,
SharedLRUCache继承自Cache抽象类,其内部实现了简单的一级缓存,并通过LRUCache实现二级缓存,
TableCache则是SSTable文件缓存。
LRUHandle(代表一条缓存记录)
1 // An entry is a variable length heap-allocated structure. Entries 2 // are kept in a circular doubly linked list ordered by access time. 3 struct LRUHandle { 4 void* value; 5 void(*deleter)(const Slice&, void* value); 6 LRUHandle* next_hash; 7 LRUHandle* next; 8 LRUHandle* prev; 9 size_t charge; // TODO(opt): Only allow uint32_t? 10 size_t key_length; 11 uint32_t refs; 12 uint32_t hash; // Hash of key(); used for fast sharding and comparisons 13 char key_data[1]; // Beginning of key 14 15 Slice key() const { 16 // For cheaper lookups, we allow a temporary Handle object 17 // to store a pointer to a key in "value". 18 if (next == this) { 19 return *(reinterpret_cast<Slice*>(value)); 20 } 21 else { 22 return Slice(key_data, key_length); 23 } 24 } 25 };
有几点需要备忘:
- Deleter:删除器。当refs == 0时,调用deleter完成value对象释放。
- char Key_data[1]。实际上,这只是一个指向Key值的指针,指向内存的实际大小由Key值的长度决定。
- Nextprev ext_hash。Nextprev用于双向链表,而next_hash则是指向相同hash值的下一条记录。
- 这是LRUCache专用的结构,因此名为LRUHandle。
HandleTable
HandleTable其实应该叫做LRUHandleTable,它只支持LRUHandle记录。
1 class HandleTable { 2 public: 3 LRUHandle* Lookup(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash); 4 LRUHandle* Insert(LRUHandle* h); 5 LRUHandle* Remove(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash); 6 };
Insert时,如果存在相同hash值、相同key值的记录存在,插入新记录,并返回之前的记录。
HandleTable是哈希表,但比较奇怪的是,查找、插入、删除动作除了传入key外,还要自备hash值。这样做是因为,hash值除了HandleTable中使用,在外部做多级缓存时也需要,后面会提到。
HandleTable内部维护了一个LRUHandle*的数组,默认大小为4。随着插入数据的增多,该数组会自动增长,并将原数组中的数据重新分配到新的数组中。Resize的触发条件为元素个数>数组大小。
1 void Resize() { 2 uint32_t new_length = 4; 3 while (new_length < elems_) { 4 new_length *= 2; 5 } 6 LRUHandle** new_list = new LRUHandle*[new_length]; 7 memset(new_list, 0, sizeof(new_list[0]) * new_length); 8 uint32_t count = 0; 9 for (uint32_t i = 0; i < length_; i++) { //注意这里 10 LRUHandle* h = list_[i]; 11 while (h != NULL) { 12 LRUHandle* next = h->next_hash; 13 Slice key = h->key(); 14 uint32_t hash = h->hash; 15 LRUHandle** ptr = &new_list[hash & (new_length - 1)]; 16 h->next_hash = *ptr; 17 *ptr = h; 18 h = next; 19 count++; 20 } 21 } 22 assert(elems_ == count); 23 delete[] list_; 24 list_ = new_list; 25 length_ = new_length; 26 }
LRUCache
有了LRUHandle、HandleTable,我们仅仅具备了一个可以存储LRUHandle结构的Hash表。和LRU缓存并没有建立联系,那么,如何通过上面的结构完成LRU缓存(LRUCache)呢?
如果由我来完成LRUCache,那么会考虑如下问题:
- LRU的判定标准是什么?是指定时间内使用的数据、最近使用的N条数据,还是通过其他设定规则判定LRU?
- Hash表是key值无序的,怎样体现每条记录的先后顺序?
- 性能上如何保证?
来看作者的实现:
1 class LRUCache { 2 public: 3 LRUCache(); 4 ~LRUCache(); 5 6 // Separate from constructor so caller can easily make an array of LRUCache 7 void SetCapacity(size_t capacity) { capacity_ = capacity; } 8 9 // Like Cache methods, but with an extra "hash" parameter. 10 Cache::Handle* Insert(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash, 11 void* value, size_t charge, 12 void(*deleter)(const Slice& key, void* value)); 13 Cache::Handle* Lookup(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash); 14 void Release(Cache::Handle* handle); 15 void Erase(const Slice& key, uint32_t hash); 16 17 private: 18 void LRU_Remove(LRUHandle* e); 19 void LRU_Append(LRUHandle* e); 20 void Unref(LRUHandle* e); 21 22 // Initialized before use. 23 size_t capacity_; 24 25 // mutex_ protects the following state. 26 port::Mutex mutex_; 27 size_t usage_; 28 uint64_t last_id_; 29 30 // Dummy head of LRU list. 31 // lru.prev is newest entry, lru.next is oldest entry. 32 LRUHandle lru_; 33 34 HandleTable table_; 35 };
回答上面的问题:
- SetCapacity指定的缓存数量,判定标准为最近使用的N条记录。
- Lru_维护了双向链表,lru_.prev指向最新的数据,lru_.next指向最旧的数据。
- Table_针对每条记录的查找时间为O(1), 插入时如不执行数组大小重分配,时间复杂度也为O(1).lru_的插入、删除时间均为O(1)。
LRUCache的插入、删除动作除了操作table_外,还要操作lru_,其他并无特殊之处。
SharedLRUCache
请看类图1.1,SharedLRUCache并不继承自LRUCache,而是采用组合的方式使用;SharedLRUCache继承了Cache,这说明SharedLRUCache才是作者认为外部可用的缓存。
SharedLRUCache自身建立了一级缓存,随后通过调用LRUCache完成二级缓存。
1 static const int kNumShardBits = 4; 2 static const int kNumShards = 1 << kNumShardBits; //16 3 4 class ShardedLRUCache : public Cache { 5 private: 6 LRUCache shard_[kNumShards]; 7 port::Mutex id_mutex_; 8 uint64_t last_id_; 9 10 static inline uint32_t HashSlice(const Slice& s) { 11 return Hash(s.data(), s.size(), 0); 12 } 13 14 static uint32_t Shard(uint32_t hash) { 15 return hash >> (32 - kNumShardBits); 16 } 17 18 public: 19 explicit ShardedLRUCache(size_t capacity) 20 : last_id_(0) { 21 const size_t per_shard = (capacity + (kNumShards - 1)) / kNumShards; 22 for (int s = 0; s < kNumShards; s++) { 23 shard_[s].SetCapacity(per_shard); 24 } 25 } 26 virtual ~ShardedLRUCache() { } 27 virtual Handle* Insert(const Slice& key, void* value, size_t charge, 28 void(*deleter)(const Slice& key, void* value)) { 29 const uint32_t hash = HashSlice(key); 30 return shard_[Shard(hash)].Insert(key, hash, value, charge, deleter); 31 } 32 virtual Handle* Lookup(const Slice& key) { 33 const uint32_t hash = HashSlice(key); 34 return shard_[Shard(hash)].Lookup(key, hash); 35 } 36 virtual void Release(Handle* handle) { 37 LRUHandle* h = reinterpret_cast<LRUHandle*>(handle); 38 shard_[Shard(h->hash)].Release(handle); 39 } 40 virtual void Erase(const Slice& key) { 41 const uint32_t hash = HashSlice(key); 42 shard_[Shard(hash)].Erase(key, hash); 43 } 44 virtual void* Value(Handle* handle) { 45 return reinterpret_cast<LRUHandle*>(handle)->value; 46 } 47 virtual uint64_t NewId() { 48 MutexLock l(&id_mutex_); 49 return ++(last_id_); 50 } 51 };
可以看到,SharedLRUCache维护了一个大小为16的LRUCache数组,通过hash值的高4位进行分组,实现一级缓存,进而再调用LRUCache实现二级缓存。这样做和采用一个LRUCache实现的好处是降低了数据在分配、重组的几率,提升了性能。
但严格来讲,SharedLRUCache实现并不是精确的LRU缓存,因为如果hash值不够均匀,大量的数据被聚集到一个LRUCache中时,该缓存被频繁换入换出,而更老的其他LRUCache中的数据却仍然得以保留。当然,对于一般应用来说,SharedLRUCache基本具备统计上的LRU。
TableCache
TableCache是SSTable文件缓存,LevelDB的所有SSTable文件查找均通过该类完成,该类在LevelDB中只有一个实例。来看接口声明
1 Iterator* NewIterator(const ReadOptions& options, 2 uint64_t file_number, 3 uint64_t file_size, 4 Table** tableptr = NULL); 5 // Evict any entry for the specified file number 6 void Evict(uint64_t file_number);
NewIterator通过传入指定的文件编号返回Iterator,该Iterator提供了完整的数据库文件查询功能。
Iterator* TableCache::NewIterator(const ReadOptions& options, uint64_t file_number, uint64_t file_size, Table** tableptr) { if (tableptr != NULL) { *tableptr = NULL; } //1. 从缓存中查找指定文件 char buf[sizeof(file_number)]; EncodeFixed64(buf, file_number); Slice key(buf, sizeof(buf)); Cache::Handle* handle = cache_->Lookup(key); if (handle == NULL) //指定文件不存在,打开文件并添加至缓存 { std::string fname = TableFileName(dbname_, file_number); RandomAccessFile* file = NULL; Table* table = NULL; Status s = env_->NewRandomAccessFile(fname, &file); if (s.ok()) { s = Table::Open(*options_, file, file_size, &table); } if (!s.ok()) { assert(table == NULL); delete file; // We do not cache error results so that if the error is transient, // or somebody repairs the file, we recover automatically. return NewErrorIterator(s); } TableAndFile* tf = new TableAndFile; tf->file = file; tf->table = table; handle = cache_->Insert(key, tf, 1, &DeleteEntry); } //3. 根据table构建迭代器并返回 Table* table = reinterpret_cast<TableAndFile*>(cache_->Value(handle))->table; Iterator* result = table->NewIterator(options); result->RegisterCleanup(&UnrefEntry, cache_, handle); if (tableptr != NULL) { *tableptr = table; } return result; }
Evict含义为”驱逐“,当Compaction时,过期的文件将会被移除,此时调用Evict从移除该文件缓存。
void TableCache::Evict(uint64_t file_number) { char buf[sizeof(file_number)]; EncodeFixed64(buf, file_number); cache_->Erase(Slice(buf, sizeof(buf))); }
至此,数据文件缓存已备忘完成。
等等,最开始还提到除SSTable外,Block也采用了缓存机制,实现如何?
LevelDB在打开数据库时,需指定一个Options参数,其中包含了如下成员:
1 // If non-NULL, use the specified cache for blocks. 2 // If NULL, leveldb will automatically create and use an 8MB internal cache. 3 // Default: NULL 4 Cache* block_cache;
作者注释:如果值非NULL,则用用户指定的缓存方式缓存数据块,否则创建一个大小为8M的内部缓存,这个内部缓存指的其实就是SharedLRUCache。