output
standard outputYou are given a tree consisting of nn nodes. You want to write some labels on the tree's edges such that the following conditions hold:
- Every label is an integer between 00 and n−2n−2 inclusive.
- All the written labels are distinct.
- The largest value among MEX(u,v)MEX(u,v) over all pairs of nodes (u,v)(u,v) is as small as possible.
Here, MEX(u,v)MEX(u,v) denotes the smallest non-negative integer that isn't written on any edge on the unique simple path from node uu to node vv.
Input
The first line contains the integer nn (2≤n≤1052≤n≤105) — the number of nodes in the tree.
Each of the next n−1n−1 lines contains two space-separated integers uu and vv (1≤u,v≤n1≤u,v≤n) that mean there's an edge between nodes uu and vv. It's guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
Output
Output n−1n−1 integers. The ithith of them will be the number written on the ithith edge (in the input order).
Examples
input
Copy
3 1 2 1 3
output
Copy
0 1
input
Copy
6 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 5 6
output
Copy
0 3 2 4 1
Note
The tree from the second sample:
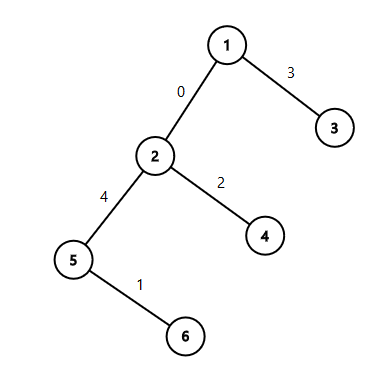
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long #define PII pair<int, int> #define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++) #define dec(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--) using namespace std; int dir[4][2] = { { 0,1 } ,{ 0,-1 },{ 1,0 },{ -1,0 } }; const long long INF = 0x7f7f7f7f7f7f7f7f; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const double pi = 3.14159265358979323846; const int mod = 998244353; const int N = 1e5+5; inline ll read() { ll x = 0; bool f = true; char c = getchar(); while (c < '0' || c > '9') { if (c == '-') f = false; c = getchar(); } while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar(); return f ? x : -x; } ll gcd(ll m, ll n) { return n == 0 ? m : gcd(n, m%n); } ll lcm(ll m, ll n) { return m*n / gcd(m, n); } int main() { ll n; cin >> n; vector<vector<int>> a(n + 1); vector<int> u(n+1),v(n+1); for (int i = 1; i<n ; i++) { cin >> u[i] >> v[i]; a[u[i]].push_back(v[i]); a[v[i]].push_back(u[i]); } if (n == 2) { cout << 0 << endl; return 0; } int k=-1; rep(i,1,n) { if(a[i].size()>=3) { k=i; break; } } if(k==-1) { rep(i,0,n-2) cout<<i<<endl; return 0; } int tot=3; rep(i,1,n-1) { if(u[i]==k) { if(a[k][0]==v[i]) cout<<0<<endl; else if(a[k][1]==v[i]) cout<<1<<endl; else if(a[k][2]==v[i]) cout<<2<<endl; else cout<<tot++<<endl; } else if(v[i]==k) { if(a[k][0]==u[i]) cout<<0<<endl; else if(a[k][1]==u[i]) cout<<1<<endl; else if(a[k][2]==u[i]) cout<<2<<endl; else cout<<tot++<<endl; } else cout<<tot++<<endl; } return 0; }