基于jdk_1.8.0
关于List,主要是有序的可重复的数据结构。jdk主要实现类有ArrayList(底层使用数组)、LinkedList(底层使用双向链表)
ArrayList:
(一)继承关系图
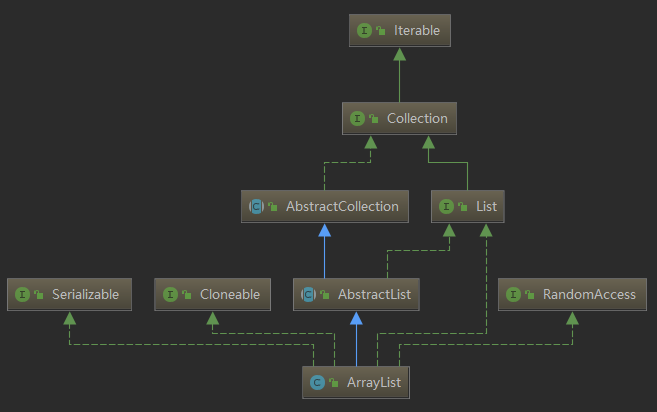
(二)源码解析
(1)关键字段

1 /** 2 * 默认初始容量 3 */ 4 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; 5 6 /** 7 * 用于空实例的共享空数组实例 8 */ 9 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 10 11 /** 12 * 用于默认大小的空实例的共享空数组实例 13 */ 14 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 15 16 /** 17 *存储ArrayList元素的数组缓冲区 18 */ 19 transient Object[] elementData; //非私有以简化嵌套类访问 20 21 /** 22 * ArrayList的大小,也是下一个元素插入的位置 23 */ 24 private int size; 25 26 /** 27 * 要分配的数组的最大大小 28 * 从hugeCapacity方法可以看到如果要分配的大小 > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE ,会返回Integer.MAX_VALUE 29 */ 30 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; // 关于-8 ,网上说是数组元数据信息要占8个字节 字节和大小有哪门子关系,这个不够让人信服
(2)构造方法

1 /** 2 * elementData指向共享的默认空数组实例,将在添加第一个元素时扩展到DEFAULT_CAPACITY 3 */ 4 public ArrayList() { 5 //默认的空数组实例,主要是为了区别 new ArrayList(0) 6 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 7 } 8 9 /** 10 * 构造一个initialCapacity大小的数组 11 */ 12 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { 13 if (initialCapacity > 0) { 14 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; 15 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { 16 //空数组实例 17 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 18 } else { 19 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ 20 initialCapacity); 21 } 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * 构造一个包含指定集合的元素的列表,这些元素按集合的迭代器返回的顺序排列 26 */ 27 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 28 //详见toArray实例方法 29 elementData = c.toArray(); 30 //集合不为空 31 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { 32 //虽然elementData 是object[]类型的,但是它指向的类型不一定是Object[] 33 //造成的原因可能是Arrays.asList详情请戳https://www.cnblogs.com/liqing-weikeyuan/p/7922306.html 34 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) 35 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); 36 } else { 37 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 38 } 39 }
(3)常用方法
a. public boolean add(E e)

1 public boolean add(E e) { 2 // 为了确保数组不越界,所以允许的数组最小容量为size + 1 3 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 4 elementData[size++] = e; 5 return true; 6 } 7 8 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { 9 // 由于calculateCapacity是静态方法,无法访问实例elementData变量 10 ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); 11 } 12 13 /** 14 * 为啥要设计成静态方法,想不通 15 */ 16 private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { 17 // 若是通过默认构造方法构造,则返回DEFAULT_CAPACITY 18 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { 19 return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); 20 } 21 return minCapacity; 22 } 23 24 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { 25 modCount++; 26 27 // overflow-conscious code 28 // 若数组不足以放下,则进行扩充 29 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 30 grow(minCapacity); 31 } 32 33 /** 34 * 新的数组容量先按之前的1.5倍进行扩充 35 * 若扩充后的大小还不足以放下,则使用minCapacity 36 * 若minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,最大容量Integer.MAX_VALUE,否则内存溢出异常 37 * @param minCapacity 38 */ 39 private void grow(int minCapacity) { 40 // overflow-conscious code 41 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 42 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 43 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) 44 newCapacity = minCapacity; 45 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 46 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); 47 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 48 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 49 } 50 51 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { 52 // 容量超过Integer.MAX_VALUE 53 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 54 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); 55 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? 56 Integer.MAX_VALUE : 57 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; 58 }
b. public void add(int index, E element)

1 /** 2 * 向指定位置添加元素,不常用,性能也不好 3 * @param index 4 * @param element 5 */ 6 public void add(int index, E element) { 7 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 8 9 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 10 // [index, size -1] 向后移动一位 11 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, 12 size - index); 13 elementData[index] = element; 14 size++; 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * A version of rangeCheck used by add and addAll. 19 */ 20 private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { 21 if (index > size || index < 0) 22 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * 详见 a. public boolean add(E e) 不再展开 27 * @param minCapacity 28 */ 29 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { 30 ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); 31 }
c. public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)

1 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 2 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 3 int numNew = a.length; 4 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // 详见a. add 5 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); 6 size += numNew; 7 return numNew != 0; //??? 暂时没看懂 8 }
d. public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)

1 /** 2 * 向指定位置添加集合元素 3 * @param index 4 * @param c 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 8 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 9 10 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 11 int numNew = a.length; 12 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount 13 14 // 需要移动元素个数 15 int numMoved = size - index; 16 if (numMoved > 0) 17 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, 18 numMoved); //从index开始复制numMoved个元素到index + numNew (即[index, index + numMoved -1] 复制到[index + numNew, index + numNew + numMoved - 1]) 19 20 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); 21 size += numNew; 22 return numNew != 0; //??? 没看懂 23 }
e. public E remove(int index)

1 /** 2 * 删除指定位置的元素 3 * @param index 4 * @return 被删除的元素 5 * @throws java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 6 */ 7 public E remove(int index) { 8 rangeCheck(index); 9 10 modCount++; 11 E oldValue = elementData(index); 12 13 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 14 if (numMoved > 0) 15 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 16 numMoved); //把[index + 1, size -1]元素 复制到 [index, size -2] 17 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 18 19 return oldValue; 20 } 21 22 private void rangeCheck(int index) { 23 if (index >= size) 24 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 25 } 26 27 private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { 28 return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * @throws java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 33 */ 34 E elementData(int index) { 35 return (E) elementData[index]; 36 }
f. public boolean remove(Object o)

1 /** 2 * 删除第一个值为o的元素 3 * @param o 4 * @return 5 */ 6 public boolean remove(Object o) { 7 if (o == null) { 8 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 9 if (elementData[index] == null) { 10 fastRemove(index); 11 return true; 12 } 13 } else { 14 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 15 if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { 16 fastRemove(index); 17 return true; 18 } 19 } 20 return false; 21 } 22 23 private void fastRemove(int index) { 24 modCount++; 25 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 26 if (numMoved > 0) 27 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 28 numMoved); 29 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 30 }
g. public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)

1 public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { 2 Objects.requireNonNull(c); 3 return batchRemove(c, false); 4 } 5 6 // Objects.class 7 public static <T> T requireNonNull(T obj) { 8 if (obj == null) 9 throw new NullPointerException(); 10 return obj; 11 } 12 13 private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { 14 final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; 15 int r = 0, w = 0; 16 boolean modified = false; 17 try { 18 for (; r < size; r++) 19 if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) 20 elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; // 把没有包含的统一移动到数组的一端 21 } finally { 22 // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, 23 // even if c.contains() throws. 24 if (r != size) { 25 // 前r个元素已经过滤完毕,这里只是简单的把[r, size-1]的元素复制移动到[w, w + size -r -1] 26 System.arraycopy(elementData, r, 27 elementData, w, 28 size - r); 29 w += size - r; 30 } 31 if (w != size) { 32 // clear to let GC do its work 33 for (int i = w; i < size; i++) 34 elementData[i] = null; 35 modCount += size - w; 36 size = w; 37 modified = true; 38 } 39 } 40 return modified; 41 }
h. public E set(int index, E element)

1 public E set(int index, E element) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 4 E oldValue = elementData(index); //强制转换成E 5 elementData[index] = element; 6 return oldValue; 7 }
i. public E get(int index)

1 public E get(int index) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 4 return elementData(index); // 强制转化成E 5 }
j. public int indexOf(Object o)

1 /** 2 * 获取指定元素的下标 3 * @param o 4 * @return 5 */ 6 public int indexOf(Object o) { 7 if (o == null) { 8 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 9 if (elementData[i]==null) 10 return i; 11 } else { 12 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 13 if (o.equals(elementData[i])) 14 return i; 15 } 16 return -1; 17 }
k. public int lastIndexOf(Object o)

1 public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { 2 if (o == null) { 3 for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) 4 if (elementData[i]==null) 5 return i; 6 } else { 7 for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) 8 if (o.equals(elementData[i])) 9 return i; 10 } 11 return -1; 12 }
l. public Iterator<E> iterator()

1 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 2 return new Itr(); 3 } 4 5 /** 6 * An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr 7 */ 8 private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { 9 int cursor; // index of next element to return 10 int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such 11 int expectedModCount = modCount; 12 13 Itr() {} 14 15 public boolean hasNext() { 16 return cursor != size; 17 } 18 19 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 20 public E next() { 21 checkForComodification(); 22 int i = cursor; 23 if (i >= size) //数组内实际存储的元素个数 24 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 25 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 26 if (i >= elementData.length) 27 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 28 cursor = i + 1; 29 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; 30 } 31 32 public void remove() { 33 if (lastRet < 0) //没有首先调用next(), 直接remove会抛IllegalStateException 34 throw new IllegalStateException(); 35 checkForComodification(); 36 37 try { 38 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); //详见e. public E remove(int index) 39 cursor = lastRet; 40 lastRet = -1; 41 expectedModCount = modCount; 42 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { //该异常什么情况下会被触发??? 43 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 44 } 45 } 46 47 @Override 48 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 49 public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) { 50 Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); 51 final int size = ArrayList.this.size; 52 int i = cursor; 53 if (i >= size) { 54 return; 55 } 56 final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 57 if (i >= elementData.length) { 58 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 59 } 60 while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { 61 consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]); 62 } 63 // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic 64 cursor = i; 65 lastRet = i - 1; 66 checkForComodification(); 67 } 68 69 final void checkForComodification() { 70 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 71 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 72 } 73 }
m. public ListIterator<E> listIterator()

1 public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { 2 return new ListItr(0); 3 } 4 5 /** 6 * An optimized version of AbstractList.ListItr 7 */ 8 private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> { 9 // 初始化游标位置,默认0 10 ListItr(int index) { 11 super(); 12 cursor = index; 13 } 14 15 // 只有第一个元素没有前继节点 16 public boolean hasPrevious() { 17 return cursor != 0; 18 } 19 20 public int nextIndex() { 21 return cursor; 22 } 23 24 public int previousIndex() { 25 return cursor - 1; 26 } 27 28 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 29 public E previous() { 30 checkForComodification(); 31 int i = cursor - 1; 32 if (i < 0) 33 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 34 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 35 if (i >= elementData.length) 36 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 37 cursor = i; 38 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; 39 } 40 41 public void set(E e) { 42 if (lastRet < 0) 43 throw new IllegalStateException(); 44 checkForComodification(); 45 46 try { 47 ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e); // 详见 h. public E set(int index, E element) 48 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 49 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 50 } 51 } 52 53 /** 54 * 由于底层调用的是add(int index, E element), 还要有一次数组拷贝,性能不如 add(E element) 55 * @param e 56 */ 57 public void add(E e) { 58 checkForComodification(); 59 60 try { 61 int i = cursor; 62 ArrayList.this.add(i, e); //详见b. public void add(int index, E element) 63 cursor = i + 1; 64 lastRet = -1; 65 expectedModCount = modCount; 66 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 67 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 68 } 69 } 70 }
n. public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)

1 /** 2 * 指定游标 3 * @param index 4 * @return 5 */ 6 public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { 7 if (index < 0 || index > size) 8 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); 9 return new ListItr(index); // 详情请看 j. public ListIterator<E> listIterator() 10 }
o. public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action)

1 @Override 2 public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) { 3 Objects.requireNonNull(action); 4 final int expectedModCount = modCount; 5 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 6 final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData; 7 final int size = this.size; 8 for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { 9 action.accept(elementData[i]); //使用见下面解析 10 } 11 if (modCount != expectedModCount) { 12 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 13 } 14 } 15 16 // Consumer.class 17 @FunctionalInterface // 使用该注解就表明可以使用lambda,只要接口只有一个抽象方法就可以用lambda 18 public interface Consumer<T> { 19 20 void accept(T t); 21 22 /** 23 * 可以看到andThen方法返回的是一个Consumer匿名类对象c 24 * 程序运行中如果不调用c.accept(),则什么也不会发生 25 * @param after 26 * @return 27 */ 28 default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) { 29 Objects.requireNonNull(after); 30 return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); }; //重写了accept方法 31 } 32 } 33 34 // TestConsumer.class 35 public void testAccept(String[] args) { 36 // jdk8 之前写法 37 Consumer<String> c = new Consumer<String>() { 38 @Override 39 public void accept(String s) { 40 System.out.println(s.toLowerCase()); 41 } 42 }; 43 44 // jdk8 lambda写法 45 Consumer<String> c = (s) -> System.out.println(s.toLowerCase()); 46 c.accept("HELLO world!"); // hello world! 47 } 48 49 public void testAndthen(String[] args) { 50 /** 51 * 通过这个例子可以看出首先调用了a.accept(),然后调用了b.accept() 52 */ 53 Consumer<String> a = (x) -> System.out.print(x.toLowerCase()); 54 Consumer<String> b = (x) -> { 55 System.out.println("...andThen..." + x); 56 }; 57 Consumer<String> c = a.andThen(b); 58 c.accept("HELLO world!"); // hello world!...andThen...HELLO world! 59 }
p. public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) //TODO 先不展开

1 @Override 2 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 3 public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) { 4 final int expectedModCount = modCount; 5 Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c); 6 if (modCount != expectedModCount) { 7 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 8 } 9 modCount++; 10 }
q. public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)

1 /** 2 * 注意,该subList并没有new一个新的object[], 对subList对象的修改,都会作用到原大对象上 3 */ 4 public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 5 subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); 6 return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex); 7 } 8 9 static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) { 10 if (fromIndex < 0) 11 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex); 12 if (toIndex > size) 13 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex); 14 if (fromIndex > toIndex) 15 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex + 16 ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")"); 17 } 18 19 /** 20 * subList 并没有再new一个object[],而是复用 21 */ 22 private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess { 23 private final AbstractList<E> parent; 24 private final int parentOffset; 25 private final int offset; 26 int size; 27 28 SubList(AbstractList<E> parent, 29 int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 30 this.parent = parent; 31 this.parentOffset = fromIndex; 32 this.offset = offset + fromIndex; 33 this.size = toIndex - fromIndex; 34 this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; 35 } 36 37 public E set(int index, E e) { 38 rangeCheck(index); 39 checkForComodification(); 40 E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); 41 ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e; 42 return oldValue; 43 } 44 45 public E get(int index) { 46 rangeCheck(index); 47 checkForComodification(); 48 return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); 49 } 50 51 public int size() { 52 checkForComodification(); 53 return this.size; 54 } 55 56 public void add(int index, E e) { 57 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 58 checkForComodification(); 59 parent.add(parentOffset + index, e); 60 this.modCount = parent.modCount; 61 this.size++; 62 } 63 64 public E remove(int index) { 65 rangeCheck(index); 66 checkForComodification(); 67 E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index); 68 this.modCount = parent.modCount; 69 this.size--; 70 return result; 71 } 72 73 protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 74 checkForComodification(); 75 parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex, 76 parentOffset + toIndex); 77 this.modCount = parent.modCount; 78 this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex; 79 } 80 81 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 82 return addAll(this.size, c); 83 } 84 85 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 86 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 87 int cSize = c.size(); 88 if (cSize==0) 89 return false; 90 91 checkForComodification(); 92 parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c); 93 this.modCount = parent.modCount; 94 this.size += cSize; 95 return true; 96 } 97 98 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 99 return listIterator(); 100 } 101 102 public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) { 103 checkForComodification(); 104 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 105 final int offset = this.offset; 106 107 return new ListIterator<E>() { 108 int cursor = index; 109 int lastRet = -1; 110 int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; 111 112 public boolean hasNext() { 113 return cursor != SubList.this.size; 114 } 115 116 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 117 public E next() { 118 checkForComodification(); 119 int i = cursor; 120 if (i >= SubList.this.size) 121 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 122 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 123 if (offset + i >= elementData.length) 124 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 125 cursor = i + 1; 126 return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)]; 127 } 128 129 public boolean hasPrevious() { 130 return cursor != 0; 131 } 132 133 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 134 public E previous() { 135 checkForComodification(); 136 int i = cursor - 1; 137 if (i < 0) 138 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 139 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 140 if (offset + i >= elementData.length) 141 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 142 cursor = i; 143 return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)]; 144 } 145 146 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 147 public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) { 148 Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); 149 final int size = SubList.this.size; 150 int i = cursor; 151 if (i >= size) { 152 return; 153 } 154 final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 155 if (offset + i >= elementData.length) { 156 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 157 } 158 while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { 159 consumer.accept((E) elementData[offset + (i++)]); 160 } 161 // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic 162 lastRet = cursor = i; 163 checkForComodification(); 164 } 165 166 public int nextIndex() { 167 return cursor; 168 } 169 170 public int previousIndex() { 171 return cursor - 1; 172 } 173 174 public void remove() { 175 if (lastRet < 0) 176 throw new IllegalStateException(); 177 checkForComodification(); 178 179 try { 180 SubList.this.remove(lastRet); 181 cursor = lastRet; 182 lastRet = -1; 183 expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; 184 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 185 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 186 } 187 } 188 189 public void set(E e) { 190 if (lastRet < 0) 191 throw new IllegalStateException(); 192 checkForComodification(); 193 194 try { 195 ArrayList.this.set(offset + lastRet, e); 196 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 197 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 198 } 199 } 200 201 public void add(E e) { 202 checkForComodification(); 203 204 try { 205 int i = cursor; 206 SubList.this.add(i, e); 207 cursor = i + 1; 208 lastRet = -1; 209 expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; 210 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 211 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 212 } 213 } 214 215 final void checkForComodification() { 216 if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this.modCount) 217 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 218 } 219 }; 220 } 221 222 public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 223 subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); 224 return new SubList(this, offset, fromIndex, toIndex); 225 } 226 227 private void rangeCheck(int index) { 228 if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) 229 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 230 } 231 232 private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { 233 if (index < 0 || index > this.size) 234 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 235 } 236 237 private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { 238 return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size; 239 } 240 241 private void checkForComodification() { 242 if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount) 243 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 244 } 245 246 public Spliterator<E> spliterator() { 247 checkForComodification(); 248 return new ArrayListSpliterator<E>(ArrayList.this, offset, 249 offset + this.size, this.modCount); 250 } 251 }
r. public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a)

1 /** 2 * 推荐使用 toArray(T[] a) 3 */ 4 public Object[] toArray() { 5 return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); 6 } 7 8 /** 9 * 如果a.length不足以放下所有的元素,则新建一个size大小的数组拷贝返回 10 * 如果a.length足够放下,遍历的时候小心空指针 11 * 推荐a.length == size new T[list.size()] 12 */ 13 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { 14 if (a.length < size) // 传过来的数组大小不足以放下全部元素 15 // Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents: 16 return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass()); 17 System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size); 18 if (a.length > size) 19 a[size] = null; // ???没懂用意 20 return a; 21 }
s. 其它简单方法

1 /** 2 * 返回当前列表元素个数 3 * @return 4 */ 5 public int size() { 6 return size; 7 } 8 9 /** 10 * 当前列表是否为空 11 * @return 12 */ 13 public boolean isEmpty() { 14 return size == 0; 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * 当前列表是否包含元素o 19 * @return 20 */ 21 public boolean contains(Object o) { 22 return indexOf(o) >= 0; //详情请看 j. public int indexOf(Object o) 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * 将elementData中未使用的空间 释放掉 27 */ 28 public void trimToSize() { 29 modCount++; 30 if (size < elementData.length) { 31 elementData = (size == 0) 32 ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 33 : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); 34 } 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * 清空所有引用 39 */ 40 public void clear() { 41 modCount++; 42 43 // clear to let GC do its work 44 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 45 elementData[i] = null; 46 47 size = 0; 48 }
t. 序列化相关方法

1 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) 2 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 3 elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 4 5 // Read in size, and any hidden stuff 6 s.defaultReadObject(); 7 8 // Read in capacity 9 s.readInt(); // ignored 10 11 if (size > 0) { 12 // be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity 13 int capacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size); 14 SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity); 15 ensureCapacityInternal(size); 16 17 Object[] a = elementData; 18 // Read in all elements in the proper order. 19 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { 20 a[i] = s.readObject(); 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 25 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) 26 throws java.io.IOException{ 27 // Write out element count, and any hidden stuff 28 int expectedModCount = modCount; 29 s.defaultWriteObject(); 30 31 // Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone() 32 s.writeInt(size); 33 34 // Write out all elements in the proper order. 35 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { 36 s.writeObject(elementData[i]); 37 } 38 39 if (modCount != expectedModCount) { 40 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 41 } 42 }
写在最后:
使用ArrayList进行存储的元素,务必要重写Object的equals方法。像IndexOf、lastIndexOf、remove等方法底层都是调用元素的equals方法进行比较;
通过get、set方法可以看出,ArrayList随机读写指定位置的元素速度非常快,但是remove、add等方法可能还需要有移动操作,故速度较慢;
通过remove indexOf 等方法可以看出ArrayList可以存储null值;
ArrayList.size 区间范围[0, Integer.MAX_VALUE], 超过Integer.MAX_VALUE,抛OutOfMemoryError。实际应用中还需要具体调整JVM内存大小;
通过代码可以看出,ArrayList任何方法均没有锁,故ArrayList是非线程安全的,若要在多线程环境下使用,要么调用者在外部同步要么参考Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());
ListIterator增强了Iterator一些功能,添加了add、set、hasPrevious、previousIndex、previous、nextIndex方法,调用remove方法时,务必首先调用next或者previous;
subList 应该注意,对subList对象的任何修改都会作用到原对象上;
toArray,返回的是一个全新的对象,对其修改不会影响原list对象。
Q1:for-each与iterator使用场景
A1:如果一个集合或者数组需要更新元素(修改|删除),那么需要使用iterator或者普通for循环;
如果对于集合List使用iterator,建议优先选择使用listIterator;
如果只遍历集合元素,建议优先使用forEach或者支持并行的stream(jdk8以上),否则使用for-each。
